
Concept explainers
a)
To determine: The cost of direct labor for the bicycle.
a)
Explanation of Solution
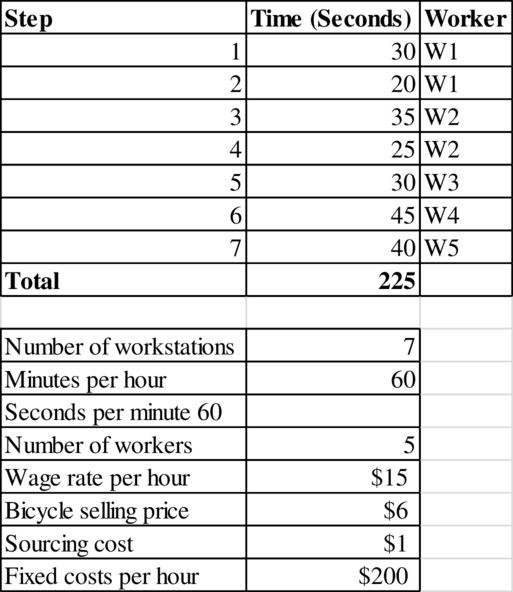
Given information:
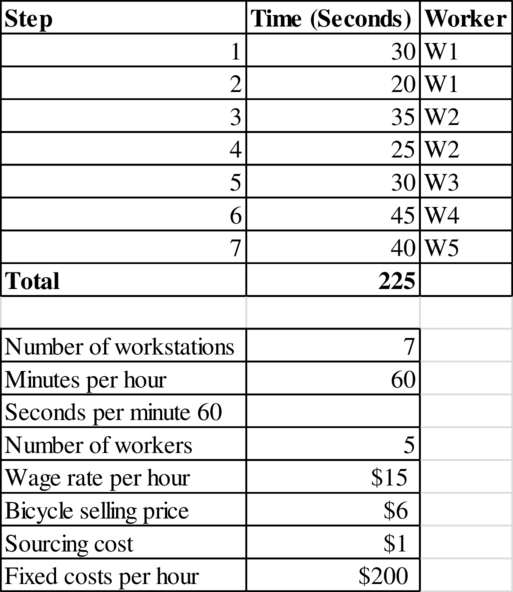
Identification of bottleneck:
Worker 1 performs Step 1 and Step 2 with a total time of 50 seconds.
Worker 2 performs Step 3 and Step 4 with a total time of 60 seconds.
Worker 3 performs Step 5 with a time of 50 seconds.
Worker 4 performs Step 6 with a time of 45 seconds.
Worker 5 performs Step 7 with a time of 40 seconds.
Therefore, the bottleneck is Worker 2 with 60 seconds.
Calculation of cost of direct labor for the bicycle:
The cost of direct labor per bicycle is $1.25.
b)
To determine: The profit per hour of the company.
b)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
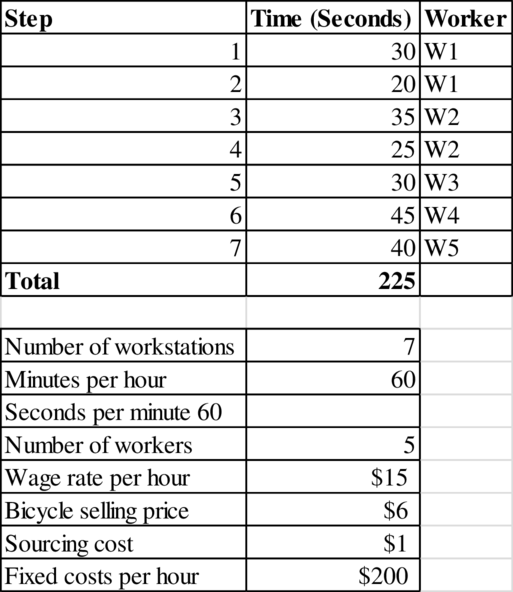
Calculation of profit per hour:
The bottleneck time is 60 seconds. Therefore, 60 units are produced every hour. Therefore, the flow rate is 60 units per hour.
The profit per hour is $25.
c)
To determine: The profit per hour of the company if the sourcing cost is 10% cheaper.
c)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
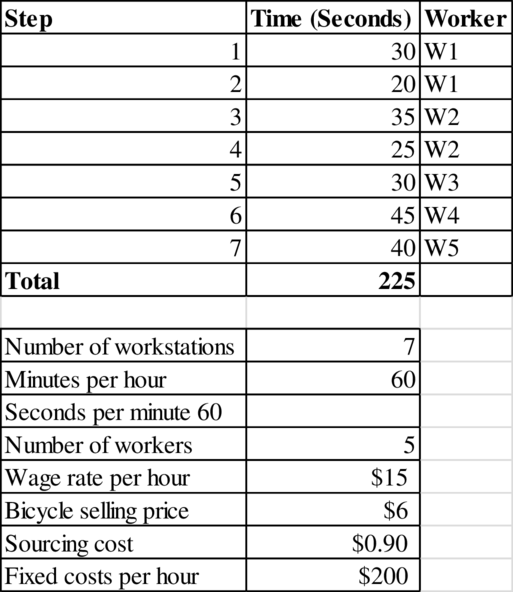
Calculation of profit per hour:
The bottleneck time is 60 seconds. Therefore, 60 units are produced every hour. Therefore, the flow rate is 60 units per hour.
The profit per hour is $31.
d)
To determine: The profit per hour of the company if the fixed cost is 10% less.
d)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
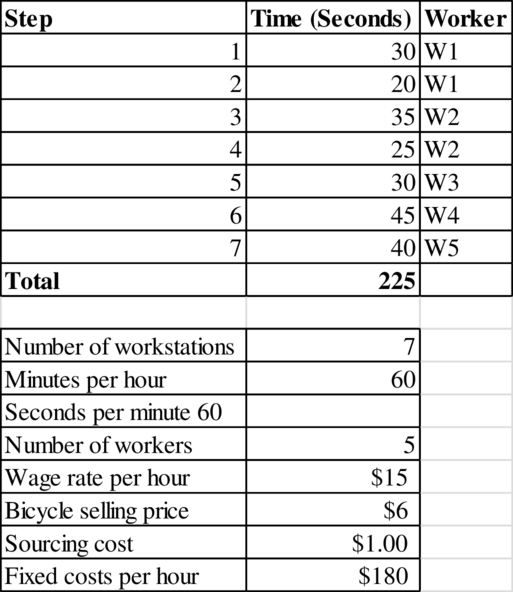
Calculation of profit per hour:
The bottleneck time is 60 seconds. Therefore, 60 units are produced every hour. Therefore, the flow rate is 60 units per hour.
The profit per hour is $45.
e)
To determine: The profit per hour of the company if the bottleneck time is reduced by 5 seconds per unit.
e)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation of profit per hour:
The bottleneck time is 55 seconds. Therefore, the flow rate is:
The profit per hour is $52.25.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- Agan Interior Design provides home and office decorating assistance to its customers. In normal operation, an average of 2.6 customers arrive each hour. One design consultant is available to answer customer questions and make product recommendations. The consultant averages 10 minutes with each customer. (a) Compute the operating characteristics of the customer waiting line, assuming Poisson arrivals and exponential service times. (Round your answers to four decimal places. Report time in hours.) λ= μ = = L = Wa W = P. W h (b) Service goals dictate that an arriving customer should not wait for service more than an average of 5 minutes. Is this goal being met? (Round your answer to one decimal place.) W₁ (in minutes) = min, which is ---Select--- than the desired wait time, so the goal ---Select--- met. What action do you recommend? (Select all that apply.) Hire another consultant. Increase the hours of operation. Decrease the mean service rate. Increase the mean service rate. There is…arrow_forwardCommunication Tips (2015) Tactful bragging Respond to the question "So, what do you do?" Whether you are student or have a job/internship, how can you tactfully brag in your answer to this question? Use the three elements from the video (listed below) when crafting your brag statement: Focus on results vs title Process vs job description Loop back to listener Example of an instructor's brag statement: "I help hundreds of students each semester to connect with one another, develop communication skills and prepare for upcoming interviews. Through improv games we explore presence, flexibility, and storytelling. How have your networking experiences on campus been so far?"arrow_forwardAccounting problemarrow_forward
- Government's new plan to shift cargo from roads back to rail 26TH JANUARY 2024 Government is seeking to finalise a plan aimed at improving its rail network and move cargo away from a billion rand per day to its logistics crises, government has said an urgentturnaround is needed to improve its 31 000km locomotive network as more and more cargo moves from rail to trucks. The Department of Transport (DoT) hosted a discussion with industry stakeholders regarding the Freight Road to Rail Migration Plan on Thursday - the latest development in the wake of President Cyril Ramphosa forming the National Logistics Crisis Committee last year. Transnet, the South African National Roads Agency (Sanral) and private sector companies were all in attendance. The Freight Road to Rail Migration Plan is part of government's strategies to improve the country's ongoing logistics crises. In October last year, the government unveiled its Freight Logistics Roadmap to improve the ports and rail networks and…arrow_forwardAssess what led to such logistical inefficiencies / collapse of a previously world class freight networkarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements concerning the evaluation of training programs is true? Most companies thoroughly evaluate the return on investment of their training programs It is relatively easy to establish a control group and a treatment group for evaluation Results level of evaluation measures how well participants liked the program Behavior level criteria measure whether skills learned in training result in behavior changes back on the jobarrow_forward
- Eligibility testing is an disparate impact validation method none of the above a method to validate promotions and progressive discipline activity a test an employee administers to ensure that the potential employee is capable and qualified to perform the requirements of the positionarrow_forwardA no-strike pledge by a union in a collective bargaining agreement is given in return for management’s agreement to: a grievance procedure a union shop a wage increase a fringe benefit increase binding arbitration of grievancesarrow_forwardWhich is the major OD technique that is used for increasing the communication, cooperation, and cohesiveness of work units? Leadership analysis Developing objectives Groupthink Strategic Planning team Buildingarrow_forward
- An American multinational firm usually is less than fully successful in adapting itself to local practices in each country because: American managers are often ignorant of local conditions None of the above management direction may be centralized in the home office All of the above Foreign subsidiaries often have American managersarrow_forwardWhen salary increases are based on inputs, or performance, companies are following: agency theory equality theory equity theory compliance theory need theoryarrow_forwardThe most frequently used techniques for measuring job satisfaction involves Direct observation Questionnaires Interviews Psychological testsarrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,

