
College Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781938168000
Author: Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher: OpenStax College
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 31PE
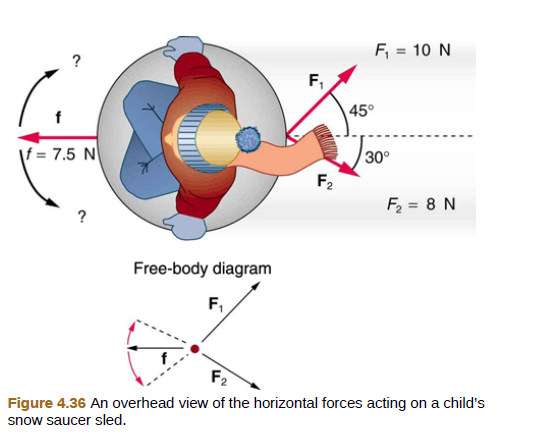
Two children pull a third child on a snow saucer sled exerting forces F1 and F2 as shown from above in Figure 4.36. Find the acceleration of the 49.00-kg sled and child system. Note that the direction of the frictional force is unspecified; it will be in the opposite direction of the sum of F1 and F2.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 4 Solutions
College Physics
Ch. 4 - Propose a force standard different from the...Ch. 4 - What properties do forces have that allow us to...Ch. 4 - How are inertia and mass related?Ch. 4 - What is the relationship between weight and mass?...Ch. 4 - Which statement is correct? (a) Net force causes...Ch. 4 - Why can we neglect forces such as those holding a...Ch. 4 - Explain how the choice of the “Stem of interest”...Ch. 4 - Describe a situation in which the net external...Ch. 4 - A system can have a nonzero velocity while the net...Ch. 4 - A rock is thrown straight up. What is the net...
Ch. 4 - (a) Give an example of different net external...Ch. 4 - If the acceleration of a system is zero, are no...Ch. 4 - If a constant, nonzero force is applied to an...Ch. 4 - The gravitational force on the basketball in...Ch. 4 - When you take off in a jet aircraft, there is a...Ch. 4 - A device used since the 1940s to measure the kick...Ch. 4 - Describe a Situation in which one a force on and,...Ch. 4 - Why does an ordinary rifle recoil (kick backward)...Ch. 4 - An American football lineman reasons that it is...Ch. 4 - Newton's third law of motion tells us that forces...Ch. 4 - If a leg is suspended by a traction setup as shown...Ch. 4 - Ina traction setup a broken bone, with pulleys and...Ch. 4 - To simulate the apparent weightlessness of space...Ch. 4 - A cartoon shows the toupee coming off the head of...Ch. 4 - Explain, in terms of the properties of the four...Ch. 4 - What is the dominant force between astronomical...Ch. 4 - Give a detailed example of the exchange of a...Ch. 4 - A 63.0-kg sprinter starts a race with an...Ch. 4 - If the sprinter from the previous problem...Ch. 4 - A cleaner pushes a 4.50-kg laundry cart in such a...Ch. 4 - Since astronauts in orbit are apparently...Ch. 4 - In Figure 4.7, the net external force on the 24-kg...Ch. 4 - The same rocket sled drawn in Figure 4.31 is...Ch. 4 - (a) If the rocket sled shown in Figure 4.32 starts...Ch. 4 - What is the deceleration of the rocket sled if it...Ch. 4 - Suppose two children push horizontally, but in...Ch. 4 - A powerful motorcycle can produce an acceleration...Ch. 4 - The rocket sled shown in Figure 4.33 accelerates...Ch. 4 - Repeat the previous problem for the situation in...Ch. 4 - The weight of an astronaut plus his space suit on...Ch. 4 - Suppose the mass of a fully loaded module in which...Ch. 4 - What net external force is exerted on a 1100-kg...Ch. 4 - A brave but inadequate rugby player is being...Ch. 4 - Two teams of nine members each engage in a tug of...Ch. 4 - What force does a trampoline have to apply to a...Ch. 4 - (a) Calculate the tension in a vertical strand of...Ch. 4 - Suppose a 60.0-kg gymnast climbs a rope. (a) What...Ch. 4 - Show that, as stated in the text, a force F...Ch. 4 - Consider the baby being weighed in Figure 4.34....Ch. 4 - A 5.00105 -kg rocket is accelerating straight up....Ch. 4 - The wheels of a midsize car exert a force of 2100...Ch. 4 - Calculate the force a 70.0-kg high jumper must...Ch. 4 - When landing after a spectacular somersault, a...Ch. 4 - A freight train consists of two 8.00104 -kg...Ch. 4 - Commercial airplanes are sometimes pushed out of...Ch. 4 - A 1100-kg car pulls a boat on a trailer. (a) What...Ch. 4 - (a) Find the magnitudes of the forces F1 and F2...Ch. 4 - Two children pull a third child on a snow saucer...Ch. 4 - Suppose your car was mired deeply in the mud and...Ch. 4 - What force is exerted on the tooth in Figure 4.38...Ch. 4 - Figure 4.39 shows Superhero and Trusty Sidekick...Ch. 4 - A nurse pushes a cart by exerting a force on the...Ch. 4 - Construct Your Own Problem Consider the tension in...Ch. 4 - Construct Your Own Problem Consider people pushing...Ch. 4 - Unreasonable Results (a) Repeat Exercise 4.29, but...Ch. 4 -
Ch. 4 - A flea jumps by exerting a force of 1.20105 N...Ch. 4 - Two muscles in the back of the leg pull upward on...Ch. 4 - A 76.0-kg person is being pulled away from a...Ch. 4 - Integrated Concepts A 35.0-kg dolphin decelerates...Ch. 4 - Integrated Concepts When starting a foot race, a...Ch. 4 - Integrated Concepts A large rocket has a mass of...Ch. 4 - Integrated Concepts A basketball player jumps...Ch. 4 - Integrated Concepts A 2.50-kg fireworks shell is...Ch. 4 - Integrated Concepts Repeat Exercise 4.47 for a...Ch. 4 - Integrated Concepts An elevator filled with...Ch. 4 - Unreasonable Results (a) What is the final...Ch. 4 - Unreasonable Results A 75.0-kg man stands on a...Ch. 4 - (a) What is the strength of the weak nuclear force...Ch. 4 - (a) What is the ratio of the strength of the...Ch. 4 - What is the ratio of the strength of the strong...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Answer the following questions for each compound: a. How many signals are in its 13C NMR spectrum? b. Which sig...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
1. ___ Mitosis 2. ___ Meiosis 3. __ Homologous chromosomes 4. __ Crossing over 5. __ Cytokinesis A. Cytoplasmic...
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
1. A person gets in an elevator on the ground floor and rides it to the top floor of a building. Sketch a veloc...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
2. Define equilibrium population. Outline the conditions that must be met for a population to stay in genetic e...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Distinguish between microevolution, speciation, and macroevolution.
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
If someone at the other end of a room smokes a cigarette, you may breathe in some smoke. The movement of smoke ...
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are standing a distance x = 1.75 m away from this mirror. The object you are looking at is y = 0.29 m from the mirror. The angle of incidence is θ = 30°. What is the exact distance from you to the image?arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank youarrow_forwardA planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).arrow_forward
- What are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V) ammeter I =arrow_forwardsimple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forwardA circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forward
- An L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forwardA long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forwardDescribe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forward
- Discuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forwardExplain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's Second Law of Motion: F = ma; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xzA6IBWUEDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY