
Concept explainers
Rank the following ions in order of increasing number of unpaired electrons: Tr3+, Fe2+, V3+, Cu+, Mn4+.
Interpretation: It should be ranked the given set of ions in increasing order of number of unpaired electrons.
Concept Introduction:
- Aufbau Principle tells that the orbital with the lower energy is filled with electrons first and then the filling of higher energy orbital follows. By using this, valence orbital diagram can be draw for any atoms or ions.
- Electronic configuration is the arrangement of the electrons of atoms in the orbital. The electronic configurations are writing for atoms and ions, in accordance with Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund’s rule.
- According to Pauli Exclusion Principle, no two electrons having the same spin can occupy the same orbital.
- According to Hund’s rule, the orbital in the subshell is filled singly by one electron before the same orbital is doubly filled. When the orbital is singly filled, all the electrons have same spin. In a doubly filled orbital, there are two electrons with opposite spin.
To determine the increasing order of unpaired electrons present in the given set of ions.
Answer to Problem 4.79QP
Ions in increasing order of unpaired electrons,
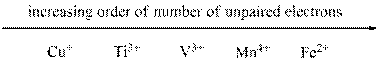
Explanation of Solution
Electronic configuration of
The valence orbital diagram of
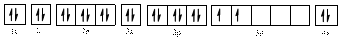
The electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
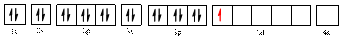
The electronic configuration of
The valence orbital diagram is drawn as shown above. From this, we can find that there is one unpaired electron and which is highlighted in red colour.
Electronic configuration of
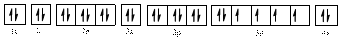
The electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
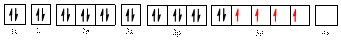
The electronic configuration of
The valence orbital diagram is drawn as shown above. From this, we can find that there are four unpaired electrons that are highlighted in red colour.
Electronic configuration of
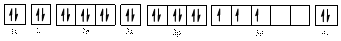
The electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
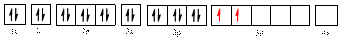
The electronic configuration of
The valence orbital diagram is drawn as shown above. From this, we can find that there are two unpaired electrons, that are highlighted in red colour.
Electronic configuration of
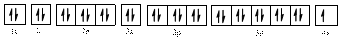
The electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
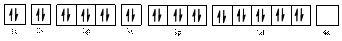
The electronic configuration of
The valence orbital diagram is drawn as shown above. From this we can find that there are no unpaired electrons present.
Electronic configuration of
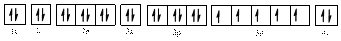
The electronic configuration of
Electronic configuration of
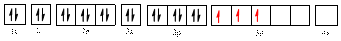
The electronic configuration of
The valence orbital diagram is drawn as shown above. From this, we can find that there are three unpaired electrons present and the same is highlighted in red colour.
Given ions were ranked in increasing order of unpaired electron as follows,
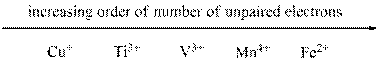
From the number of unpaired electrons for each of the given ions found out in the previous steps we can arrange them in increasing order of number of unpaired electrons as shown above.
The given sets of ions were ranked in increasing order of number of unpaired electrons.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
CHEMISTRY: ATOMS FIRST VOL 1 W/CONNECT
- Write all of Me Possible Products For each Of the Following reactions. In each case identity all pains of enantiomers, all digsterzoners and all Meso compounds 9. 11-60 11-0-11 V-G Η Η H ~ C-11 +HB+ - 1 H b. पन्ना 171-0-11 H-C-H Н C-C=c-call +HBr Perendez ==arrow_forwardHow can i draw the mechanisms for this molecule?arrow_forwarda. Discuss and explain he difference IN Stability between the Chai and Boat Гольцу от судомехане b. For the Following Molecule draw both possible Clain conformations and explain which one is more stable and for what Reason. H. CH₂ CH₂ H "Harrow_forward
- Please provide the mechanism for this reacitonarrow_forwardQuestion 5: Name the following compound in two ways using side chain and using prefix amine (Common name and IUPAC name both) CH3NH2 CH3CH2NHCH3 CH₂CH₂N(CH3)2 Draw the structure of diethyl methyl amine Question 6. Write the balanced combustion reaction for: a. Hexane b. Propyne c. 2-pentene Question 7: Write the following electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene: Hint: Use notes if you get confused a. Halogenation reaction: b. Nitration reaction : c. Sulphonation reaction: d. Alkylation reaction: e. Aceylation reaction:arrow_forwardQuestion 4. Name the following structures ○ CH3-C-N-H H CH3CH2-C-N-H H CH3CH2-C-N-CH3 Harrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





