
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the two given molecules are constitutional isomers of each other.
Concept introduction:
The compounds having same molecular formula but different connectivity of the atoms are constitutional isomers. The arrangement of the atoms is different for constitutional isomers. From the total number of atoms and arrangement of atoms, it is decided that whether the two molecules are constitutional isomers or not.
Answer to Problem 4.16P
The two given molecules are not constitutional isomers of each other.
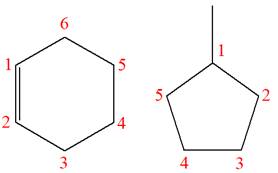
Explanation of Solution
The structures of the given molecules are
The molecular formula of the first compound is
The first molecule contains ten hydrogens, and the second molecule contains twelve hydrogens. However, the total number of hydrogens is different in each molecule. In case of constitutional isomers, the total number of atoms remains the same in the molecular formula. So both molecules are not constitutional isomers of each other.
The constitutional isomers are determined from the molecular formula and connectivity of the atoms.
(b)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the two given molecules are constitutional isomers of each other.
Concept introduction:
The compounds having same molecular formula but different connectivity of the atoms are constitutional isomers. The arrangement of the atoms is different for constitutional isomers. From the total number of atoms and arrangement of atoms, it is decided that whether the two molecules are constitutional isomers or not.
Answer to Problem 4.16P
The two given molecules are not constitutional isomers of each other.
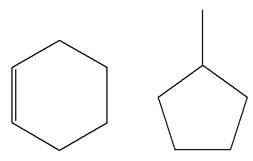
Explanation of Solution
The structures of the given molecules are
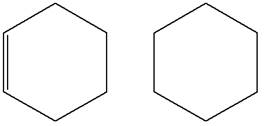
The molecular formula of the first compound is
The first molecule contains ten hydrogens, and the second molecule contains twelve hydrogens. However, the total number of hydrogens is different in each molecule. In case of constitutional isomers, the total number of atoms remains the same in the molecular formula. So both molecules are not constitutional isomers of each other.
The constitutional isomers are determined from the molecular formula and connectivity of the atoms.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the two given molecules are constitutional isomers of each other.
Concept introduction:
The compounds having same molecular formula but different connectivity of the atoms are constitutional isomers. The arrangement of the atoms is different for constitutional isomers. From the total number of atoms and arrangement of atoms, it is decided that whether the two molecules are constitutional isomers or not.
Answer to Problem 4.16P
The two given molecules are not constitutional isomers of each other.
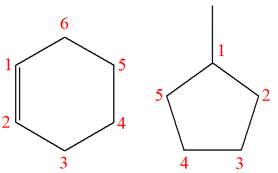
Explanation of Solution
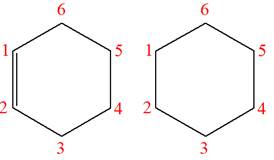
The structures of the given molecules are
The molecular formula of the first compound is

The first molecule contains ten hydrogens, and the second molecule contains twelve hydrogens. However, the total number of hydrogens is different in each molecule. In case of constitutional isomers, the total number of atoms remains the same in the molecular formula. So both molecules are not constitutional isomers of each other.
The constitutional isomers are determined from the molecular formula and connectivity of the atoms.
(d)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the two given molecules are constitutional isomers of each other.
Concept introduction:
The compounds having same molecular formula but different connectivity of the atoms are constitutional isomers. The arrangement of the atoms is different for constitutional isomers. From the total number of atoms and arrangement of atoms, it is decided that whether the two molecules are constitutional isomers or not.
Answer to Problem 4.16P
The two given molecules are constitutional isomers of each other.
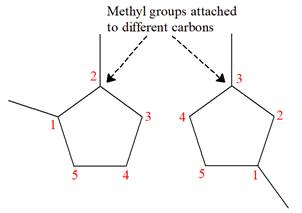
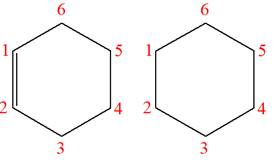
Explanation of Solution
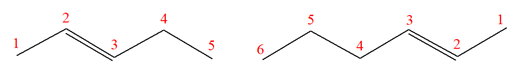
The structures of the given molecules are
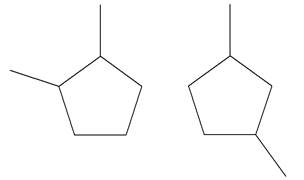
The molecular formula of both molecules is
The number assigned to carbon atoms are same in each molecule based on the first methyl group attached to the ring. However, the connectivity of the methyl group is not the same. In the first molecule, the methyl group is attached to the
The constitutional isomers are determined from the molecular formula and connectivity of the atoms.
(e)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the two given molecules are constitutional isomers of each other.
Concept introduction:
The compounds having same molecular formula but different connectivity of the atoms are constitutional isomers. The arrangement of the atoms is different for constitutional isomers. From the total number of atoms and arrangement of atoms, it is decided that whether the two molecules are constitutional isomers or not.
Answer to Problem 4.16P
The two given molecules are not constitutional isomers of each other.
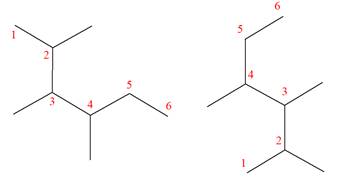
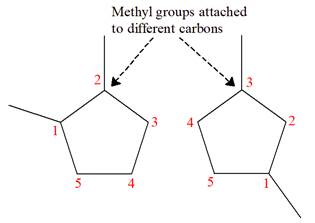
Explanation of Solution
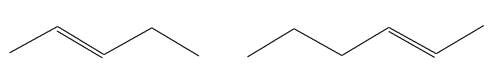
The structures of the given molecules are
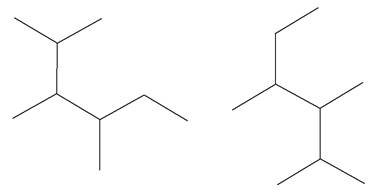
The molecular formula of both molecules is
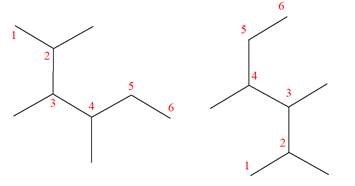
The numbers assigned to carbon atoms are the same in each molecule based on the first methyl group attached to the longest carbon chain. Both molecules have methyl groups attached to the
The constitutional isomers are determined from the molecular formula and connectivity of the atoms.
(f)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the two given molecules are constitutional isomers of each other.
Concept introduction:
The compounds having same molecular formula but different connectivity of the atoms are constitutional isomers. The arrangement of the atoms is different for constitutional isomers. From the total number of atoms and arrangement of atoms, it is decided that whether the two molecules are constitutional isomers or not.
Answer to Problem 4.16P
The two given molecules are not constitutional isomers of each other.
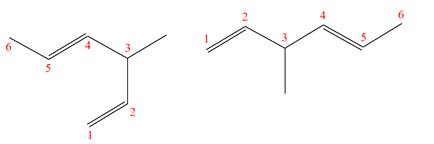
Explanation of Solution
The structures of the given molecules are
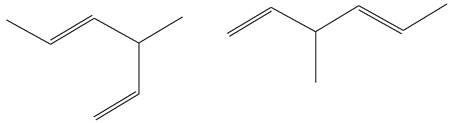
The molecular formula of both molecules is

The numbers assigned to double-bonded carbon atoms are the same in each molecule. In both compounds, the methyl group is connected to
The constitutional isomers are determined from the molecular formula and connectivity of the atoms.
(g)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the two given molecules are constitutional isomers of each other.
Concept introduction:
The compounds having same molecular formula but different connectivity of the atoms are constitutional isomers. The arrangement of the atoms is different for constitutional isomers. From the total number of atoms and arrangement of atoms, it is decided that whether the two molecules are constitutional isomers or not.
Answer to Problem 4.16P
The two given molecules are not constitutional isomers of each other.
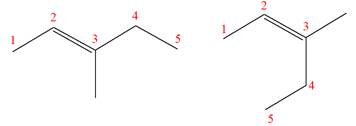
Explanation of Solution
The structures of the given molecules are
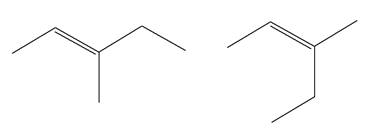
The molecular formula of both molecules is
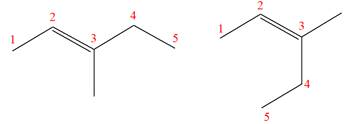
The number assigned to double-bonded carbon atoms are the same in each molecule. In both compounds, the methyl group is connected to
The constitutional isomers are determined from the molecular formula and connectivity of the atoms.
(h)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the two given molecules are constitutional isomers of each other.
Concept introduction:
The compounds having same molecular formula but different connectivity of the atoms are constitutional isomers. The arrangement of the atoms is different for constitutional isomers. From the total number of atoms and arrangement of atoms, it is decided that whether the two molecules are constitutional isomers or not.
Answer to Problem 4.16P
The two given molecules are not constitutional isomers of each other.
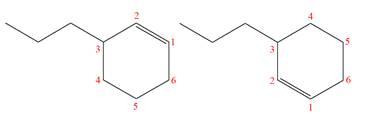
Explanation of Solution
The structures of the given molecules are
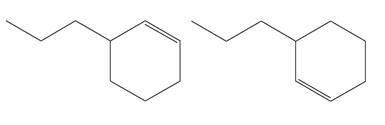
The molecular formula of both molecules is
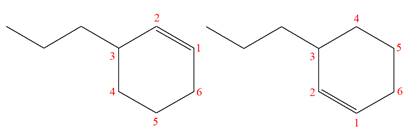
The numbers assigned to double-bonded carbon atoms are the same in each molecule. In both compounds, the propyl group is connected to
The constitutional isomers are determined from the molecular formula and connectivity of the atoms.
(i)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the two given molecules are constitutional isomers of each other.
Concept introduction:
The compounds having same molecular formula but different connectivity of the atoms are constitutional isomers. The arrangement of the atoms is different for constitutional isomers. From the total number of atoms and arrangement of atoms, it is decided that whether the two molecules are constitutional isomers or not.
Answer to Problem 4.16P
The two given molecules are constitutional isomers of each other.
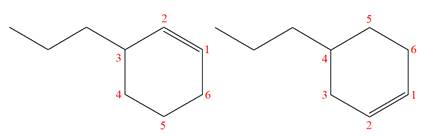
Explanation of Solution
The structures of the given molecules are
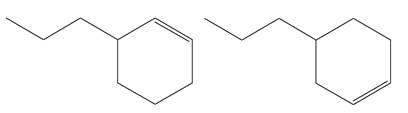
The molecular formula of both molecules is
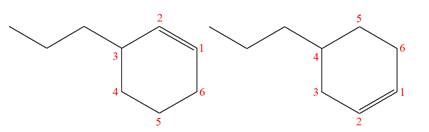
The numbers assigned to double-bonded carbon atoms are the same in each molecule.
However, the connectivity of the propyl group is not the same. In the first molecule, the propyl group is attached to the
The constitutional isomers are determined from the molecular formula and connectivity of the atoms.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- Provide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forwardGiven the attached data, provide the drawing for the corresponding structure.arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

