
Concept explainers
The load in Fig. 4-7 is hanging at rest. Take the ropes to all be vertical and the pulleys to be weightless and frictionless. (a) How many segments of rope support the combination of the lower pulley and load? (b) What is the downward force on the lowest pulley (the “floating” one)? (c) What must be the total upward force exerted on the floating pulley by the two lengths of rope? (d) What is the upward force exerted on the floating pulley by each length of rope supporting it? (e) What is the tension in the rope wound around the two pulleys? (f) How much force is the man exerting? (g) What is the net downward force acting on the uppermost pulley? (h) How much force acts downward on the hook in the ceiling?
(a)
The segments of the rope that support the combination of the lower pulley given inFigure
Answer to Problem 16SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The weight of the hanging block is
The load is hanging on rest, so there will be no acceleration.
Formula used:
Write the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Here,
Explanation:
Draw the free body diagram of the system:
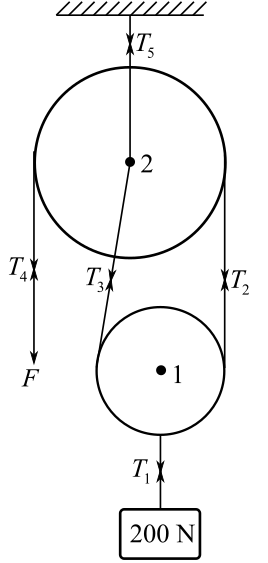
In the above diagram, point
Since the same rope is passing over theupper pulleyand lower pulley, the magnitude of tensionthroughout the rope should be same. Therefore,
Refer to the above diagram and consider the pulley 1. In this case,
Consider the upward forces as positive and the downward forces as negative. Therefore,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, two segments of the rope support the combination of the lower pulley and load.
(b)
The magnitude of the downward force applied to the lowest pulleyin the Figure
Answer to Problem 16SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The load is
The load is hanging on rest, so there will be no acceleration.
Formula used:
Write the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Here,
Explanation:
Draw the free body diagram when
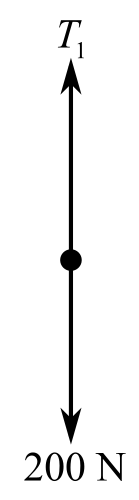
Recall the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Consider the direction of the upward forces is positive and the direction of the downward forces is negative. Therefore,
Substitute
The tension forces of 200 N, acting in the rope, pule the load in upward direction and weight of the
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the downward force on the lowest pulley is
(c)
The magnitude of the total upward force exertedon the floating pulley by the two lengths of ropein the Figure
Answer to Problem 16SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The load is
The load is hanging on rest, so there will be no acceleration.
Formula used:
Write the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Here,
Explanation:
Draw the free body diagram of the lowermost pulley:
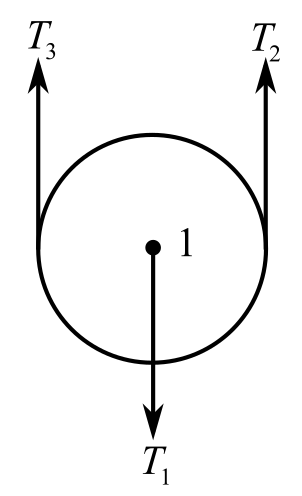
Recall the expression for the first condition of the force equilibrium:
Consider the direction of the upward forces is positive and the direction of the downward forces is negative. Hence,
Substitute
Conclusion:
The magnitude of the total upward force applied on the pulley by the two lengths of the rope is
(d)
The magnitude of the upward force applied on the floating pulley by each length of rope supporting the pulleyin the figure
Answer to Problem 16SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The weight of the person is
The load is hanging on rest, so there will be no acceleration.
Formula used:
Write the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Here,
Explanation:
Draw the free body diagram of the lowermost pulley:

Recall the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Consider the direction of the upward forces is positive and the direction of the downward forces is negative. Hence,
Substitute
Conclusion:
The magnitude of the upward force applied on the floating pulley by each length of the rope is
(e)
The magnitude of the tensionin the rope wound around the two pulleysin the Figure
Answer to Problem 16SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The load is
The load is hanging on rest, so there will be no acceleration.
Formula used:
Write the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Here,
Explanation:
Refer to the diagram drawn in the subpart (a). A single rope is wounded on the both the polis. So, the magnitude of tension should be same throughout the rope. Therefore,
Substitute
Conclusion:
The magnitude of the tension in the rope wound around the pulley is
(f)
The maximum force applied by the man to pull the ropein the Figure
Answer to Problem 16SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The load is
The load is hanging on rest, so there will be no acceleration.
Formula used:
Write the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Here,
Explanation:
Draw the free body diagram of the unwound rope, which is in the right side of the upper pulley, when a man exerts a force F to pull the rope.
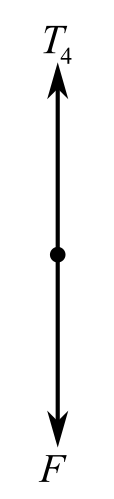
To observed the schematic diagram of the problem,
The force
Recall the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Consider the direction of the upward forces is positive and the direction of the downward forces is negative. Hence,
Substitute
Conclusion:
The magnitude of the maximum force applied by the man is
(g)
The magnitude of the net downward force acting on the uppermost pulleyin the Figure
Answer to Problem 16SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The load is
The load is hanging on rest, so there will be no acceleration.
Formula used:
Write the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Here,
Explanation:
Draw the free body diagram of the upper pulley:
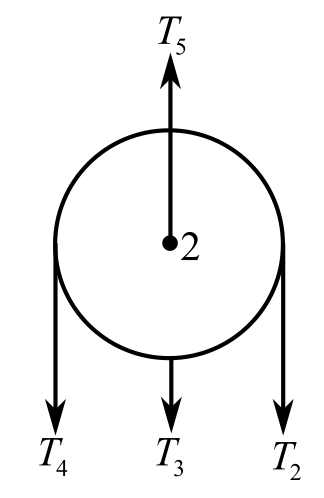
Recall the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Consider the direction of the upward forces is positive and the direction of the downward forces is negative. Hence,
Substitute
The net downward force acting on the uppermost pulleyhas the same magnitude as the tension of the rope, which is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the total downward force acting on the upper pulley is
(h)
The maximum force that is acting downward on the hook in the ceilingin the Figure
Answer to Problem 16SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The load is
The load is hanging on rest, so there will be no acceleration.
Formula used:
Write the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Here,
Explanation:
Refer to the schematic diagram of the problem from the subpart (a).
The maximum force applied downward on the hook in the ceiling is equal to the same magnitude of the tension
Conclusion:
Therefore, themaximum force applied downward on the hook in the ceilingis
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Schaum's Outline of College Physics, Twelfth Edition (Schaum's Outlines)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Organic Chemistry
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Chemistry: Atoms First
MARINE BIOLOGY
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
- Can someone help me asnwer this thank youarrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the problem correctly please. Be sure to give explanations on each step and write neatlyplease. Thank you!! ( preferably type the explantion, steps and solution please )arrow_forwardA square coil that has 17.5 cm on each side containing 17 loops lies flat on your desk as shown on this page. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 4.60 × 10-ST points into this page. If a 8.50-A clockwise Current flows through the coil. ca) determine the torque on the coil. N.m (b) which edge of the coil rises up? choose one 。 Bottom отор and explain. O Right • None of these О Left.arrow_forward
- A circular loop of wire with a diameter of 13.0 cm is in the horizontal plane and carries of 1.70 A clockwise, as viewed from underneath. What is the magnitude magnetic field as the center of the loop? -T what is the direction of magnetic field at the center or down? please explain. of the loop? uparrow_forwardStarlord has a mass of 89.3 kg and Groot is pulling the bag with a force of 384. N at an angle of 35.0˚ as is shown in the figure below. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction if they are moving at a constant speed of 2.31 m/s?arrow_forwardEarly on in the video game Shadow of the Tomb Raider Lara Croft uses a winch to pull a heavy crate of stone up a 23.6° incline. If Lara causes the 66.0 kg crate to accelerate at 2.79 m/s2 up the ramp, what is the tension in the rope pulling the block? The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the ground is 0.503.arrow_forward
- A player kicks a football at the start of the game. After a 4 second flight, the ball touches the ground 50 m from the kicking tee. Assume air resistance is negligible and the take-off and landing height are the same (i.e., time to peak = time to fall = ½ total flight time). (Note: For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.) Calculate and answer all parts. Only use equations PROVIDED:arrow_forwardA shot putter releases a shot at 13 m/s at an angle of 42 degrees to the horizontal and from a height of 1.83 m above the ground. (Note: For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.) Calculate and answer all parts. Only use equations PROVIDED:arrow_forwardIf a person jumps upwards with a vertical velocity of 5 m/s, What is their velocity 0.5 second into the jump?arrow_forward
- A solid sphere 22 cm in radius carries 17 μC, distributed uniformly throughout its volume. Part A Find the electric field strength 12 cm from the sphere's center. Express your answer using two significant figures. E₁ = ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ха Хь b Submit Previous Answers Request Answer <☑ × Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining ▾ Part B ? |X| X.10" <☑ Find the electric field strength 22 cm from the sphere's center. Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ E2 = Submit Request Answer ▾ Part C ? MN/C Find the electric field strength 44 cm from the sphere's center. Express your answer using two significant figures. ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ E3 = Submit Request Answer ? MN/C MN/Carrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forwardIn a naval battle, a battleship is attempting to fire on a destroyer. The battleship is a distance d1 = 2,150 m to the east of the peak of a mountain on an island, as shown in the figure below. The destroyer is attempting to evade cannon shells fired from the battleship by hiding on the west side of the island. The initial speed of the shells that the battleship fires is vi = 245 m/s. The peak of the mountain is h = 1,840 m above sea level, and the western shore of the island is a horizontal distance d2 = 250 m from the peak. What are the distances (in m), as measured from the western shore of the island, at which the destroyer will be safe from fire from the battleship? (Note the figure is not to scale. You may assume that the height and width of the destroyer are small compared to d1 and h.)arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill





