
Concept explainers
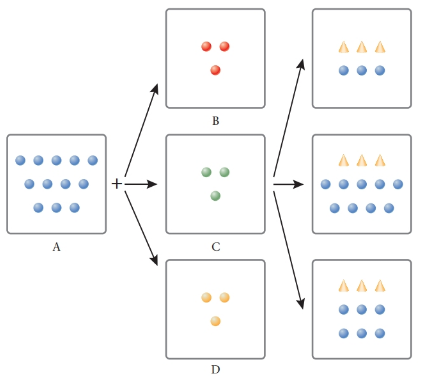
Consider four beakers. Beaker A has an aqueous solution of NaOH in which the OH- ions are represented by blue circles. Beaker B has a weak acid; HX is represented by red circles. Beaker C has a weak acid; H2X is represented by green circles. Beaker D has a weak acid; H3X is represented by yellow circles. X- ions are represented by triangles. Match the pictorial representations with the reactions given below.
(a)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry: Principles and Reactions, 8th, Loose-Leaf + OWLv2, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card
- Question 10 1 pts Which of the following is the most accurate nomenclature? 1-hydroxy-1-methyldecane-4,7-dione 2-hydroxy-2-methyldecane-5,8-dione 4,6-dioxo-2-methyldecane-2-ol 9-hydroxy-9-methyldecane-3,6-dione 8-hydroxy-8-methylnonane-3,6-dione OHarrow_forwardCould you please explain whether my thinking is correct or incorrect regarding how I solved it? Please point out any mistakes in detail, with illustrations if needed.arrow_forwardWhat are the most proper reagents to achieve these products? سد 1. 2. OH ○ 1. BrMgC6H6; 2. H+ ○ 1. BrMgCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3; 2. H+ O 1. CH3CH2CHO; 2. H+ O 1. BrMgCH2CH3; 2. H+arrow_forward
- Provide the IUPAC (systematic) name only for the following compound. Dashes, commas, and spaces must be correct. Harrow_forwardPlease use the nernst equation to genereate the Ion Selective Electrode Analysis standard curve within my excel spread sheet. Nernst Equation: E = Eo + m (ln a) Link: https://mnscu-my.sharepoint.com/:x:/g/personal/vi2163ss_go_minnstate_edu/EaREe1-PfGNKq1Cbink6kkYB5lBy05hEaE3mbGPUb22S6w?rtime=zQaSX3xY3Ugarrow_forwarda) b) c) H NaOH heat, dehydration + KOH heat, dehydration NaOH + (CH3)3CCHO heat, dehydration Pharrow_forward
- Indicate if the aldehyde shown reacts with the provided nucleophiles in acid or base conditions. a NaBH4 be Li eli -NH2 P(Ph3) f KCN g OH excess h CH3OH i NaCHCCH3arrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: + A ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centearrow_forwardPolar solutes are most likely to dissolve into _____, and _____ are most likely to dissolve into nonpolar solvents. A. nonpolar solutes; polar solvents B. nonpolar solvents; polar solvents C. polar solvents; nonpolar solutes D. polar solutes; nonpolar solventsarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





