
Concept explainers
Fill in the blanks in each line of the following table. The first line is already completed as an example.
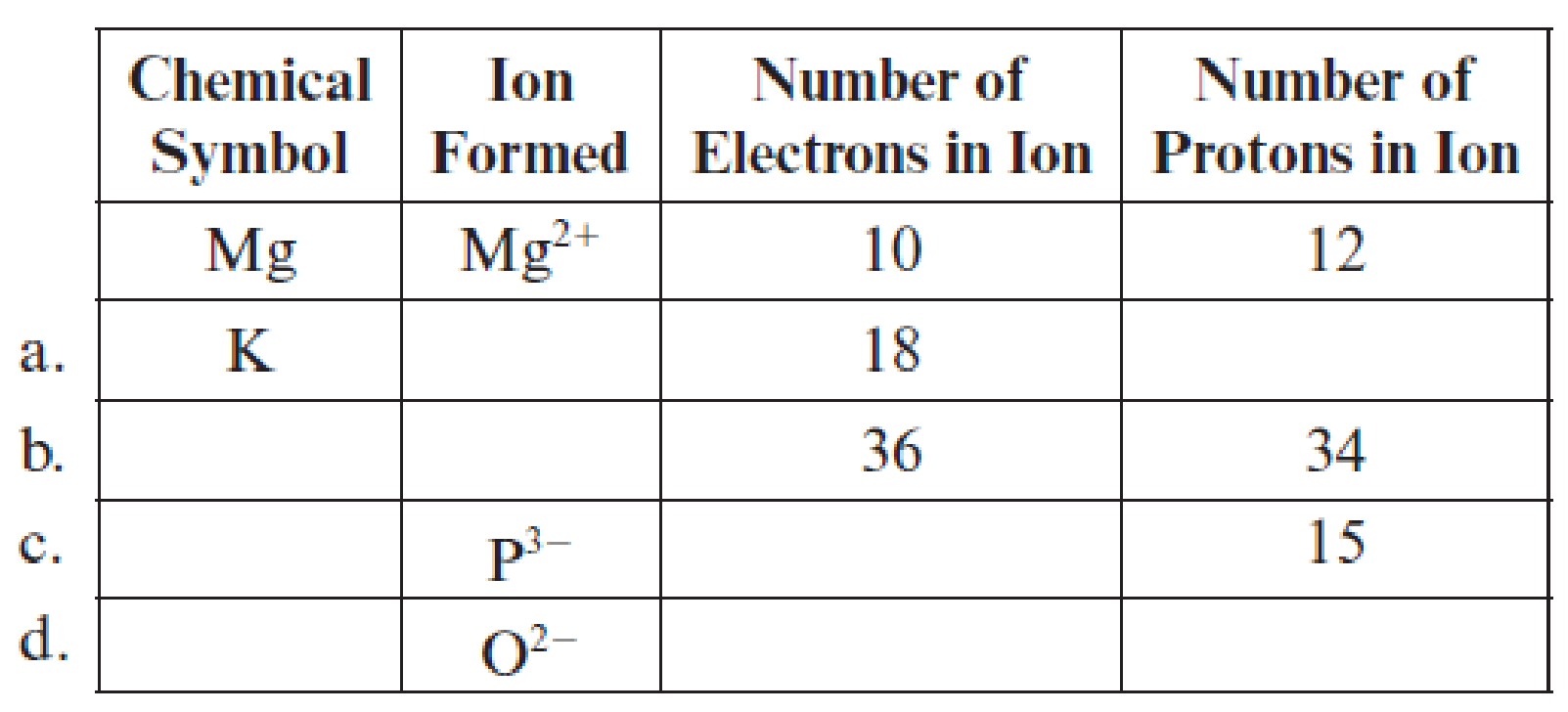
(a)
Interpretation:
Filling of each blank in the following table has to be done:
Concept Introduction:
Atoms are composed of three types of particles called subatomic particles. They are as follows:
- Protons: Positively charged particles in an atom.
- Neutrons: Neutral charged particles in an atom.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles in an atom.
The neutral atom has equal number of protons and electrons. Gaining or loosing of electrons of an atom forms ion.
Negative charged ions are formed by gaining one or more electrons and it has more electrons than protons.
Positive charged ions are formed by losing one or more electrons and it has more protons than electrons.
Answer to Problem 4.30EP
Complete table is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
The chemical symbol of the potassium element is
One electron is lesser than the number protons means it lost one electron and the charge of the potassium ion is
Hence, the symbol of potassium ion
(b)
Interpretation:
Filling of each blank in the following table has to be done:
Concept Introduction:
Atoms are composed of three types of particles called subatomic particles. They are as follows:
- Protons: Positively charged particles in an atom.
- Neutrons: Neutral charged particles in an atom.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles in an atom.
The neutral atom has equal number of protons and electrons. Gaining or loosing of electrons of an atom forms ion.
Negative charged ions are formed by gaining one or more electrons and it has more electrons than protons.
Positive charged ions are formed by losing one or more electrons and it has more protons than electrons.
Answer to Problem 4.30EP
Complete table is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
The element has
Hence, the number of protons are
(c)
Interpretation:
Filling of each blank in the following table has to be done:
Concept Introduction:
Atoms are composed of three types of particles called subatomic particles. They are as follows:
- Protons: Positively charged particles in an atom.
- Neutrons: Neutral charged particles in an atom.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles in an atom.
The neutral atom has equal number of protons and electrons. Gaining or loosing of electrons of an atom forms ion.
Negative charged ions are formed by gaining one or more electrons and it has more electrons than protons.
Positive charged ions are formed by losing one or more electrons and it has more protons than electrons.
Answer to Problem 4.30EP
Complete table is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
The ion
Hence, ion
(d)
Interpretation:
Filling of each blank in the following table has to be done:
Concept Introduction:
Atoms are composed of three types of particles called subatomic particles. They are as follows:
- Protons: Positively charged particles in an atom.
- Neutrons: Neutral charged particles in an atom.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles in an atom.
The neutral atom has equal number of protons and electrons. Gaining or loosing of electrons of an atom forms ion.
Negative charged ions are formed by gaining one or more electrons and it has more electrons than protons.
Positive charged ions are formed by losing one or more electrons and it has more protons than electrons.
Answer to Problem 4.30EP
Complete table is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
The given ion is
The charge of oxygen atom is
Hence, ion is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, AND BIOLOGICAL CH
- This entire structure using lifecycle terminology is called what? megastrobilus microstrobilus megasporophyll microsporophyll microsporangium megasporangium none of thesearrow_forwardHow much protein should Sarah add to her diet if she gets pregnant? Sarah's protein requirements during pregnancy would be higher. See Hint B2. During calculations, use numbers rounded to the first decimal place. In your answer, round the number of grams to the nearest whole number. _______ g ?arrow_forwardC MasteringHealth MasteringNu X session.healthandnutrition-mastering.pearson.com/myct/itemView?assignment ProblemID=17396422&attemptNo=1&offset=prevarrow_forwardMost people, even those who exercise regularly at low to average intensity (1 hour at the gym or a 2- to 3-mile walk several times per week), do not need an increased protein intake. What would be the protein needs of a man named Josh who exercises moderately and is the same age and size as Wayne? Josh is 5 ft, 8 in tall and weighs 183 lb. Round the number of grams to the nearest whole number. During calculations, use numbers rounded to the first decimal place. Because protein requirement is a range, please enter two numbers: lower and upper range values, respectively. Separate the lower and upper range values, in that order, by a comma. ___, ___ g ?arrow_forwardC MasteringHealth MasteringNu X session.healthandnutrition-mastering.pearson.com/myct/itemView?assignment ProblemID=17396422&attemptNo=1&offset=prevarrow_forwardIf left untreated, most HIV-infected individuals will develop AIDS. Current treatments are focused on highlyactive antiretroviral therapy (HAART). HAART usually consists of an orally delivered drug cocktail containingtwo different reverse transcriptase inhibitors and one other drug, such as a protease inhibitor. Question: Develop a pharmacokinetic model of HAART treatment. Consider all 3 drugs. Make sure to include adiagram that illustrates your thinking, state all assumptions, and define your variables. Whatparameters would you need to know to find the concentration of drug in the plasma? In the T cells?(You do not need to write out or solve any equations.)arrow_forwardnot use ai pleseaarrow_forward(A) 25 20 20 15 NPP (Mg C/ha/yr) 10 10 5 0 0 2,000 4,000 6,000 ECOLOGY 4e, Figure 20.11 (Part 1) 2017 Sinauer Associates, Inc. Average annual precipitation (mm) 8,000arrow_forwardexplain the cascade of events (starting with relaxing trade winds) that occurs during El Niño in the eastern Pacific (off the coasts of California/North America and Peru/South America) and which lead to food-chain collapse - start with changes in the physical/oceanographic conditions, andthen systematically describe the cascading effects at each level of the food chain -arrow_forward3) Which statement(s) about the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) is/are TRUE? CIRCLE ALL THAT APPLY. A. It is a major driver of salmon populations in the Pacific B. It affects sea surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific C. Its cycles typically do not last as long as those of ENSO D. Evidence that it has occurred over many centuries has been gathered from tree ring dataarrow_forward4.arrow_forward2arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage LearningEssentials Health Info Management Principles/Prac...Health & NutritionISBN:9780357191651Author:BowiePublisher:Cengage
Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage LearningEssentials Health Info Management Principles/Prac...Health & NutritionISBN:9780357191651Author:BowiePublisher:Cengage- Case Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage LearningEssentials Health Info Management Principles/Prac...Health & NutritionISBN:9780357191651Author:BowiePublisher:CengageCase Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage
Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage LearningEssentials Health Info Management Principles/Prac...Health & NutritionISBN:9780357191651Author:BowiePublisher:CengageCase Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
