
Concept explainers
Consider steady, incompressible, two-dimensional shear flow for which the velocity field is
(a) In similar fashion, calculate the location of each of the other three corners of the fluid particle at time t+dt.
(b) From the fundamental definition of linear strain rate (the rate of increase in length per unit length), calculate linear strain rates
(c) Compare your results with those obtained from the equations for
(a)
The location of each of the other three corners of the fluid particle at time
Answer to Problem 66P
The location of the lower left corner after time
The location of the lower right corner after time
The location of the upper left corner after time
The location of the upper right corner after time
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Two-dimensional shear flow, flow is incompressible, the velocity field is
Write the expression for the two-dimensional velocity field in the vector form.
Here, the constants are
The following figure shows the position of the corners at time
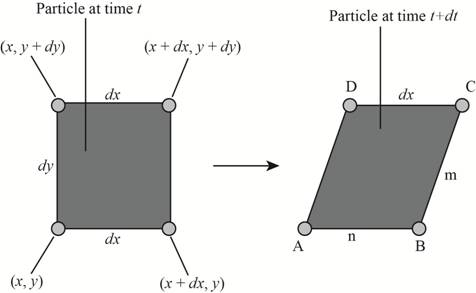
Figure-(1)
Here, the length of the lower edge at time
Write the expression for location of the lower left corner after time
Write the expression for location of the lower right corner after time
Write the expression for location of the upper left corner after time
Write the expression for location of the upper right corner after time
Write the expression for velocity along x direction.
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The location of the lower left corner after time
The location of the lower right corner after time
The location of the upper left corner after time
The location of the upper right corner after time
(b)
The linear strain rates.
Answer to Problem 66P
The linear strain rate along x axis is
The linear strain rate along y axis is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the strain rate along x direction.
Write the expression for the strain rate along y direction.
Write the expression for the length of the lower edge at time
Write the expression for the length of the lower edge at time
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The linear strain rate along x axis is
The linear strain rate along y axis is
(c)
The linear strain rates in Cartesian coordinates.
Comparison of the linear strain rate by fundamental principal to the linear strain rates in Cartesian coordinates.
Answer to Problem 66P
The linear strain rate in Cartesian coordinates along x axis is
The linear strain rate in Cartesian coordinates along y axis is
The linear strain rate by fundamental principal and the linear strain rates in Cartesian coordinates are same
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Linear strain along x axis is
Write the expression for the velocity along y direction.
Write the expression for the linear strain rate along x direction in Cartesian coordination.
Write the expression for the linear strain rate along y direction in Cartesian coordination.
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The linear strain rate in Cartesian coordinates along x axis is
The linear strain rate in Cartesian coordinates along y axis is
The linear strain rate by fundamental principal and the linear strain rates in Cartesian coordinates are the same.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
FLUID MECHANICS FUNDAMENTALS+APPS
- auto controlsarrow_forward1 Pleasearrow_forwardA spring cylinder system measures the pressure. Determine which spring can measure pressure between 0-1 MPa with a large excursion. The plate has a diameter of 20 mm. Also determine the displacement of each 0.1 MPa step.Spring power F=c x fF=Springpower(N)c=Spring constant (N/mm)f=Suspension (mm) How do I come up with right answer?arrow_forward
- A lift with a counterweight is attached to the ceiling. The attachment is with 6 stainless and oiled screws. What screw size is required? What tightening torque? - The lift weighs 500 kg and can carry 800 kg. - Counterweight weight 600 kg - Durability class 12.8 = 960 MPa- Safety factor ns=5+-Sr/Fm= 0.29Gr =0.55arrow_forwardKnowing that a force P of magnitude 750 N is applied to the pedal shown, determine (a) the diameter of the pin at C for which the average shearing stress in the pin is 40 MPa, (b) the corresponding bearing stress in the pedal at C, (c) the corresponding bearing stress in each support bracket at C. 75 mm 300 mm- mm A B P 125 mm 5 mm C Darrow_forwardAssume the B frame differs from the N frame through a 90 degree rotation about the second N base vector. The corresponding DCM description is: 1 2 3 4 5 6 9 # adjust the return matrix values as needed def result(): dcm = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] return dcmarrow_forward
- Find the reaction at A and B The other response I got was not too accurate,I need expert solved answer, don't use Artificial intelligence or screen shot it solvingarrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forwardSolve for the reaction of all the forces Don't use artificial intelligence or screen shot it, only expert should solvearrow_forward
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardA six cylinder petrol engine has a compression ratio of 5:1. The clearance volume of each cylinder is 110CC. It operates on the four-stroke constant volume cycle and the indicated efficiency ratio referred to air standard efficiency is 0.56. At the speed of 2400 rpm. 44000KJ/kg. Determine the consumes 10kg of fuel per hour. The calorific value of fuel average indicated mean effective pressure.arrow_forwardThe members of a truss are connected to the gusset plate as shown in (Figure 1). The forces are concurrent at point O. Take = 90° and T₁ = 7.5 kN. Part A Determine the magnitude of F for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. F= 7.03 Submit ? kN Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 21 attempts remaining ▾ Part B Determine the magnitude of T2 for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure T₂ = 7.03 C T2 |? KN Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 23 attempts remaining Provide Feedbackarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





