
Concept explainers
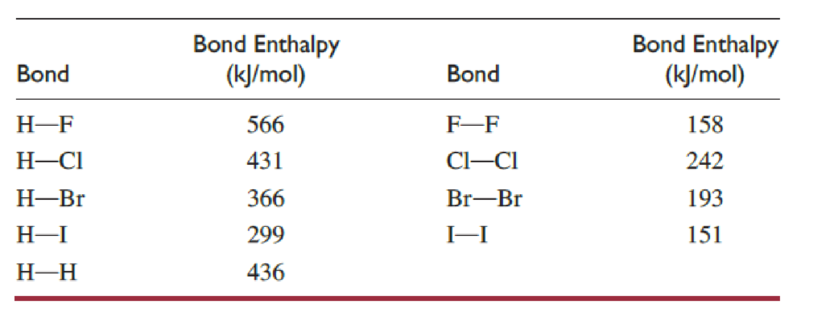
For the reactions of molecular hydrogen with fluorine and with chlorine:
- (a) Calculate the enthalpy change for breaking all the bonds in the reactants.
- (b) Calculate the enthalpy change for forming all the bonds in the products.
- (c) From the results in parts (a) and (b), calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction.
- (d) Which reaction is most exothermic?
(a)
Interpretation:
The enthalpy change for breaking of all bonds present in all reactants of given reaction has to be calculated.
Answer to Problem 61QRT
The enthalpy change value for breaking of bonds for fluorine reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of molecular hydrogen with fluorine and chlorine is as follows,
Above both reactions, involves breaking of1
(b)
Interpretation:
The enthalpy change for forming of all bonds present in all products of given reaction has to be calculated.
Answer to Problem 61QRT
The enthalpy change value for forming of bonds in fluorine reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of molecular hydrogen with fluorine and chlorine is as follows,
Above both reactions involve formation of 2 hydrogen-halogen bonds. The
(c)
Interpretation:
The enthalpy change given reaction has to be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
The enthalpy change in a system
Where,
Answer to Problem 61QRT
The enthalpy change value for fluorine reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of molecular hydrogen with fluorine and chlorine is as follows,
The enthalpy change value for each reaction is determined by considering the formula,
(d)
Interpretation:
From the two given reactions, the exothermic reaction has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Enthalpy is the amount energy absorbed or released in a process. Under constant pressure conditions the enthalpy change will be equal to molar q.
Exothermic reaction: Exothermic reactions are those in which evolution of heat takes place during any chemical reaction. They release heat because the reactant molecules require less heat for breakage of bonds than the product molecules.
Endothermic reaction: Endothermic reactions are those in which heat is absorbed during any chemical reaction. In such type of reactions, external energy is needed.
Answer to Problem 61QRT
The reaction between molecular hydrogen and fluorine is more exothermic than the other one.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of molecular hydrogen with fluorine is more exothermic since
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
- The following product was made from diethyl ketone and what other reagent(s)? £ HO 10 2-pentyne 1-butyne and NaNH2 ☐ 1-propanol ☐ pyridine butanal ☐ pentanoatearrow_forwardWhich pair of reagents will form the given product? OH X + Y a. CH3 b. CH2CH3 ༧་་ C. CH3- CH2CH3 d.o6.(རི॰ e. CH3 OCH2CH3 -MgBr f. CH3-MgBr g. CH3CH2-MgBr -C-CH3 CH2CH3arrow_forwardQuestion 3 What best describes the product of the following reaction? 1. CH3CH2MgBr (2 eq) 2. H a new stereocenter will not be formed a new stereocenter will be formed an alkyl halide will result an alkane will result an aromatic compound will result 1 ptsarrow_forward
- Rank the following from most to least reactive toward nucleophilic attack. 1. [Select] [Select] 2. Acyl halide Aldehyde 3. Carboxylate ion 4. Carboxylic acid Ketone 5. [Select]arrow_forwardQuestion 10 1 pts Which of the following is the most accurate nomenclature? 1-hydroxy-1-methyldecane-4,7-dione 2-hydroxy-2-methyldecane-5,8-dione 4,6-dioxo-2-methyldecane-2-ol 9-hydroxy-9-methyldecane-3,6-dione 8-hydroxy-8-methylnonane-3,6-dione OHarrow_forwardCould you please explain whether my thinking is correct or incorrect regarding how I solved it? Please point out any mistakes in detail, with illustrations if needed.arrow_forward
- What are the most proper reagents to achieve these products? سد 1. 2. OH ○ 1. BrMgC6H6; 2. H+ ○ 1. BrMgCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3; 2. H+ O 1. CH3CH2CHO; 2. H+ O 1. BrMgCH2CH3; 2. H+arrow_forwardProvide the IUPAC (systematic) name only for the following compound. Dashes, commas, and spaces must be correct. Harrow_forwardPlease use the nernst equation to genereate the Ion Selective Electrode Analysis standard curve within my excel spread sheet. Nernst Equation: E = Eo + m (ln a) Link: https://mnscu-my.sharepoint.com/:x:/g/personal/vi2163ss_go_minnstate_edu/EaREe1-PfGNKq1Cbink6kkYB5lBy05hEaE3mbGPUb22S6w?rtime=zQaSX3xY3Ugarrow_forward
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning





