
4-31 Predict whether a precipitate will form when aqueous solutions of the following compounds are mixed. If a precipitate will form, write its formula and write a net ionic equation for its formation. To make your predictions, use the solubiity generalizations in
Section 4-3.
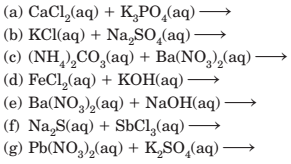
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the given reaction gives precipitate or not should be determined. If yes, the formula of the product should be written along with the net ionic equation.
Concept Introduction:
When two aqueous solutions are mixed together, this may or may not result in formation of an insoluble solid in the solution. This insoluble solid is called precipitate and this reaction is called precipitation reaction.
For example, a reaction in which A and C displace each other from their respective solutions. Since two displacement takes place, this reaction is also called double displacement reaction.
Here,
Answer to Problem 4.31P
Phosphate of calcium are insoluble, hence they separate out as precipitate.
Precipitate -
Net Reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is as-
If the double displacement-reaction takes place ,then the product of the reaction would be-
The products are phosphate of calcium and chloride of potassium.
Phosphates of calcium are insoluble; hence, they separate out as precipitate, chlorides of potassium are soluble, they remain as aqueous solution.
The net reaction is as-
(b)
Interpretation:
The precipitation or double-displacement reaction is to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
When two aqueous solutions are mixed together, this may or may not result in formation of an insoluble solid in the solution. This insoluble solid is called precipitate and this reaction is called precipitation reaction.
For example, a reaction in which A and C displace each other from their respective solutions. Since two displacement takes place, this reaction is also called double displacement reaction.
Here, AD(s) represents a precipitate.
Answer to Problem 4.31P
No precipitate.
Net Reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is as-
If the double displacement-reaction takes place ,then the product of the reaction would be-
The products are sulphate of potassium and chloride of Sodium.
Sulphates of potassium are soluble, they remain as aqueous solution.
Chlorides of sodium are soluble, they remain as aqueous solution.
The net reaction is as-
(c)
Interpretation:
The precipitation or double-displacement reaction is to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
When two aqueous solutions are mixed together, this may or may not result in formation of an insoluble solid in the solution. This insoluble solid is called precipitate and this reaction is called precipitation reaction.
For example, a reaction in which A and C displace each other from their respective solutions. Since two displacement takes place, this reaction is also called double displacement reaction.
Here, AD(s) represents a precipitate.
Answer to Problem 4.31P
Phosphate of Calcium are insoluble, hence they separate out as precipitate.
Precipitate -
Net Reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is as-
If the double displacement-reaction takes place ,then the product of the reaction would be-
The products are Carbonate of Barium and Nitrate of Ammonium.
Carbonate of Barium are insoluble, hence they separate out as precipitate.
Nitrate of Ammonium are soluble, they remain as aqueous solution.
The net reaction is as-
(d)
Interpretation:
The precipitation or double-displacement reaction is to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
When two aqueous solutions are mixed together, this may or may not result in formation of an insoluble solid in the solution. This insoluble solid is called precipitate and this reaction is called precipitation reaction.
For example, a reaction in which A and C displace each other from their respective solutions. Since two displacement takes place, this reaction is also called double displacement reaction.
Here, AD(s) represents a precipitate.
Answer to Problem 4.31P
No precipitate.
Net Reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is as-
If the double displacement-reaction takes place, then the product of the reaction would be-
The products are Chloride of Potassium and Hydroxide of Iron.
Chloride of Potassium are soluble, they remain as aqueous solution.
Hydroxide of Iron are soluble, they remain as aqueous solution.
The net reaction is as-
(e)
Interpretation:
The precipitation or double-displacement reaction is to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
When two aqueous solutions are mixed together, this may or may not result in formation of an insoluble solid in the solution. This insoluble solid is called precipitate and this reaction is called precipitation reaction.
For example, a reaction in which A and C displace each other from their respective solutions. Since two displacement takes place, this reaction is also called double displacement reaction.
Here, AD(s) represents a precipitate.
Answer to Problem 4.31P
No precipitate.
Net Reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is as-
If the double displacement-reaction takes place, then the product of the reaction would be-
The products are Hydroxide of Barium and Nitrate of Sodium.
Hydroxide of Barium are soluble, they remain as aqueous solution.
Nitrate of Sodium are soluble, they remain as aqueous solution.
The net reaction is as-
(f)
Interpretation:
The precipitation or double-displacement reaction is to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
When two aqueous solutions are mixed together, this may or may not result in formation of an insoluble solid in the solution. This insoluble solid is called precipitate and this reaction is called precipitation reaction.
For example, a reaction in which A and C displace each other from their respective solutions. Since two displacement takes place, this reaction is also called double displacement reaction.
Here, AD(s) represents a precipitate.
Answer to Problem 4.31P
Phosphate of Calcium are insoluble, hence they separate out as precipitate.
Precipitate -
Net Reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is as-
If the double displacement-reaction takes place, then the product of the reaction would be-
The products are Chloride of Sodium and Sulphide of Antimony.
Chloride of Sodium are soluble, they remain as aqueous solution.
Sulphide of Antimony are insoluble, hence they separate out as precipitate.
The net reaction is as-
(g)
Interpretation:
The precipitation or double-displacement reaction is to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
When two aqueous solutions are mixed together, this may or may not result in formation of an insoluble solid in the solution. This insoluble solid is called precipitate and this reaction is called precipitation reaction.
For example, a reaction in which A and C displace each other from their respective solutions. Since two displacement takes place, this reaction is also called double displacement reaction.
Here, AD(s) represents a precipitate.
Answer to Problem 4.31P
Sulphate of Lead are insoluble, hence they separate out as precipitate.
Precipitate -
Net Reaction.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is as-
If the double displacement-reaction takes place, then the product of the reaction would be-
The products are Sulphate of Lead and Nitrate of Potassium.
Chloride of Sodium are soluble, they remain as aqueous solution.
Sulphate of Lead are insoluble, hence they separate out as precipitate.
The net reaction is as-
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Bundle: Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry, 11th + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H conc. HBr Drawing Qarrow_forwardCalculate the atomic packing factor of diamond knowing that the number of Si atoms per cm3 is 2.66·1022 and that the atomic radii of silicon and oxygen are, respectively, 0.038 and 0.117 nm.arrow_forwardA pdf file of your hand drawn, stepwise mechanisms for the reactions. For each reaction in the assignment, you must write each mechanism three times (there are 10 reactions, so 30 mechanisms). (A) do the work on a tablet and save as a pdf., it is expected to write each mechanism out and NOT copy and paste the mechanism after writing it just once. Everything should be drawn out stepwise and every bond that is formed and broken in the process of the reaction, and is expected to see all relevant lone pair electrons and curved arrows. Aldol: NaOH HO H Δ NaOH Δarrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardDraw structures corresponding to the following names and give IUPAC names for the following compounds: (8 Point) a) b) c) CH3 CH2CH3 CH3CHCH2CH2CH CH3 C=C H3C H H2C=C=CHCH3 d) CI e) (3E,5Z)-2,6-Dimethyl-1,3,5,7-octatetraene f) (Z)-4-bromo-3-methyl-3-penten-1-yne g) cis-1-Bromo-2-ethylcyclopentane h) (5R)-4,4,5-trichloro-3,3-dimethyldecanearrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Which of the following would you expect to be antiaromatic? Please provide a detailed explanation.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardDraw a Newman projection from carbon 3 to carbon 2 in the highest energy conformation for the following molecule. What is this conformation called? What kind of strain is present? Brarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





