
University Physics with Modern Physics, Books a la Carte Edition; Modified MasteringPhysics with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card -- for ... eText -- Valuepack Access Card (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780134308142
Author: Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 4.14E
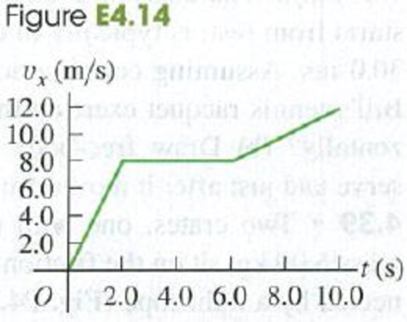
A 2.75-kg cat moves in a straight line (the x-axis). Figure E4.14 shows a graph of the x-component of this cat’s velocity as a function of time, (a) Find the maximum net force on this cat. When does this force occur? (b) When is the net force on the cat equal to zero? (c) What is the net force at time 8.5 s?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The coefficient of static friction between the tires of a car and a horizontal road is 0.2. If the net force on the car is the force of static friction exerted by the road, what is the maximum acceleration of the car when it is braked? The acceleration clue to gravity is 9.81 m/s^2 . Answer in units of m/s^2. What is the shortest distance in which the car can stop if it is initially traveling at 30 m/s? Answer in units of m.
Moments after making the dreaded decision to jump out the door of the airplane, a
skydiver's 86.4-kg body experiences 121 N of air resistance. The magnitude of the
m/s2. Use the
skydiver's downward acceleration at this instant in time is
approximation g 10 m/s?.
A hockey puck slides with an initial speed of 56.7 m/s on a large frozen lake. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the puck and the ice is 0.05.
What is the acceleration on the hockey puck caused by friction? Assume the puck's velocity is in the positive-x direction. And what is the speed of the puck after 6 s?
Chapter 4 Solutions
University Physics with Modern Physics, Books a la Carte Edition; Modified MasteringPhysics with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card -- for ... eText -- Valuepack Access Card (14th Edition)
Ch. 4.1 - Figure 4.5 shows a force F acting on a crate. With...Ch. 4.2 - In which of the following situations is there zero...Ch. 4.3 - Rank the following situations in order of the...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 4.4TYUCh. 4.5 - You are driving a car on a country road when a...Ch. 4 - Can a body be in equilibrium when only one force...Ch. 4 - A ball thrown straight up has zero velocity at its...Ch. 4 - A helium balloon hovers in midair, neither...Ch. 4 - When you fly in an airplane at night in smooth...Ch. 4 - If the two ends of a rope in equilibrium are...
Ch. 4 - You tie a brick lo the end of a rope and whirl the...Ch. 4 - When a car stops suddenly, the passengers tend to...Ch. 4 - Some people say that the force of inertia (or...Ch. 4 - A passenger in a moving bus with no windows...Ch. 4 - Suppose you chose the fundamental physical...Ch. 4 - Why is the earth only approximately an inertial...Ch. 4 - Does Newtons second law hold true for an observer...Ch. 4 - Some students refer to the quantity ma as the...Ch. 4 - The acceleration of a falling body is measured in...Ch. 4 - You can play catch with a softball in a bus moving...Ch. 4 - Students sometimes say that the force of gravity...Ch. 4 - Why can it hurt your foot more to kick a big rock...Ch. 4 - Its not the fall that hurts you; its the sudden...Ch. 4 - A person can dive into water from a height of 10 m...Ch. 4 - Why are cars designed to crumple in front and back...Ch. 4 - When a string barely strong enough lifts a heavy...Ch. 4 - A large crate is suspended from the end of a...Ch. 4 - Which feels a greater pull due to the earths...Ch. 4 - Why is it incorrect to say that 1.0 kg equals 2.2...Ch. 4 - A horse is hitched to a wagon. Since the wagon...Ch. 4 - True or false? You exert a push P on an object and...Ch. 4 - A large truck and a small compact car have a...Ch. 4 - When a car comes to a stop on a level highway,...Ch. 4 - A small compact car is pushing a large van that...Ch. 4 - Consider a tug-of-war between two people who pull...Ch. 4 - Boxes A and B are in contact on a horizontal,...Ch. 4 - A manual for student pilots contains this passage:...Ch. 4 - If your hands are wet and no towel is handy, you...Ch. 4 - If you squat down (such as when you examine the...Ch. 4 - When a car is hit from behind, the occupants may...Ch. 4 - In a head-on auto collision, passengers who are...Ch. 4 - In a head-on collision between a compact 1000-kg...Ch. 4 - Suppose you are in a rocket with no windows,...Ch. 4 - Two dogs pull horizontally on ropes attached to a...Ch. 4 - To extricate an SUV stuck in the mud, workmen use...Ch. 4 - BIO Jaw Injury. Due to a jaw injury, a patient...Ch. 4 - A man is dragging a trunk up the loading ramp of a...Ch. 4 - Forces F1 and F2act at a point. The magnitude of...Ch. 4 - An electron (mass = 9.11 1031 kg) leaves one end...Ch. 4 - A 68.5-kg skater moving initially at 2.40 m/s on...Ch. 4 - You walk into an elevator, step onto a scale, and...Ch. 4 - A box rests on a frozen pond, which serves as a...Ch. 4 - A dockworker applies a constant horizontal force...Ch. 4 - A hockey puck with mass 0.160 kg is at rest at the...Ch. 4 - A crate with mass 32.5 kg initially at rest on a...Ch. 4 - A 4.50-kg experimental cart undergoes an...Ch. 4 - A 2.75-kg cat moves in a straight line (the...Ch. 4 - A small 8.00-kg rocket burns fuel that exerts a...Ch. 4 - An astronauts pack weighs 17.5 N when she is on...Ch. 4 - Superman throws a 2400-N boulder at an adversary....Ch. 4 - BIO (a) An ordinary flea has a mass of 210 g. How...Ch. 4 - At the surface of Jupiters moon Io, the...Ch. 4 - A small car of mass 380 kg is pushing a large...Ch. 4 - BIO World-class sprinters can accelerate out of...Ch. 4 - The upward normal force exerted by the floor is...Ch. 4 - Boxes A and B are in contact on a horizontal,...Ch. 4 - A student of mass 45 kg jumps off a high diving...Ch. 4 - Section 4.6 Free-Body Diagrams 4.25Crates A and B...Ch. 4 - You pull horizontally on block B in Fig. F4.26,...Ch. 4 - A ball is hanging from a long siring that is tied...Ch. 4 - CP A .22-caliber rifle bullet traveling at 350 m/s...Ch. 4 - A chair of mass 12.0 kg is sitting on the...Ch. 4 - A large box containing your new computer sits on...Ch. 4 - CP A 5.60-kg bucket of water is accelerated upward...Ch. 4 - CP You have just landed on Planet X. You release a...Ch. 4 - Two adults and a child want to push a wheeled cart...Ch. 4 - CP An oil tankers engines have broken down, and...Ch. 4 - CP BIO A Standing Vertical Jump. Basketball player...Ch. 4 - CP An advertisement claims that a particular...Ch. 4 - BIO Human Biomechanics. The fastest pitched...Ch. 4 - BIO Human Biomechanics. The fastest served tennis...Ch. 4 - Two crates, one with mass 4.00 kg and the other...Ch. 4 - CP Two blocks connected by a light horizontal rope...Ch. 4 - CALC To study damage to aircraft that collide with...Ch. 4 - CP A 6.50-kg instrument is hanging by a vertical...Ch. 4 - BIO Insect Dynamics. The froghopper (Philaenus...Ch. 4 - A loaded elevator with very worn cables has a...Ch. 4 - CP After an annual checkup, you leave your...Ch. 4 - CP A nail in a pine board stops a 4.9-N hammer...Ch. 4 - CP Jumping to the Ground. A 75.0-kg man steps off...Ch. 4 - The two blocks in Fig. P4.48 are connected by a...Ch. 4 - CP Boxes A and B are connected to each end of a...Ch. 4 - CP Extraterrestrial Physics. You have landed on an...Ch. 4 - CP CALC A mysterious rocket-propelled object of...Ch. 4 - CALC The position of a training helicopter (weight...Ch. 4 - DATA The table gives automobile performance data...Ch. 4 - DATA An 8.00-kg box sits on a level floor. You...Ch. 4 - DATA You are a Starfleet captain going boldly...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.56CPCh. 4 - BIO FORCES ON A DANCER'S BODY. Dancers experience...Ch. 4 - BIO FORCES ON A DANCERS BODY. Dancers experience...Ch. 4 - BIO FORCES ON A DANCER'S BODY. Dancers experience...Ch. 4 - The forces on a dancer can be measured directly...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
58. ** EST Comet crash On June 30, 1908, a monstrous comet fragment of mass greater than kg is thought to have...
College Physics
3. What is free-fall, and why does it make you weightless? Briefly describe why astronauts are weightless in th...
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
2. Two very large charged parallel metal plates are 10.0 cm apart and produce a uniform electric field of 2.80 ...
College Physics (10th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. An astronomical unit is (a) any planet...
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
The computer program assumes a particular coordinate system. Describe this coordinate system.
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
117. The bricks in this road were originally straight. Describe evidence for tires pushing the bricks in the wa...
Conceptual Physical Science (6th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 9500-kg test missile blasts off vertically from the ground with a constant upward acceleration of 2.28 m/s2 . When it has reached a height of 550 m, its engines suddenly fail; the only force acting on it is now gravity. a) What is the maximum height reached? b) How much time will elapse after engine failure before the rocket comes crashing down the ground, and how fast will it be moving just before it crashes?arrow_forwardA 68 kg man drops to a concrete patio from a window 0.45 m above the patio. He neglects to bend his knees on landing, taking 2.4 cm to stop. (a) What is his average acceleration from when his feet first touch the patio to when he stops?(b) What is the magnitude of the average stopping force exerted on him by the patio?arrow_forwardA crate of mass 43 kg is loaded onto the back of a flatbed truck. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the truck bed is 0.12. What is the maximum acceleration a (in m/s2) the truck can have without the crate sliding off?arrow_forward
- In Fig E4.4, consider that the trunk has mass M travels at a constant velocity along a frictionless inclined and the angles involved are θi and θs, where θs corresponds to the angle with respect to the direction of motion and θi is the angle of the inclined. What are the simplified expressions for the tension on the rope and the normal force on the trunk in terms of M, g and the angles?arrow_forwardYou're driving along at 25m/s with your aunt's valuable antiques in the back of your pickup truck when suddenly you see a giant hole in the road 55 m ahead of you. Fortunately, your foot is right beside the brake and your reaction time is zero! If the coefficients of friction are μs =0.6 and uk =0.3, how much time does it take you to stop if you don't want the antiques to slide and be damaged?arrow_forwarda)A 10 kg block slides down a frictionless slope which is at angle θ = 26◦. Starting from rest, the time to slide down is t = 1.79 s. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . ai)What total distance s did the block slide? aii) What is the total vertical height through which the block descended? b)A small metal ball is suspended from the ceiling by a thread of negligible mass. The ball is then set in motion in a horizontal circle at an angle of 29 degrees from the top, so that the thread describes a cone. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . bi) What is the speed of the ball when it is in circular motion in m/s? bii)How long does it take Tperiod for the ball to rotate once around the axis?arrow_forward
- A crate of mass m= 32 kg rides on the bed of a truck attached by a cord to the back of the cab as in Figure P4.34. The cord can with- stand a maximum tension of 68 N before breaking. Figure P4.34 Neglecting friction between the crate and truck bed, find the maximum acceleration the truck can have before the cord breaks.arrow_forwardA strong boy throws a rock straight up with a force of 100 N. At what rate does the rock initially accelerate upwards, in m/s2? Assume the mass of the rock is 2 kg and the local gravitational acceleration is 9.74 m/s2.arrow_forwardA penguin slides at a constant velocity of 1.4m/s down an inclined sandy surface. The incline slopes above the horizontal at an angle of 6.9degrees. At the bottom of the incline the penguin slides onto a horizontal patch of sand. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the penguin and the sand is the same for the horizontal patch. Calculate how much time is required for the penguin to slide to a halt after entering the horizontal patch of sand.?arrow_forward
- Two forces are applied to a 22 kg cart on a frictionless surface as shown. At a certain instant, Force A is 86 N to the right, and Force B is 10 N to the left. What is the acceleration of the cart at this instant, in m/s2?arrow_forwardA small block travels up a frictionless incline that is at an angle of 30.0° above the horizontal. The block has speed 5.10 m/s at the bottom of the incline. Assume g = 9.80 m/s2. How far up the incline (measured parallel to the surface of the incline) does the block travel before it starts to slide back down?arrow_forwardSuppose you throw an object from a great height, so that it reaches very nearly terminal velocity by time it hits the ground. By measuring the impact, you determine that this terminal velocity is -49 mi sec.A. Write the equation representing the velocity v(t) of the object at time t seconds given the initial velocity v0 and the fact that acceleration due to gravity 9.8 m/sec2. (Here, assume you're modeling the falling body with the differential equation dy/dt = g-kv, and use the resulting formula or v(t) found in the Tutorial. Of course, you can derive it if you'd like.)B. Determine the value of k, the "continuous percentage growth rate" from the velocity equation, by utilizing the information given concerning the terminal velocity.C. Using the value of k you derived above, at what velocity must the object be thrown upward if you want it to reach its peak height after 3 sec? Approximate your solution to three decimal places, and justify your answer.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
Newton's Third Law of Motion: Action and Reaction; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y61_VPKH2B4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY