
Follow the directions of Question 7 for solutions of the following:
(a) silver nitrate and sodium chloride
(b) cobalt(II) nitrate and sodium hydroxide
(c) ammonium phosphate and potassium hydroxide
(d) copper(II) sulfate and sodium carbonate
(e) lithium sulfate and barium hydroxide
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether a precipitate will form when the given solutions are mixed should be determined along with the net ionic equation should be written, if precipitate will form.
Silver nitrate and sodium chloride
Concept introduction:
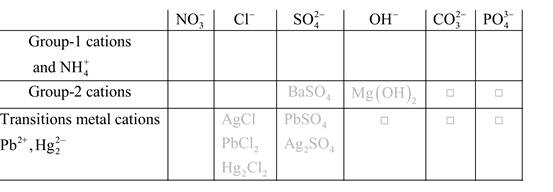
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with grey small box will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Precipitation reactions: It is a type of chemical reactions where two soluble salts react with each other and formed different products, out of which one product must be insoluble in solution which is known as precipitate.
A chemical equation which shows only the species that are participated in the reaction is said to be net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 8QAP
Precipitation occurs
The net ionic equation is:
Explanation of Solution
Silver nitrate:
Sodium chloride:
Reaction for the solution of silver nitrate and sodium chloride is written as:
Reactants:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Products:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Now,
So, the equation will be:
Now, cancelling out the ions which appear on both sides of the equation (
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether a precipitate will form when the given solutions are mixed should be determined along with the net ionic equation should be written, if precipitate will form.
Cobalt(II) nitrate and sodium hydroxide
Concept introduction:
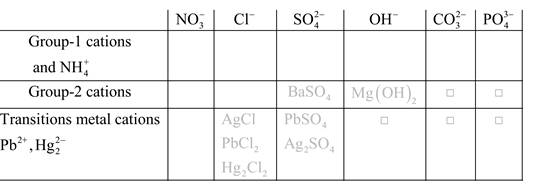
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with grey small box will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Precipitation reactions: It is a type of chemical reactions where two soluble salts react with each other and formed different products, out of which one product must be insoluble in solution which is known as precipitate.
A chemical equation which shows only the species that are participated in the reaction is said to be net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 8QAP
Precipitation occurs
The net ionic equation is:
Explanation of Solution
Cobalt(II) nitrate:
Sodium hydroxide:
Reaction for the solution of cobalt(II) nitrate and sodium hydroxide is written as:
Reactants:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Products:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Now,
So, the equation will be:
Now, cancelling out the ions which appear on both sides of the equation (
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether a precipitate will form when the given solutions are mixed should be determined along with the net ionic equation should be written, if precipitate will form.
Ammonium phosphate and potassium hydroxide
Concept introduction:
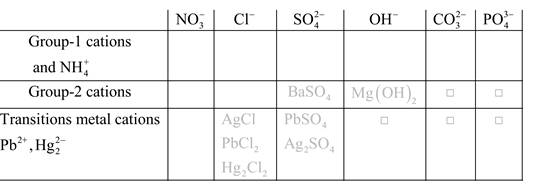
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with grey small box will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Precipitation reactions: It is a type of chemical reactions where two soluble salts react with each other and formed different products, out of which one product must be insoluble in solution which is known as precipitate.
A chemical equation which shows only the species that are participated in the reaction is said to be net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 8QAP
No precipitation occurs.
Explanation of Solution
Ammonium phosphate:
Potassium hydroxide:
Reaction for the solution of ammonium phosphate and potassium hydroxide is written as:
Reactants:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Products:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Now,
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether a precipitate will form when the given solutions are mixed should be determined along with the net ionic equation should be written, if precipitate will form.
Copper(II) sulfate and sodium carbonate
Concept introduction:
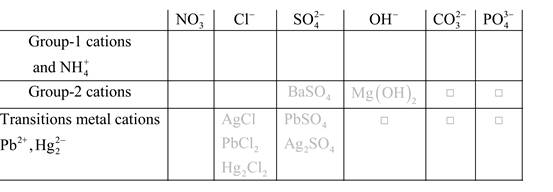
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with grey small box will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Precipitation reactions: It is a type of chemical reactions where two soluble salts react with each other and formed different products, out of which one product must be insoluble in solution which is known as precipitate.
A chemical equation which shows only the species that are participated in the reaction is said to be net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 8QAP
Precipitation occurs
The net ionic equation is:
Explanation of Solution
Copper(II) sulfate:
Sodium carbonate:
Reaction for the solution of copper(II) sulfate and sodium carbonate is written as:
Reactants:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Products:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Now,
So, the equation will be:
Now, cancelling out the ions which appear on both sides of the equation (
(e)
Interpretation:
Whether a precipitate will form when the given solutions are mixed should be determined along with the net ionic equation should be written, if precipitate will form.
Lithium sulfate and barium hydroxide
Concept introduction:
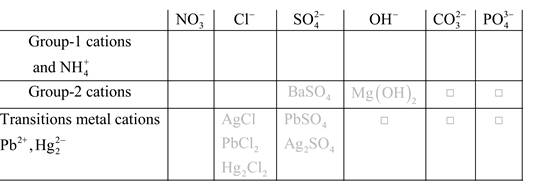
Solubility of any compound is predicted by above solubility chart.
Blank boxes indicate no precipitate formation occurs which means soluble in dilute solution.
Boxes with grey small box will form precipitate from dilute solutions and boxes where formula is written this is a cation-anion combination that will form precipitate.
Precipitation reactions: It is a type of chemical reactions where two soluble salts react with each other and formed different products, out of which one product must be insoluble in solution which is known as precipitate.
A chemical equation which shows only the species that are participated in the reaction is said to be net ionic equation.
Answer to Problem 8QAP
Precipitation occurs
The net ionic equation is:
Explanation of Solution
Lithium sulfate:
Barium hydroxide:
Reaction for the solution of lithium sulfate and barium hydroxide is written as:
Reactants:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Products:
Ions in solution:
Ions in solution:
Now,
So, the equation will be:
Now, cancelling out the ions which appear on both sides of the equation (
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry: Principles and Reactions, 8th, Loose-Leaf + OWLv2, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardQ1: Curved Arrows, Bronsted Acids & Bases, Lewis Acids & Bases Considering the following reactions: a) Predict the products to complete the reactions. b) Use curved electron-pushing arrows to show the mechanism for the reaction in the forward direction. Redraw some of the compounds to explicitly illustrate all bonds that are broken and all bonds that are formed. c) Label Bronsted acids and bases in the left side of the reactions. Label conjugate acids and bases in the right side of the reactions. d) Label Lewis acids and bases, nucleophiles and electrophiles in the left side of the reactions. A. + OH CH30: OH B. + HBr C. H₂SO4 D. CF 3. CH 3 + HCI N H fluoxetine antidepressant 1↓ JDownloadarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Part 3: AHm,system Mass of 1.00 M HCI Vol. of 1.00 M HCI Mass of NaOH(s) Total Mass in Calorimeter Mole product if HCI limiting reactant Trial 1 62.4009 1.511g Mole product if NaOH limiting reactant Limiting reactant Initial Temperature Final Temperature 23.8°C 37.6°C Change in Temperature AHm,system (calculated) Average AHm,system (calculated) (calculated) (calculated) Trial 2 64.006g 1.9599 (calculated) (calculated) (calculated) (calculated) (calculated) (calculated) 24.7°C 41.9°C (calculated) (calculated) (2 pts. each)arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardWhat is the numerical value of the slope using the equation y=-1.823x -0.0162 please show calculationsarrow_forward
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forward1.) Using the graph below (including the line equation of y = -1.823x - 0.0162) What is the numerical value for the slope shown? 2.) What are the Unit(s) associated with the slope of the line shown? for we all remember that numerical data always has units. 3.) What would be a good title for this graph and explain your choice. 0.00 0.0 02 0.4 10.6 08 10 12 -0.20 -0.40 -0.60 -0.80 Temp, freezing, in degrees Celcius 5-1.00 -1.20 -1.40 -1:60 y=-1.823x-0.0162 -180 -2.00 Concentration of Sucrose (m)arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Identify the Functional Groups (FG) in the following molecules. Classify C atoms as tertiary, 30, or quaternary 40. Identify secondary 20 and tertiary, 30 hydrogen atoms. Please provide steps to undertand each labeling. Please label in the image, so it fits explanation. I am still very unsure I undertand this.arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





