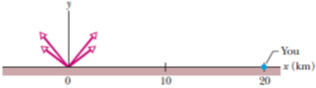
Problem 1Q: Figure 4-21 shows the path taken by a skunk foraging for trash food, from initial point i. The skunk... Problem 2Q Problem 3Q: When Paris was shelled from 100 km away with the WWI long-range artillery piece Big Bertha, the... Problem 4Q: You are to launch a rocket, from just above the ground, with one of the following initial velocity... Problem 5Q: Figure 4-23 shows three situations in which identical projectiles are launched at the same level at... Problem 6Q: The only good use of a fruitcake is in catapult practice. Curve 1 in Fig. 4-24 gives the height y of... Problem 7Q: An airplane flying horizontally at a constant speed of 350 km/h over level ground releases a bundle... Problem 8Q: In Fig. 4-25, a cream tangerine is thrown up past windows 1, 2, and 3, which are identical in size... Problem 9Q: Figure 4-26 shows three paths for a football kicked from ground level. Ignoring the effects of air,... Problem 10Q: A ball is shot from ground level over level ground at a certain initial speed. Figure 4-27 gives the... Problem 11Q: Figure 4-28 shows four tracks either half- or quarter-circles that can be taken by a train, which... Problem 12Q: In Fig. 4-29, particle P is in uniform circular motion, centered on the origin of an xy coordinate... Problem 13Q: a Is it possible to be accelerating while traveling at constant speed? Is it possible to round a... Problem 14Q: While riding in a moving car, you toss an egg directly upward. Does the egg tend to land behind you,... Problem 15Q: A snowball is thrown from ground level by someone in a hole with initial speed v0 at an angle of 45... Problem 16Q: You are driving directly behind a pickup truck, going at the same speed as the truck. A crate falls... Problem 17Q: At what point in the path of a projectile is the speed a minimum? Problem 18Q: In shot put, the shot is put thrown from above the athletes shoulder level. Is the launch angle that... Problem 1P Problem 2P: A watermelon seed has the following coordinates: x = 5.0 m, y = 8.0 m, and z = 0 m. Find its... Problem 3P: A positron undergoes a displacement r = 2.0 i 3.0 j 6.0 k, ending with the position vector r = 3.0... Problem 4P: The minute hand of a wall clock measures 10 cm from its tip to the axis about which it rotates. The... Problem 5P: SSM A train at a constant 60.0 km/h moves east for 40.0 min, then in a direction 50.0 east of due... Problem 6P: An electrons position is given by r=3.00ti4.00t2j+2.00k, with t in seconds and r in meters. a In... Problem 7P: An ions position vector is initially r=5.0i6.0j+2.0k, and 10 s later it is r=2.0i+8.0j2.0k, all in... Problem 8P: A plane flies 483 km east from city A to city B in 45.0 min and then 966 km south from city B to... Problem 9P: Figure 4-30 gives the path of a squirrel moving about on level ground, from point A at time t = 0,... Problem 10P: The position vector r=5.00ti+(et+ft2)j locates a particle as a function of time t. Vector r is in... Problem 11P Problem 12P: At one instant a bicyclist is 40.0 m due east of a parks flagpole, going due south with a speed of... Problem 13P: SSM A particle moves so that its position in meters as a function of time in seconds is r=i+4t2j+tk.... Problem 14P: A proton initially has v=4.0i2.0j+3.0k and then 4.0 s later has v=2.0i2.0j+5.0k in meters per... Problem 15P: SSM ILW A particle leaves the origin with an initial velocity v=(3.00i) m/s and a constant... Problem 16P: GO The velocity v of a particle moving in the xy plane is given by v=(6.0t4.0t2)i+8.0j, with v in... Problem 17P: A cart is propelled over an xy plane with acceleration components ax = 4.0 m/s2 and ay = 2.0 m/s2.... Problem 18P: A moderate wind accelerates a pebble over a horizontal x plane with a constant acceleration... Problem 19P: The acceleration of a particle moving only on a horizontal xy plane is given by a=3ti+4tj, where a... Problem 20P: GO In Fig. 4-32, particle A moves along the line y = 30 m with a constant velocity v of magnitude... Problem 21P: A dart is thrown horizontally with an initial speed of 10 m/s toward point P, the bulls-eye on a... Problem 22P: A small ball rolls horizontally off the edge of a tabletop that is 1.20 m high. It strikes the floor... Problem 23P: A projectile is fired horizontally from a gun that is 45.0 m above flat ground, emerging from the... Problem 24P: In the 1991 World Track and Field Championships in Tokyo, Mike Powell jumped 8.95 m, breaking by a... Problem 25P: The current world-record motorcycle jump is 77.0 m, set by Jason Renie. Assume that he left the... Problem 26P: A stone is catapulted at time t = 0, with an initial velocity of magnitude 20.0 m/s and at an angle... Problem 27P: ILW A certain airplane has a speed of 290.0 km/h and is diving at an angle of = 30.0 below the... Problem 28P: GO In Fig. 4-34, a stone is projected at a cliff of height h with an initial speed of 42.0 m/s... Problem 29P: A projectiles launch speed is five times its speed at maximum height. Find launch angle 0 Problem 30P: GO A soccer ball is kicked from the ground with an initial speed of 19.5 m/s at an upward angle of... Problem 31P: In a jump spike, a volleyball player slams the ball from overhead and toward the opposite floor.... Problem 32P: GO You throw a ball toward a wall at speed 25.0 m/s and at angle 0 = 40.0 above the horizontal Fig.... Problem 33P: SSM A plane, diving with constant speed at an angle of 53.0 with the vertical, releases a projectile... Problem 34P: A trebuchet was a hurling machine built to attack the walls of a castle under siege. A large stone... Problem 35P: SSM A rifle that shoots bullets at 460 m/s is to be aimed at a target 45.7 m away. If the center of... Problem 36P: GO During a tennis match, a player serves the ball at 23.6 m/s, with the center of the ball leaving... Problem 37P: SSM WWW A lowly high diver pushes off horizontally with a speed of 2.00 m/s from the platform edge... Problem 38P: A golf ball is struck at ground level. The speed of the golf ball as a function of the time is shown... Problem 39P: In Fig. 4-37, a ball is thrown leftward from the left edge of the roof, at height h above the... Problem 40P: Suppose that a shot putter can put a shot at the world-class speed v0 = 15.00 m/s and at a height of... Problem 41P: GO Upon spotting an insect on a twig overhanging water, an archer fish squirts water drops at the... Problem 42P: In 1939 or 1940, Emanuel Zacchini took his human cannonball act to an extreme: After being shot from... Problem 43P: ILW A ball is shot from the ground into the air. At a height of 9.1 m, its velocity is v=(7.6i+6.1j)... Problem 44P: A baseball leaves a pitchers hand horizontally at a speed of 161 km/h. The distance to the batter is... Problem 45P: In Fig. 4-40, a ball is launched with a velocity of magnitude 10.0 m/s, at an angle of 50.0 to the... Problem 46P: GO In basketball, hang is an illusion in which a player seems to weaken the gravitational... Problem 47P Problem 48P: GO In Fig. 4-41, a ball is thrown up onto a roof, landing 4.00 s later at height h = 20.0 m above... Problem 49P: SSM A football kicker can give the ball an initial speed of 25 m/s. What are the a least and b... Problem 50P: GO Two seconds after being projected from ground level, a projectile is displaced 40 m horizontally... Problem 51P: A skilled skier knows to jump upward before reaching a downward slope. Consider a jump in which the... Problem 52P: A ball is to be shot from level ground toward a wall at distance x Fig. 4-43a. Figure 4-43b shows... Problem 53P: GO In Fig. 4-44, a baseball is hit at a height h = 1.00 m and then caught at the same height. It... Problem 54P: GO A ball is to be shot from level ground with a certain speed. Figure 4-45 shows the range R it... Problem 55P: SSM A ball rolls horizontally off the top of a stairway with a speed of 1.52 m/s. The steps are 20.3... Problem 56P: An Earth satellite moves in a circular orbit 640 km uniform circular motion above Earths surface... Problem 57P: A carnival merry-go-round rotates about a vertical axis at a constant rate. A man standing on the... Problem 58P: A rotating fan completes 1200 revolutions every minute. Consider the tip of a blade, at a radius of... Problem 59P: ILW A woman rides a carnival Ferris wheel at radius 15 m, completing five turns about its horizontal... Problem 60P: A centripetal-acceleration addict rides in uniform circular motion with radius r = 3.00 m. At one... Problem 61P: When a large star becomes a supernova, its core may be compressed so tightly that it becomes a... Problem 62P: What is the magnitude of the acceleration of a sprinter running at 10 m/s when rounding a turn of... Problem 63P: GO At t1 = 2.00 s, the acceleration of a particle in counterclockwise circular motion is (6.00m/s2)... Problem 64P: GO A particle moves horizontally in uniform circular motion, over a horizontal xy plane. At one... Problem 65P: A purse at radius 2.00 m and a wallet at radius 3.00 m travel in uniform circular motion on the... Problem 66P: A particle moves along a circular path over a horizontal xy coordinate system, at constant speed. At... Problem 67P: SSM WWW A boy whirls a stone in a horizontal circle of radius 1.5 m and at height 2.0 m above level... Problem 68P: GO A cat rides a merry-go-round turning with uniform circular motion. At time t1 = 2.00 s, the cats... Problem 69P: A cameraman on a pickup truck is traveling westward at 20 km/h while he records a cheetah that is... Problem 70P: A boat is traveling upstream in the positive direction of an x axis at 14 km/h with respect to the... Problem 71P: A suspicious-looking man runs as fast as he can along a moving sidewalk from one end to the other,... Problem 72P: A rugby player runs with the ball directly toward his opponents goal, along the positive direction... Problem 73P: Two highways intersect as shown in Fig. 4-46. At the instant shown, a police car P is distance dP =... Problem 74P: After flying for 15 min in a wind blowing 42 km/h at an angle of 20 south of east, an airplane pilot... Problem 75P: SSM A train travels due south at 30 m/s relative to the ground in a rain that is blown toward the... Problem 76P: A light plane attains an airspeed of 500 km/h. The pilot sets out for a destination 800 km due north... Problem 77P: SSM Snow is falling vertically at a constant speed of 8.0 m/s. At what angle from the vertical do... Problem 78P: In the overhead view of Fig. 4-47, Jeeps P and B race along straight lines, across flat terrain, and... Problem 79P: SSM ILW Two ships, A and B, leave port at the same time. Ship A travels northwest at 24 knots, and... Problem 80P: GO A 200-m-wide river flows due east at a uniform speed of 2.0 m/s. A boat with a speed of 8.0 m/s... Problem 81P: GO Ship A is located 4.0 km north and 2.5 km east of ship B. Ship A has a velocity of 22 km/h toward... Problem 82P: GO A 200-m-wide river has a uniform flow speed of 1.1 m/s through a jungle and toward the east. An... Problem 83P: A woman who can row a boat at 6.4 km/h in still water faces a long, straight river with a width of... Problem 84P: In Fig. 4-48a, a sled moves in the negative x direction at constant speed vx while a ball of ice is... Problem 85P: You are kidnapped by political-science majors who are upset because you told them political science... Problem 86P: A radar station detects an airplane approaching directly from the east. At first observation, the... Problem 87P: SSM A baseball is hit at ground level. The ball reaches its maximum height above ground level 3.0 s... Problem 88P: Long flights at midlatitudes in the Northern Hemisphere encounter the jet stream, an eastward... Problem 89P: SSM A particle starts from the origin at t = 0 with a velocity of 8.0 j m/s and moves in the xy... Problem 90P: At what initial speed must the basketball player in Fig. 4-50 throw the ball, at angle 0 = 55 above... Problem 91P: During volcanic eruptions, chunks of solid rock can be blasted out of the volcano these projectiles... Problem 92P: An astronaut is rotated in a horizontal centrifuge at a radius of 5.0 m. a What is the astronauts... Problem 93P: SSM Oasis A is 90 km due west of oasis B. A desert camel leaves A and takes 50 h to walk 75 km at 37... Problem 94P: Curtain of death. A large metallic asteroid strikes Earth and quickly digs a crater into the rocky... Problem 95P: Figure 4-53 shows the straight path of a particle across an xy coordinate system as the particle is... Problem 96P: For womens volleyball the top of the net is 2.24 m above the floor and the court measures 9.0 m by... Problem 97P: SSM A rifle is aimed horizontally at a target 30 m away. The bullet hits the target 1.9 cm below the... Problem 98P: A particle is in uniform circular motion about the origin of an xy coordinate system, moving... Problem 99P: In Fig. 4-54, a lump of wet putty moves in uniform circular motion as it rides at a radius of 20.0... Problem 100P: An iceboat sails across the surface of a frozen lake with constant acceleration produced by the... Problem 101P: In Fig. 4-55, a ball is shot directly upward from the ground with an initial speed of v0 = 7.00 m/s.... Problem 102P: A magnetic field forces an electron to move in a circle with radial acceleration 3.0 1014 m/s2, a... Problem 103P: In 3.50 h, a balloon drifts 21.5 km north, 9.70 km east, and 2.88 km upward from its release point... Problem 104P: A ball is thrown horizontally from a height of 20 m and hits the ground with a speed that is three... Problem 105P: A projectile is launched with an initial speed of 30 m/s at an angle of 60 above the horizontal.... Problem 106P: The position vector for a proton is initially r=5.0i 6.0j+2.0k and then later is r=2.0i+6.0j+2.0k,... Problem 107P: A particle P travels with constant speed on a circle of radius r = 3.00 m Fig. 4-56 and completes... Problem 108P: The fast French train known as the TGV Train Grande Vitesse has a scheduled average speed of 216... Problem 109P: a If an electron is projected horizontally with a speed of 3.0 106 m/s, how far will it fall in... Problem 110P: A person walks up a stalled 15-m-long escalator in 90s. When standing on the same escalator, now... Problem 111P: a What is the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of an object on Earths equator due to the... Problem 112P: The range of a projectile depends not only on v0 and 0 but also on the value g of the free-fall... Problem 113P: Figure 4-57 shows the path taken by a drunk skunk over level ground, from initial point i to final... Problem 114P: The position vector r of a particle moving in the xy plane is r=2ti+2sin[(/4rad/s)t]j, with r in... Problem 115P: An electron having an initial horizontal velocity of magnitude 1.00 109 cm/s travels into the... Problem 116P: An elevator without a ceiling is ascending with a constant speed of 10 m/s. A boy on the elevator... Problem 117P: A football player punts the football so that it will have a hang time time of flight of 4.5 s and... Problem 118P: An airport terminal has a moving sidewalk to speed passengers through a long corridor. Larry does... Problem 119P Problem 120P: A sprinter running on a circular track has a velocity of constant magnitude 9.20 m/s and a... Problem 121P: Suppose that a space probe can withstand the stresses of a 20g acceleration. a What is the minimum... Problem 122P: GO You are to throw a ball with a speed of 12.0 m/s at a target that is height h = 5.00 m above the... Problem 123P: A projectile is fired with an initial speed v0 = 30.0 m/s from level ground at a target that is on... Problem 124P: A graphing surprise. At time t = 0, a burrito is launched from level ground, with an initial speed... Problem 125P: A cannon located at sea level fires a ball with initial speed 82 m/s and initial angle 45. The ball... Problem 126P: The magnitude of the velocity of a projectile when it is at its maximum height above ground level is... Problem 127P: A frightened rabbit moving at 6.00 m/s due east runs onto a large area of level ice of negligible... Problem 128P: The pilot of an aircraft flies due east relative to the ground in a wind blowing 20.0 km/h toward... Problem 129P: The pitcher in a slow-pitch softball game releases the ball at a point 3.0 ft above ground level. A... Problem 130P: Some state trooper departments use aircraft to enforce highway speed limits. Suppose that one of the... Problem 131P: A golfer tees off from the top of a rise, giving the golf ball an initial velocity of 43.0 m/s at an... Problem 132P: A track meet is held on a planet in a distant solar system. A shot-putter releases a shot at a point... Problem 133P: A helicopter is flying in a straight line over a level field at a constant speed of 6.20 m/s and at... Problem 134P: A car travels around a flat circle on the ground, at a constant speed of 12.0 m/s. At a certain... Problem 135P: You throw a ball from a cliff with an initial velocity of 15.0 m/s at an angle of 20.0 below the... Problem 136P: A baseball is hit at Fenway Park in Boston at a point 0.762 m above home plate with an initial... Problem 137P: A transcontinental flight of 4350 km is scheduled to take 50 min longer westward than eastward. The... Problem 138P: A woman can row a boat at 6.40 km/h in still water. a If she is crossing a river where the current... format_list_bulleted


 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning




