
Concepts of Genetics (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780321948915
Author: William S. Klug, Michael R. Cummings, Charlotte A. Spencer, Michael A. Palladino
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 42ESP
In four o’clock plants, many flower colors are observed. In a cross involving two true-breeding strains, one crimson and the other white, all of the F1 generation were rose color. In the F2, four new
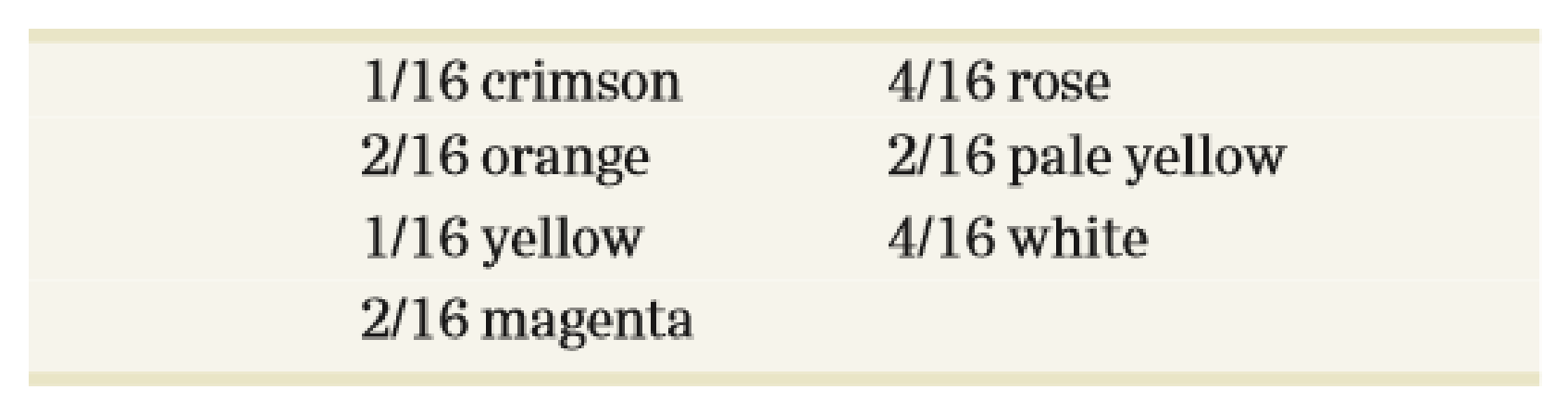
Propose an explanation for the inheritance of these flower colors.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
You have returned to college to become a phylogeneticist. One of the first things you wish to do is determine how mammals, birds, and reptiles are related.
Like any good scientist, you need to consider all available data objectively and without a preconceived “correct” answer. In pursuit of that, you should produce a phylogenetic tree based only on morphological features that show birds and mammals are more closely related. You will then produce a totally different tree, also using morphological features, that shows birds and reptiles are more closely related. Do not forget to include all three groups in both your trees.
Based solely off the trees you produce, which relationship would you consider the more likely and why? Once you have answered that question, provide a brief summary of the “modern” understanding of the relationship between these three groups.
true or false, the reason geckos can walk on walls is hydrogen bonding between their foot pads and the moisture on the wall.
Biology laboratory problem
Please help. thank you
You have 20 ul of DNA solution and 6X DNA loading buffer solution. You have to mix your DNA solution and DNA loading buffer before load DNA in an agarose gel. The concentration of the DNA loading buffer must be 1X in the DNA and DNA-loading buffer mixture after you mix them. For that, I will add _____ ul of 6X loading buffer to the 20 ul DNA solution.
Chapter 4 Solutions
Concepts of Genetics (11th Edition)
Ch. 4 - In the guinea pig, one locus involved in the...Ch. 4 - In some plants a red flower pigment, cyanidin, is...Ch. 4 - Below are three pedigrees. For each trait,...Ch. 4 - Prob. 1CSCh. 4 - Prob. 2CSCh. 4 - Prob. 3CSCh. 4 - HOW DO WE KNOW? In this chapter, we focused on...Ch. 4 - CONCEPT QUESTION Review the Chapter Concepts list...Ch. 4 - In shorthorn cattle, coat color may be red, white,...Ch. 4 - In foxes, two alleles of a single gene, P and p,...
Ch. 4 - In mice, a short-tailed mutant was discovered....Ch. 4 - List all possible genotypes for the A, B, AB, and...Ch. 4 - With regard to the ABO blood types in humans,...Ch. 4 - In a disputed parentage case, the child is blood...Ch. 4 - The A and B antigens in humans may be found in...Ch. 4 - In chickens, a condition referred to as creeper...Ch. 4 - In rabbits, a series of multiple alleles controls...Ch. 4 - Three gene pairs located on separate autosomes...Ch. 4 - As in Problem 12, flower color may be red, white,...Ch. 4 - Horses can be cremello (a light cream color),...Ch. 4 - With reference to the eye color phenotypes...Ch. 4 - Pigment in mouse fur is only produced when the C...Ch. 4 - In rats, the following genotypes of two...Ch. 4 - Given the inheritance pattern of coat color in...Ch. 4 - In a species of the cat family, eye color can be...Ch. 4 - In a plant, a tall variety was crossed with a...Ch. 4 - In a unique species of plants, flowers may be...Ch. 4 - Five human matings (15), identified by both...Ch. 4 - A husband and wife have normal vision, although...Ch. 4 - In humans, the ABO blood type is under the control...Ch. 4 - In Drosophila, an X-linked recessive mutation,...Ch. 4 - Another recessive mutation in Drosophila, ebony...Ch. 4 - In Drosophila, the X-linked recessive mutation...Ch. 4 - While vermilion is X-linked in Drosophila and...Ch. 4 - In a cross in Drosophila involving the X-linked...Ch. 4 - Consider the three pedigrees below, all involving...Ch. 4 - In goats, the development of the beard is due to a...Ch. 4 - Predict the F1 and F2 results of crossing a male...Ch. 4 - Two mothers give birth to sons at the same time at...Ch. 4 - Discuss the topic of phenotypic expression and the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 35PDQCh. 4 - Labrador retrievers may be black, brown...Ch. 4 - A true-breeding purple-leafed plant isolated from...Ch. 4 - In Dexter and Kerry cattle, animals may be polled...Ch. 4 - A geneticist from an alien planet that prohibits...Ch. 4 - The following pedigree is characteristic of an...Ch. 4 - Students taking a genetics exam were expected to...Ch. 4 - In four oclock plants, many flower colors are...Ch. 4 - Proto-oncogenes stimulate cells to progress...Ch. 4 - Below is a partial pedigree of hemophilia in the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Biology lab problem To make 20 ul of 5 mM MgCl2 solution using 50 mM MgCl2 stock solution and distilled water, I will mix ________ ul of 50 mM MgCl2 solution and ________ ul of distilled water. Please help . Thank youarrow_forwardBiology Please help. Thank you. Biology laboratory question You need 50 ml of 1% (w/v) agarose gel. Agarose is a powder. How would you make it? You can ignore the volume of agarose powder. Don't forget the unit.TBE buffer is used to make an agarose gel, not distilled water. I will add _______ of agarose powder into 50 ml of distilled water (final 50 ml).arrow_forwardAn urgent care center experienced the average patient admissions shown in the Table below during the weeks from the first week of December through the second week of April. Week Average Daily Admissions 1-Dec 11 2-Dec 14 3-Dec 17 4-Dec 15 1-Jan 12 2-Jan 11 3-Jan 9 4-Jan 9 1-Feb 12 2-Feb 8 3-Feb 13 4-Feb 11 1-Mar 15 2-Mar 17 3-Mar 14 4-Mar 19 5-Mar 13 1-Apr 17 2-Apr 13 Forecast admissions for the periods from the first week of December through the second week of April. Compare the forecast admissions to the actual admissions; What do you conclude?arrow_forward
- Analyze the effectiveness of the a drug treatment program based on the needs of 18-65 year olds who are in need of treatment by critically describing 4 things in the program is doing effectively and 4 things the program needs some improvement.arrow_forwardI have the first half finished... just need the bottom half.arrow_forward13. Practice Calculations: 3 colonies were suspended in the following dilution series and then a viable plate count and microscope count was performed. Calculate IDF's, TDF's and then calculate the CFU/mL in each tube by both methods. Finally calculate the cells in 1 colony by both methods. Show all of your calculations in the space provided on the following pages. 3 colonies 56 cells 10 μL 10 μL 100 μL 500 με m OS A B D 5.0 mL 990 με 990 με 900 με 500 μL EN 2 100 με 100 μL 118 colonies 12 coloniesarrow_forward
- Describe and give a specific example of how successionary stage is related to species diversity?arrow_forwardExplain down bellow what happens to the cell in pictures not in words: Decreased pH in mitochondria Increased ATP Decreased pH in cytosol Increased hydrolysis Decreasing glycogen and triglycerides Increased MAP kinase activity Poor ion transport → For each one:→ What normally happens?→ What is wrong now?→ How does it mess up the cell?arrow_forward1.) Community Diversity: The brown and orange line represent two different plant communities. a. Which color represents the community with a higher species richness? b. Which color represents the community with a higher species evenness? Relative abundance 0.1 0.04 0.001 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Rank abundance c. What is the maximum value of the Simpson's diversity index (remember, Simpson's index is D = p², Simpson's diversity index is 1-D)? d. If the Simpson's diversity index equals 1, what does that mean about the number of species and their relative abundance within community being assessed?arrow_forward
- 1.) Community Diversity: The brown and orange line represent two different plant communities. a. Which color represents the community with a higher species richness? b. Which color represents the community with a higher species evenness? Relative abundance 0.1 0.04 0.001 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Rank abundance c. What is the maximum value of the Simpson's diversity index (remember, Simpson's index is D = p², Simpson's diversity index is 1-D)? d. If the Simpson's diversity index equals 1, what does that mean about the number of species and their relative abundance within community being assessed?arrow_forwardwhat measures can a mother to take to improve the produce of her to milk to her newborn baby ?arrow_forward1. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Eastern white pine tree green (but only the ancestral line NOT shared with other organisms) 2. Oncle the last common ancestor of the Colorado blue spruce tree and Eastern white pine tree. 3. Put a box around the last common ancestor of the sugar maple tree and the dogwood tree. 4. Put a triangle around the last common ancestor of the red pine tree and the american holly bush. 5. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Ponderosa pine tree red (including all shared ancestors). 6. Color the line that represents all ancestors of the American elm tree blue (including all shared ancestors). 7 Color the line that represents all ancestors of the Sabal palm tree purple (including all shared ancestors) 8. Using a yellow highlighter or colored pencil, circle the clade that includes all pine trees. 9. Using a orange highlighter or colored pencil, circle the clade that includes all gymnosperms 10. Can you tell…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
How to solve genetics probability problems; Author: Shomu's Biology;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R0yjfb1ooUs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Beyond Mendelian Genetics: Complex Patterns of Inheritance; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-EmvmBuK-B8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY