
Concept explainers
A traffic-signal pole may be supported in the three ways show part c, the tension in cable BC is known to be 1950 N. Determ the reactions for each type of support shown.
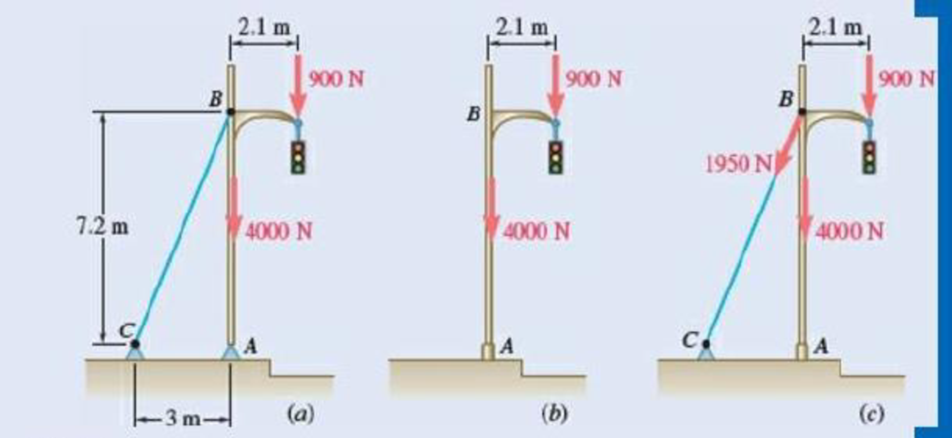
Fig. P4.50
The reaction forces acting on the support.
Answer to Problem 4.50P
The reaction forces acting on the support in figure (a) are
Explanation of Solution
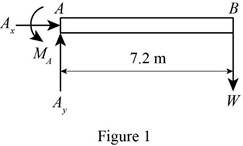
The free body diagram of the traffic signal pole (a) and its support is given in the figure 1.
The free body diagram of the traffic signal pole (b) and its support is given in the figure 2.

The free body diagram of the traffic signal pole (c) and its support is given in the figure 3.

Write the equation to find the moment of force.
Here,
Write the equation to find the total moment about the point
Write the equations for equilibrium for the free body diagram.
Here,
Write the equation for the Pythagoras theorem to find the side
Write the equation to find the angle of orientation of the reaction force on
Write the expression to find the vector
Write the equation to find the angle of orientation of the components of
Conclusion:
Refer figure P4.50(a) and figure 1.
Substitute
Solve equation (I) using the figure 1.
Here,
Substitute
Solve equation (II) using figure 1.
Here,
Substitute
Solve equation (III) using figure 1.
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Refer figure P4.50(b) and figure 2.
Solve equation (I) using the figure 2.
Here,
Substitute
Solve equation (II) using figure 2.
Solve equation (III) using figure 2.
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Refer figure P4.50(c) and figure 3.
Solve equation (I) using the figure 3.
Here,
Substitute
Solve equation (II) using figure 3.
Here,
Substitute
Solve equation (III) using figure 1.
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the reaction forces acting on the support in figure (a) are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS
- You are working as an engineer in a bearing systems design company. The flow of lubricant inside a hydrodynamic bearing (p = 0.001 kg m-1 s-1) can be approximated as a parallel, steady, two-dimensional, incompressible flow between two parallel plates. The top plate, representing the moving part of the bearing, travels at a constant speed, U, while the bottom plate remains stationary (Figure Q1). The plates are separated by a distance of 2h = 1 cm and are W = 20 cm wide. Their length is L = 10 cm. By applying the above approximations to the Navier-Stokes equations and assuming that end effects can be neglected, the horizontal velocity profile can be shown to be y = +h I 2h = 1 cm x1 y = -h u(y) 1 dP 2μ dx -y² + Ay + B moving plate stationary plate U 2 I2 L = 10 cm Figure Q1: Flow in a hydrodynamic bearing. The plates extend a width, W = 20 cm, into the page.arrow_forwardQuestion 1 You are working as an engineer in a bearing systems design company. The flow of lubricant inside a hydrodynamic bearing (µ = 0.001 kg m¯¹ s¯¹) can be approximated as a parallel, steady, two-dimensional, incompressible flow between two parallel plates. The top plate, representing the moving part of the bearing, travels at a constant speed, U, while the bottom plate remains stationary (Figure Q1). The plates are separated by a distance of 2h = 1 cm and are W = 20 cm wide. Their length is L = 10 cm. By applying the above approximations to the Navier-Stokes equations and assuming that end effects can be neglected, the horizontal velocity profile can be shown to be 1 dP u(y) = 2μ dx -y² + Ay + B y= +h Ꮖ 2h=1 cm 1 x1 y = −h moving plate stationary plate 2 X2 L = 10 cm Figure Q1: Flow in a hydrodynamic bearing. The plates extend a width, W = 20 cm, into the page. (a) By considering the appropriate boundary conditions, show that the constants take the following forms: U U 1 dP A =…arrow_forwardQuestion 2 You are an engineer working in the propulsion team for a supersonic civil transport aircraft driven by a turbojet engine, where you have oversight of the design for the engine intake and the exhaust nozzle, indicated in Figure Q2a. The turbojet engine can operate when provided with air flow in the Mach number range, 0.60 to 0.80. You are asked to analyse a condition where the aircraft is flying at 472 m/s at an altitude of 14,000 m. For all parts of the question, you can assume that the flow path of air through the engine has a circular cross section. (a) ← intake normal shock 472 m/s A B (b) 50 m/s H 472 m/s B engine altitude: 14,000 m exhaust nozzle E F exit to atmosphere diameter: DE = 0.30 m E F diameter: DF = 0.66 m Figure Q2: Propulsion system for a supersonic aircraft. a) When the aircraft is at an altitude of 14,000 m, use the International Standard Atmosphere in the Module Data Book to state the local air pressure and tempera- ture. Thus show that the aircraft speed…arrow_forward
- يكا - put 96** I need a detailed drawing with explanation or in wake, and the top edge of im below the free surface of the water. Determine the hydrothed if hydrostatic on the Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with roller follower of diameter 10 mm. The required motion is as follows; 1- Rising 60 mm in 135° with uniform acceleration and retardation motion. 2- Dwell 90° 3- Falling 60 mm for 135° with Uniform acceleration-retardation motion. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the cam is 50 mm. =--20125 7357 750 X 2.01arrow_forwardYou are working as an engineer in a bearing systems design company. The flow of lubricant inside a hydrodynamic bearing (µ = 0.001 kg m¯¹ s¯¹) can be approximated as a parallel, steady, two-dimensional, incompressible flow between two parallel plates. The top plate, representing the moving part of the bearing, travels at a constant speed, U, while the bottom plate remains stationary (Figure Q1). The plates are separated by a distance of 2h = 1 cm and are W = 20 cm wide. Their length is L = 10 cm. By applying the above approximations to the Navier-Stokes equations and assuming that end effects can be neglected, the horizontal velocity profile can be shown to be U y = +h У 2h = 1 cm 1 x1 y=-h u(y) = 1 dP 2μ dx -y² + Ay + B moving plate - U stationary plate 2 I2 L = 10 cm Figure Q1: Flow in a hydrodynamic bearing. The plates extend a width, W = 20 cm, into the page. (a) By considering the appropriate boundary conditions, show that the constants take the following forms: A = U 2h U 1 dP…arrow_forwardQuestion 2 You are an engineer working in the propulsion team for a supersonic civil transport aircraft driven by a turbojet engine, where you have oversight of the design for the engine intake and the exhaust nozzle, indicated in Figure Q2a. The turbojet engine can operate when provided with air flow in the Mach number range, 0.60 to 0.80. You are asked to analyse a condition where the aircraft is flying at 472 m/s at an altitude of 14,000 m. For all parts of the question, you can assume that the flow path of air through the engine has a circular cross section. (a) normal shock 472 m/s A B (b) intake engine altitude: 14,000 m D exhaust nozzle→ exit to atmosphere 472 m/s 50 m/s B diameter: DE = 0.30 m EX diameter: DF = 0.66 m Figure Q2: Propulsion system for a supersonic aircraft. F a) When the aircraft is at an altitude of 14,000 m, use the International Standard Atmosphere in the Module Data Book to state the local air pressure and tempera- ture. Thus show that the aircraft speed of…arrow_forward
- given below: A rectangular wing with wing twist yields the spanwise circulation distribution kbV1 roy) = kbv. (2) where k is a constant, b is the span length and V. is the free-stream velocity. The wing has an aspect ratio of 4. For all wing sections, the lift curve slope (ag) is 2 and the zero-lift angle of attack (a=0) is 0. a. Derive expressions for the downwash (w) and induced angle of attack a distributions along the span. b. Derive an expression for the induced drag coefficient. c. Calculate the span efficiency factor. d. Calculate the value of k if the wing has a washout and the difference between the geometric angles of attack of the root (y = 0) and the tip (y = tb/2) is: a(y = 0) a(y = ±b/2) = /18 Hint: Use the coordinate transformation y = cos (0)arrow_forward۳/۱ العنوان O не شكا +91x PU + 96852 A heavy car plunges into a lake during an accident and lands at the bottom of the lake on its wheels as shown in figure. The door is 1.2 m high and I m wide, and the top edge of Deine the hadrostatic force on the Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with roller follower of diameter 10 mm. The required motion is as follows; 1- Rising 60 mm in 135° with uniform acceleration and retardation motion. 2- Dwell 90° 3- Falling 60 mm for 135° with Uniform acceleration-retardation motion. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the cam is 50 mm. = -20125 750 x2.01arrow_forwardPlot the displacement diagram for a cam with roller follower of diameter 10 mm. The required motion is as follows; 1- Rising 60 mm in 135° with uniform acceleration and retardation motion. 2- Dwell 90° 3- Falling 60 mm for 135° with Uniform acceleration-retardation motion. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the cam is 50 mm.arrow_forward
- Q1/ A vertical, circular gate with water on one side as shown. Determine the total resultant force acting on the gate and the location of the center of pressure, use water specific weight 9.81 kN/m³ 1 m 4 marrow_forwardI need handwritten solution with sketches for eacharrow_forwardGiven answers to be: i) 14.65 kN; 6.16 kN; 8.46 kN ii) 8.63 kN; 9.88 kN iii) Bearing 6315 for B1 & B2, or Bearing 6215 for B1arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





