
Concept explainers
To Find: The graph of the linear regression equation for the given data and determine the equation that is better fit for the data.
Answer to Problem 1E
The required linear regression equation and the
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given table is shown in Table 1
Table 1
| Time | Height |
| 0.1 | 3.04 |
| 0.2 | 5.76 |
| 0.3 | 8.16 |
| 0.4 | 10.24 |
| 0.5 | 12 |
| 0.6 | 13.44 |
| 0.7 | 14.90 |
Calculation:
Press the start button and enter the data as shown in Figure 1
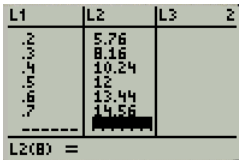
Figure 1
Press the stat button and choose CALC as shown in Figure 2
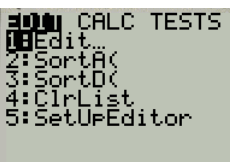
Figure 2
Press enter and select 4 as shown in Figure 3
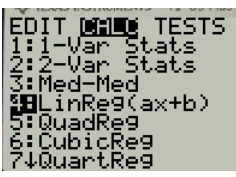
Figure 3
Press enter twice and the required linear regression is obtained as shown in Figure 4
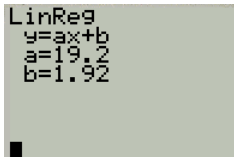
Figure 4
Press the 2nd key and then STAT PLOTS and select 1 as shown in Figure 5
Figure 5
Press the select type and mark as shown in Figure 6
Figure 6
Press zoom button and select the option 9 as shown in Figure 7
Figure 7
Press the graph button as shown in Figure 8

Figure 8
Press Y= button to obtain the linear regression as shown in Figure 9
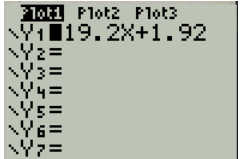
Figure 9
Then , press the graph button as shown in Figure 10
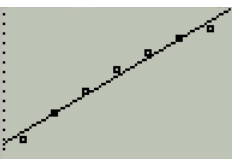
Figure 10
Press the enter and then select the option 5 as shown in Figure 11
Figure 11
Press the button 2 two times and the required quadratic regression equation is obtained as shown in Figure 12
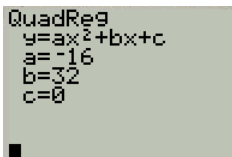
Figure 12
Press the 2nd key and then STAT PLOTS and select 1 as shown in Figure 13
Figure 13
Press the select type and mark as shown in Figure 14
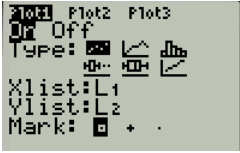
Figure 14
Press zoom button and select the option 9 as shown in Figure 15
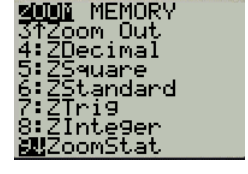
Figure 15
Press the graph button as shown in Figure 16

Figure 16
Press Y= button to obtain the linear regression as shown in Figure 17
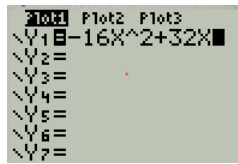
Figure 17
Then , press the graph button as shown in Figure 18
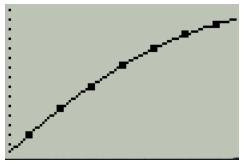
Figure 18
Thus, the required linear regression equation and the quadratic equation s are
Chapter 4 Solutions
Glencoe Algebra 2 Student Edition C2014
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
- please Solve questions by Course Name( Ordinary Differential Equations II 2)arrow_forwardInThe Northern Lights are bright flashes of colored light between 50 and 200 miles above Earth. Suppose a flash occurs 150 miles above Earth. What is the measure of arc BD, the portion of Earth from which the flash is visible? (Earth’s radius is approximately 4000 miles.)arrow_forwarde). n! (n - 1)!arrow_forward
- Suppose you flip a fair two-sided coin four times and record the result. a). List the sample space of this experiment. That is, list all possible outcomes that could occur when flipping a fair two-sided coin four total times. Assume the two sides of the coin are Heads (H) and Tails (T).arrow_forwarde). n! (n - 1)!arrow_forwardEvaluate the following expression and show your work to support your calculations. a). 6! b). 4! 3!0! 7! c). 5!2! d). 5!2! e). n! (n - 1)!arrow_forward
- Amy and Samiha have a hat that contains two playing cards, one ace and one king. They are playing a game where they randomly pick a card out of the hat four times, with replacement. Amy thinks that the probability of getting exactly two aces in four picks is equal to the probability of not getting exactly two aces in four picks. Samiha disagrees. She thinks that the probability of not getting exactly two aces is greater. The sample space of possible outcomes is listed below. A represents an ace, and K represents a king. Who is correct?arrow_forwardConsider the exponential function f(x) = 12x. Complete the sentences about the key features of the graph. The domain is all real numbers. The range is y> 0. The equation of the asymptote is y = 0 The y-intercept is 1arrow_forwardThe graph shows Alex's distance from home after biking for x hours. What is the average rate of change from -1 to 1 for the function? 4-2 о A. -2 О B. 2 О C. 1 O D. -1 ty 6 4 2 2 0 X 2 4arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





