
System Dynamics
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780073398068
Author: III William J. Palm
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 4.66P
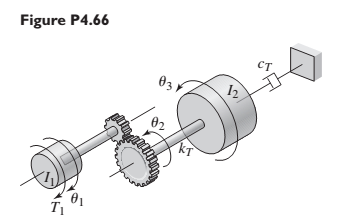
Figure P4.66 shows a drive train with a spur-gear pair. The first shaft turns N times faster than the second shaft. Develop a model of the system including the elasticity of the second shaft. Assume the first shaft is rigid, and neglect the gear and shaft masses. The input is the applied torque
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Four-bar linkage mechanism, AB=40mm, BC=60mm, CD=70mm, AD=80mm, =60°, w1=10rad/s. Determine the direction and
magnitude of w3 using relative motion graphical method.
A
B
2
3
77777
477777
Four-bar linkage mechanism, AB=40mm, BC=60mm, CD=70mm, AD=80mm, =60°, w1=10rad/s. Determine the direction and
magnitude of w3 using relative motion graphical method.
A
B
2
3
77777
477777
The evaporator of a vapor compression refrigeration cycle utilizing R-123 as the refrigerant isbeing used to chill water. The evaporator is a shell and tube heat exchanger with the water flowingthrough the tubes. The water enters the heat exchanger at a temperature of 54°F. The approachtemperature difference of the evaporator is 3°R. The evaporating pressure of the refrigeration cycleis 4.8 psia and the condensing pressure is 75 psia. The refrigerant is flowing through the cycle witha flow rate of 18,000 lbm/hr. The R-123 leaves the evaporator as a saturated vapor and leaves thecondenser as a saturated liquid. Determine the following:a. The outlet temperature of the chilled waterb. The volumetric flow rate of the chilled water (gpm)c. The UA product of the evaporator (Btu/h-°F)d. The heat transfer rate between the refrigerant and the water (tons)
Chapter 4 Solutions
System Dynamics
Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.1PCh. 4 - In the spring arrangement shown in Figure P4.2....Ch. 4 - In the arrangement shown in Figure P4.3, a cable...Ch. 4 - In the spring arrangement shown in Figure P4.4,...Ch. 4 - For the system shown in Figure P4.5, assume that...Ch. 4 - The two stepped solid cylinders in Figure P4.6...Ch. 4 - A table with four identical legs supports a...Ch. 4 - The beam shown in Figure P4.8 has been stiffened...Ch. 4 - Determine the equivalent spring constant of the...Ch. 4 - Compute the equivalent torsional spring constant...
Ch. 4 - Plot the spring force felt by the mass shown in...Ch. 4 - Calculate the expression for the natural frequency...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.13PCh. 4 - Obtain the expression for the natural frequency of...Ch. 4 - 4.15 A connecting rod having a mass of 3.6 kg is...Ch. 4 - Calculate the expression for the natural frequency...Ch. 4 - For each of the systems shown in Figure P4.17, the...Ch. 4 - The mass m in Figure P4.18 is attached to a rigid...Ch. 4 - In the pulley system shown in Figure P4.19, the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.20PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.21PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.22PCh. 4 - In Figure P4.23, assume that the cylinder rolls...Ch. 4 - In Figure P4.24 when x1=x2=0 the springs are at...Ch. 4 - 4.25 In Figure P4.25 model the three shafts as...Ch. 4 - In Figure P4.26 when 1=2=0 the spring is at its...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.27PCh. 4 - For the system shown in Figure P4.28, suppose that...Ch. 4 - For the system shown in Figure P4.29, suppose that...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.30PCh. 4 - For Figure P4.31, the equilibrium position...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.32PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.33PCh. 4 - 4.34 For Figure P4.34, assume that the cylinder...Ch. 4 - Use the Rayleigh method to obtain an expression...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.36PCh. 4 - 4.37 Determine the natural frequency of the system...Ch. 4 - Determine the natural frequency of the system...Ch. 4 - Use Rayleigh's method to calculate the expression...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.40PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.41PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.42PCh. 4 - The vibration of a motor mounted on the end of a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.44PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.45PCh. 4 - A certain cantilever beam vibrates at a frequency...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.47PCh. 4 - 4.48 The static deflection of a cantilever beam is...Ch. 4 - Figure P4.49 shows a winch supported by a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.50PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.51PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.52PCh. 4 - 4.53 In Figure P4.53 a motor supplies a torque T...Ch. 4 - Derive the equation of motion for the lever system...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.55PCh. 4 - Figure P4.56a shows a Houdaille damper, which is a...Ch. 4 - 4.57 Refer to Figure P4.57. Determine the...Ch. 4 - For the system shown in Figure P4.58, obtain the...Ch. 4 - Find the transfer function ZsXs for the system...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.60PCh. 4 - Find the transfer function YsXs for the system...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.62PCh. 4 - 4.63 In the system shown in Figure P4.63, the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.64PCh. 4 - Figure P4.65 shows a rack-and-pinion gear in which...Ch. 4 - Figure P4.66 shows a drive train with a spur-gear...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.67PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.68PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.69PCh. 4 - Figure P4.70 shows a quarter-car model that...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.71PCh. 4 - 4.72 Derive the equation of motion for the system...Ch. 4 - A boxcar moving at 1.3 m/s hits the shock absorber...Ch. 4 - For the systems shown in Figure P4.74, assume that...Ch. 4 - Refer to Figure P4.75a, which shows a ship’s...Ch. 4 - In this problem, we make all the same assumptions...Ch. 4 - Refer to Figure P4.79a, which shows a water tank...Ch. 4 - The “sky crane” shown on the text cover was a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.81PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.82PCh. 4 - Suppose a mass in moving with a speed 1 becomes...Ch. 4 - Consider the system shown in Figure 4.6.3. Suppose...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.86PCh. 4 - Figure P4.87 shows a mass m with an attached...Ch. 4 - Figure P4.88 represents a drop forging process....Ch. 4 - Refer to Figure P4.89. A mass m drops from a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.90PCh. 4 - (a) Obtain the equations of motion of the system...Ch. 4 - Refer to part (a) of Problem 4.90. Use MATLAB to...Ch. 4 - Refer to Problem 4.91. Use MATLAB to obtain the...Ch. 4 - 4.94 (a) Obtain the equations of motion of the...Ch. 4 -
4.95 (a) Obtain the equations of motion of the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (Read image) (Answer given)arrow_forwardProblem (17): water flowing in an open channel of a rectangular cross-section with width (b) transitions from a mild slope to a steep slope (i.e., from subcritical to supercritical flow) with normal water depths of (y₁) and (y2), respectively. Given the values of y₁ [m], y₂ [m], and b [m], calculate the discharge in the channel (Q) in [Lit/s]. Givens: y1 = 4.112 m y2 = 0.387 m b = 0.942 m Answers: ( 1 ) 1880.186 lit/s ( 2 ) 4042.945 lit/s ( 3 ) 2553.11 lit/s ( 4 ) 3130.448 lit/sarrow_forwardProblem (14): A pump is being used to lift water from an underground tank through a pipe of diameter (d) at discharge (Q). The total head loss until the pump entrance can be calculated as (h₁ = K[V²/2g]), h where (V) is the flow velocity in the pipe. The elevation difference between the pump and tank surface is (h). Given the values of h [cm], d [cm], and K [-], calculate the maximum discharge Q [Lit/s] beyond which cavitation would take place at the pump entrance. Assume Turbulent flow conditions. Givens: h = 120.31 cm d = 14.455 cm K = 8.976 Q Answers: (1) 94.917 lit/s (2) 49.048 lit/s ( 3 ) 80.722 lit/s 68.588 lit/s 4arrow_forward
- Problem (13): A pump is being used to lift water from the bottom tank to the top tank in a galvanized iron pipe at a discharge (Q). The length and diameter of the pipe section from the bottom tank to the pump are (L₁) and (d₁), respectively. The length and diameter of the pipe section from the pump to the top tank are (L2) and (d2), respectively. Given the values of Q [L/s], L₁ [m], d₁ [m], L₂ [m], d₂ [m], calculate total head loss due to friction (i.e., major loss) in the pipe (hmajor-loss) in [cm]. Givens: L₁,d₁ Pump L₂,d2 오 0.533 lit/s L1 = 6920.729 m d1 = 1.065 m L2 = 70.946 m d2 0.072 m Answers: (1) 3.069 cm (2) 3.914 cm ( 3 ) 2.519 cm ( 4 ) 1.855 cm TABLE 8.1 Equivalent Roughness for New Pipes Pipe Riveted steel Concrete Wood stave Cast iron Galvanized iron Equivalent Roughness, & Feet Millimeters 0.003-0.03 0.9-9.0 0.001-0.01 0.3-3.0 0.0006-0.003 0.18-0.9 0.00085 0.26 0.0005 0.15 0.045 0.000005 0.0015 0.0 (smooth) 0.0 (smooth) Commercial steel or wrought iron 0.00015 Drawn…arrow_forwardThe flow rate is 12.275 Liters/s and the diameter is 6.266 cm.arrow_forwardAn experimental setup is being built to study the flow in a large water main (i.e., a large pipe). The water main is expected to convey a discharge (Qp). The experimental tube will be built at a length scale of 1/20 of the actual water main. After building the experimental setup, the pressure drop per unit length in the model tube (APm/Lm) is measured. Problem (20): Given the value of APm/Lm [kPa/m], and assuming pressure coefficient similitude, calculate the drop in the pressure per unit length of the water main (APP/Lp) in [Pa/m]. Givens: AP M/L m = 590.637 kPa/m meen Answers: ( 1 ) 59.369 Pa/m ( 2 ) 73.83 Pa/m (3) 95.443 Pa/m ( 4 ) 44.444 Pa/m *******arrow_forward
- Find the reaction force in y if Ain = 0.169 m^2, Aout = 0.143 m^2, p_in = 0.552 atm, Q = 0.367 m^3/s, α = 31.72 degrees. The pipe is flat on the ground so do not factor in weight of the pipe and fluid.arrow_forwardFind the reaction force in x if Ain = 0.301 m^2, Aout = 0.177 m^2, p_in = 1.338 atm, Q = 0.669 m^3/s, and α = 37.183 degreesarrow_forwardProblem 5: Three-Force Equilibrium A structural connection at point O is in equilibrium under the action of three forces. • • . Member A applies a force of 9 kN vertically upward along the y-axis. Member B applies an unknown force F at the angle shown. Member C applies an unknown force T along its length at an angle shown. Determine the magnitudes of forces F and T required for equilibrium, assuming 0 = 90° y 9 kN Aarrow_forward
- Problem 19: Determine the force in members HG, HE, and DE of the truss, and state if the members are in tension or compression. 4 ft K J I H G B C D E F -3 ft -3 ft 3 ft 3 ft 3 ft- 1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lbarrow_forwardProblem 14: Determine the reactions at the pin A, and the tension in cord. Neglect the thickness of the beam. F1=26kN F2 13 12 80° -2m 3marrow_forwardProblem 22: Determine the force in members GF, FC, and CD of the bridge truss and state if the members are in tension or compression. F 15 ft B D -40 ft 40 ft -40 ft 40 ft- 5 k 10 k 15 k 30 ft Earrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
How to balance a see saw using moments example problem; Author: Engineer4Free;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d7tX37j-iHU;License: Standard Youtube License