
Concept explainers
(a)
The tension in the rope.
Answer to Problem 93QAP
The tension in the rope is
Explanation of Solution
Givendata:
Distance,
Time,
Mass of Sue,
Formula Used:
Newton's second law:
Calculation:
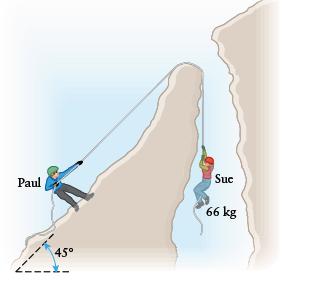
We'll use two different but related coordinate systems for the two people.
For Sue, positive y will point upward.
For Paul, the axes will be parallel and perpendicular to the inclined plane, where up the ramp and out of the ramp are positive.
Tension from the rope pulling up and gravity pulling down are the only forces acting on
Sue.
Assuming her acceleration is constant, we can use the constant acceleration equations
and Newton's second law to calculate the magnitude of the tension.
Sue's acceleration:
Free-body diagram of Sue:
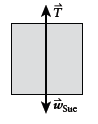
Newton's second law for Sue:
Conclusion:
Thus, from theNewton's second law for Sue we have the tension in the rope joining them as
(b)
Mass of Paul
Answer to Problem 93QAP
Mass of Paul is
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Distance,
Time,
Mass of Sue,
Formula Used:
Newton's second law:
Calculation:
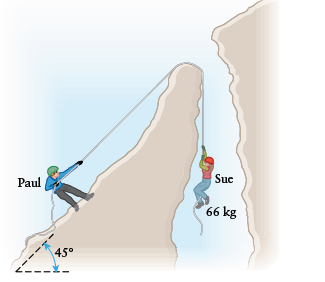
We'll use two different but relatedcoordinate systems for the two people.
For Sue,positive y will point upward.
For Paul, the axes willbe parallel and perpendicular to the inclined plane,where up the ramp and out of the ramp are positive.
Tension from the rope pulling up and gravity pulling down are the only forces acting on
Sue.
Assuming her acceleration is constant, we can use the constant acceleration equations
and Newton's second law to calculate the magnitude of the tension.
Since Paul and Sue aretethered to one another, the magnitudes of their accelerations are equal.
The tension in therope and gravity are the only forces acting on Paul that have components that are parallel tothe face of the glacier. We can then solve the parallel component of Newton's second law forPaul's mass.
Sue's acceleration:
Free-body diagram of Sue:
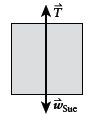
Newton's second law for Sue:
Free-body diagram of Paul:
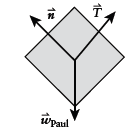
Newton's second law for Paul:
Conclusion:
Thus, by Newton's second law for Paul mass of Paul is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS
- (a) For a spherical capacitor with inner radius a and outer radius b, we have the following for the capacitance. ab C = k₂(b- a) 0.0695 m 0.145 m (8.99 × 10º N · m²/c²)( [0.145 m- 0.0695 m × 10-11 F = PF IIarrow_forwardA pendulum bob A (0.5 kg) is given an initialspeed of vA = 4 m/s when the chord ishorizontal. It then hits a stationary block B (1kg) which then slides to a maximum distanced before it stops. Determine the value of d.The coefficient of static friction between theblock and the plane is μk = 0.2. The coefficientof restitution between A and B is e = 0.8.Ans: d=1.0034 marrow_forwardFigure 29-43 Problem 12. ••13 In Fig. 29-44, point P₁ is at distance R = 13.1 cm on the perpendicular bisector of a straight wire of length L = 18.0 cm carrying current i = 58.2 mA. (Note that the wire is not long.) What is the magnitude of the magnetic field at P₁ due to i? P2° R R Larrow_forward
- Checkpoint 1 The figure shows the current i in a single-loop circuit with a battery B and a resistance R (and wires of neg- ligible resistance). (a) Should the emf arrow at B be drawn pointing leftward or rightward? At points a, B C R b, and c, rank (b) the magnitude of the current, (c) the electric potential, and (d) the electric potential energy of the charge carriers, greatest first.arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forwardPls help asaparrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





