
Concept explainers
Darren Mack owns the Gas n’ Go convenience store and gas station. After hearing a marketing lecture, he realizes that it might be possible to draw more customers to his high-margin convenience store by selling his gasoline at a lower price. However, the Gas n’ Go is unable to qualify for volume discounts on its gasoline purchases, and therefore cannot sell gasoline for profit if the price is lowered. Each new pump will cost $95,000 to install, but will increase customer traffic in the store by 1,000 customers per year. Also, because the Gas n’ Go would be selling its gasoline at no profit, Darren plans on increasing the profit margin on convenience store items incrementally over the next 5 years. Assume a discount rate of 8 percent. The projected convenience store sales per customer and the projected profit margin for the next 5 years are as follows:
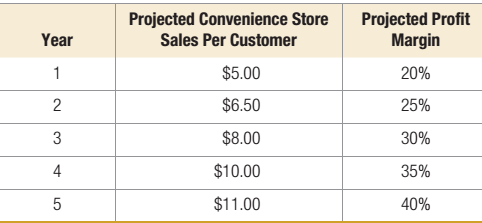
- What is the
NPV of the next 5 years of cash flows if Darren had four new pumps installed? - If Darren required a payback period of 4 years, should he go ahead with the installation of the new pumps?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
MyLab Operations Management with Pearson eText -- Access Card -- for Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Essentials of MIS (13th Edition)
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
FUNDAMENTALS OF CORPORATE FINANCE
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Business Essentials (12th Edition) (What's New in Intro to Business)
Marketing: An Introduction (13th Edition)
- What are the responsibilities and duties of a consultant for a local company who is considering expanding its operations to international markets? How can a local Agriculture and Food Processing company successfully enter international markets?arrow_forwardWhat is an example of how someone would explain how their past personal and professional experience makes you a quality candidate for a teaching position at an Elementary School as a K-6 Teacher?arrow_forwardI need answer typing clear urjent no chatgpt used pls i will give 5 Upvotes.arrow_forward
- How can a local tourism and hospitality company successfully enter international markets?arrow_forwardHow was Circuit City Company collapsed? And what was the sequence of time and events or problems? How to solve the issues, and could you help identify positions or titles. Sanitize all names and use only fictitious data. What is synthesize the qualitative research methodology of Case Study research? Please give some examples. How to use the practical of Lean Six Sigma to develop a business-facing DMAIC-based case studyarrow_forwardBUSINESS MODEL CANVAS: U.S ARMY key partners: Key activities: Key Resources: Value Propositions: Buy-in & Support: Deployment: Benficiaries: Mission budget/cost: Mission Achievement/ Impact factors: Please at least 4 for each categoryarrow_forward
- how you would best conduct a performance evaluation meeting with a subordinate (where an employee would receive their performance evaluation from their supervisor). Importantly, detail how a supervisor can best gain the concurrence from an employee on the evaluation itself, and to ensure that the employee’s performance will be modified as a result of appraisal meeting.arrow_forwardI need answer typing clear urjent no chatgpt used pls i will give 5 Upvotes.arrow_forwardassume that you are police commander which leads and supervises the department’s internal affairs division. Your goal is to reduce civilian complainants against personnel in the department. Using what you have learned and at least three scholarly sources, document two changes you see the department can implement, whether it be training, planning, mitigating, and resolving, to improve police/community relations.arrow_forward
- Ness Engineering is a private limited company mainly engaged in the continuous production and assembly of domestic products. The annual turnover is $900,000,000. The largest area of expenditure is raw materials and components where the annual spend is approximately $450,000,000. The Managing Director, Bill, considers that profit margins are too small and has asked you to suggest how profitability might be increased. Bill suggests that this might be done by appointing additional sales staff and by an advertising campaign, which would, hopefully, increase turnover and thereby reduce overhead cost per item. You find that purchasing is little more than a post-office function. Specifications are received from the design or user departments and sent either to supplies designated by the directors or to the supplier providing the cheapest quotation. The company does, in fact, deal with many suppliers and issues many orders for low-cost items. All purchasing is done by manual means. None of the…arrow_forwardThe oasis outpost of Abu Ilan, in the heart of the Negev desert, has a population of 20 Bedouin tribesmen and 20 Farima tribesmen. El Kamin, a nearby oasis, has a population of 32 Bedouins and 8 Farima. A lost Israeli soldier, accidentally separated from his army unit, is wandering through the desert and arrives at the edge of one of the oases. The soldier has no idea which oasis he has found, but the first person he spots at a distance is a Bedouin. 1. What is the probability that he wandered into Abu Ilan? 2. What is the probability that he is in El Kamin?arrow_forward2-22 The lost Israeli soldier mentioned in Problem 2-21 decides to rest for a few minutes before entering the desert oasis he has just found. Closing his eyes, he dozes off for 15 minutes, wakes, and walks toward the center of the oasis. The first person he spots this time he again recognizes as a Bedouin. What is the posterior probability that he is in El Kamin?*Note* 2-21 The oasis outpost of Abu Ilan, in the heart of the Negev desert, has a population of 20 Bedouin tribesmen and 20 Farima tribesmen. El Kamin, a nearby oasis, has a population of 32 Bedouins and 8 Farima. A lost Israeli soldier, accidentally separated from his army unit, is wandering through the desert and arrives at the edge of one of the oases. The soldier has no idea which oasis he has found, but the first person he spots at a distance is a Bedouin. What is the probability that he has wandered into Abu Ilan? What is the probability that he is in El Kamin?arrow_forward
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,- MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing



