
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977596
Author: SMITH
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 4.65P
Hydrocarbons like benzene are
phenols. This is an example of a general process in the body, in which an unwanted compound
(benzene) is converted to a more water-soluble derivative called a metabolite, so that it can be
excreted more readily from the body.
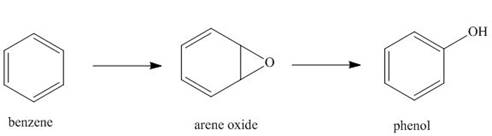
a. Classify each of these reactions as oxidation, reduction, or neither.
b. Explain why phenol is more water soluble than benzene. This means that phenol dissolves in urine, which is largely water, to a greater extent than benzene.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Briefly state why trifluoroacetic acid is more acidic than acetic acid.
Explain why acid chlorides are more reactive than amides in reactions with nucleophiles.
Calculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid
An analytical chemist is titrating 101.7 mL of a 0.3500M solution of piperidine (C5H10NH) with a 0.05700M solution of HClO4. The pK of piperidine is 2.89.
Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 682.9 mL of the HClO solution to it.
4
Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HClO solution added.
4
Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
pH = .11
00.
18
Ar
Chapter 4 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.1PCh. 4 - Problem 4.2 Which of the following is not another...Ch. 4 - Problem 4.3 Draw the five constitutional isomers...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.4PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.5PCh. 4 - Draw the five constitutional isomers that have...Ch. 4 - Problem 4.7 Give the IUPAC name for each...Ch. 4 - Give the IUPAC name for each compound. a....Ch. 4 - Problem 4.9 Give the structure corresponding to...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.10P
Ch. 4 - Give the IUPAC name for each compound.Ch. 4 - Give the structure corresponding to each IUPAC...Ch. 4 - Arrange the following compounds in order of...Ch. 4 - Problem 4.14 Draw the staggered and eclipsed...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.15PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.16PCh. 4 - Problem 4.17 a. Draw the three staggered and...Ch. 4 - Problem 4.18 Rank the following conformations in...Ch. 4 - Problem 4.19 Consider rotation around the...Ch. 4 - Calculate the destabilization present in each...Ch. 4 - Problem 4.21 Classify the ring carbons as up or...Ch. 4 - Problem 4.22 Using the cyclohexane with the C’s...Ch. 4 - Draw a second chair conformation for each...Ch. 4 - Problem 4.24 Draw both conformations for and...Ch. 4 - Problem 4.25 Draw the structure for each compound...Ch. 4 - For cis-1, 3-diethylcyclobutane, draw a a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.27PCh. 4 - Problem 4.28 Consider .
Draw structures f or the...Ch. 4 - Problem 4.29 Draw a chair conformation of...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.30PCh. 4 - Draw the products of each combustion reaction.Ch. 4 - Explain why beeswax is insoluble in H2O, slightly...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.33PCh. 4 - Name each alkane using the ball-and-stick model,...Ch. 4 - Consider the substituted cyclohexane shown in the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.36PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.37PCh. 4 - 4.38 Give the IUPAC name for each compound.
a. c....Ch. 4 - 4.39 Give the structure and IUPAC name for each of...Ch. 4 -
4.40 Draw the structure corresponding to each...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.41PCh. 4 - 4.42 Give the IUPAC name for each compound.
a....Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.43PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.44PCh. 4 - 4.45 Which conformation in each pair is higher in...Ch. 4 - 4.46 Considering rotation around the bond...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.47PCh. 4 - 4.48 (a) Using Newman projections, draw all...Ch. 4 - 4.49 Label the sites of torsional and steric...Ch. 4 - 4.50 Calculate the barrier to rotation for each...Ch. 4 - 4.51 The eclipsed conformation of is less...Ch. 4 - (a) Draw the anti and gauche conformations for...Ch. 4 - For each compound drawn below: a.Label each OH,Br...Ch. 4 - Draw the two possible chair conformations for...Ch. 4 - For each compound drawn below: a. Draw...Ch. 4 - 4.56 Convert each of the following structures into...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.57PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.58PCh. 4 - 4.59 Classify each pair of compounds as...Ch. 4 - Classify each pair of compounds as constitutional...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.61PCh. 4 - 4.62 Draw the three constitutional isomers having...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.63PCh. 4 - 4.64 Draw the products of combustion of each...Ch. 4 - 4.65 Hydrocarbons like benzene are metabolized in...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.66PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.67PCh. 4 - Cyclopropane and cyclobutane have similar strain...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.69PCh. 4 - Haloethanes (CH3CH2X,X=Cl,Br,I) have similar...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.71PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.72PCh. 4 - Consider the tricyclic structure B (a) Label each...Ch. 4 - Read Appendix B on naming branched alkyl...Ch. 4 - Read Appendix B on naming bicyclic compounds. Then...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
To test your knowledge, discuss the following topics with a study partner or in writing ideally from memory. Th...
HUMAN ANATOMY
45. Calculate the mass of nitrogen dissolved at room temperature in an 80.0-L home aquarium. Assume a total pre...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Separate the list P,F,V,,T,a,m,L,t, and V into intensive properties, extensive properties, and nonproperties.
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Why is it unlikely that two neighboring water molecules would be arranged like this?
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
How could you separate a mixture of the following compounds? The reagents available to you are water, either, 1...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following is a two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 340.0 262.7 QUESTION: For both groups of data provide answers to the calculations attached in the imagearrow_forward7. Concentration and uncertainty in the estimate of concentration (class data) Class mean for sample (Regular) |[Cl-] (mmol/L) class mean Sn za/2 95% Confidence Interval (mmol/L) [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 95% Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardThe following is a two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 223.4 148.7 353.7 278.2 334.6 268.7 305.6 234.4 340.0 262.7 304.3 283.2 244.7 143.6 QUESTION: For both groups of data calculate the answers attached in the image.arrow_forward
- Give reason(s) for six from the followings [using equations if possible] a. Addition of sodium carbonate to sulfanilic acid in the Methyl Orange preparation. b. What happened if the diazotization reaction gets warmed up by mistake. c. Addition of sodium nitrite in acidified solution in MO preparation through the diazotization d. Using sodium dithionite dihydrate in the second step for Luminol preparation. e. In nitroaniline preparation, addition of the acid mixture (nitric acid and sulfuric acid) to the product of step I. f. What is the main reason of the acylation step in nitroaniline preparation g. Heating under reflux. h. Fusion of an organic compound with sodium. HAND WRITTEN PLEASEarrow_forwardedict the major products of the following organic reaction: u A + ? CN Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Te LMUNDARYarrow_forwardSketch the intermediates for A,B,C & D.arrow_forward
- Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? O ? A . If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. . If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ㅇ 80 F5 F6 A 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Cente FIGarrow_forwardIn methyl orange preparation, if the reaction started with 0.5 mole of sulfanilic acid to form the diazonium salt of this compound and then it converted to methyl orange [0.2 mole]. If the efficiency of the second step was 50%, Calculate: A. Equation(s) of Methyl Orange synthesis: Diazotization and coupling reactions. B. How much diazonium salt was formed in this reaction? C. The efficiency percentage of the diazotization reaction D. Efficiency percentage of the whole reaction.arrow_forwardHand written equations pleasearrow_forward
- Hand written equations pleasearrow_forward> each pair of substrates below, choose the one that will react faster in a substitution reaction, assuming that: 1. the rate of substitution doesn't depend on nucleophile concentration and 2. the products are a roughly 50/50 mixture of enantiomers. Substrate A Substrate B Faster Rate X Ś CI (Choose one) (Choose one) CI Br Explanation Check Br (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Farrow_forwardNMR spectrum of ethyl acetate has signals whose chemical shifts are indicated below. Which hydrogen or set of hydrogens corresponds to the signal at 4.1 ppm? Select the single best answer. The H O HỌC—C—0—CH, CH, 2 A ethyl acetate H NMR: 1.3 ppm, 2.0 ppm, 4.1 ppm Check OA B OC ch B C Save For Later Submit Ass © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center |arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Lipids - Fatty Acids, Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Terpenes, Waxes, Eicosanoids; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7dmoH5dAvpY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY