
Concept explainers
(a) A 600-N load hangs motionlessly in Fig. 4-8. Assume the ropes to all be vertical and the pulleys to be weightless and frictionless. (a) What is the tension in the bottom hook attached, via a ring, to the load? (b) How many lengths of rope support the movable pulley? (c) What is the tension in the long rope? (d) How much force does the man apply? (e) How much force acts downward on the ceiling?
(a)
The magnitude of the tension in the bottom hook that is attached by a ring to the load in the Figure
Answer to Problem 17SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to the figure 4-8.
Theload hanging motionlessly is
Formula used:
Write the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Here,
Explanation:
Consider all pulleys and hook as a system and draw its free body diagram:
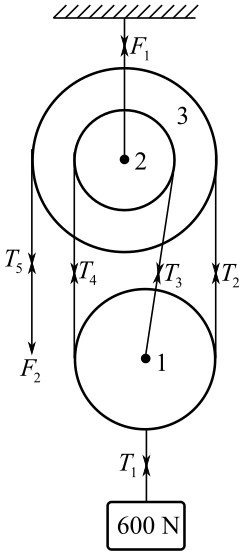
In the above diagram,
Here, pulley
Since thesame long rope is passing over the pulley
Draw the free body diagram of the bottom hook, which is attached via a ring to the load.
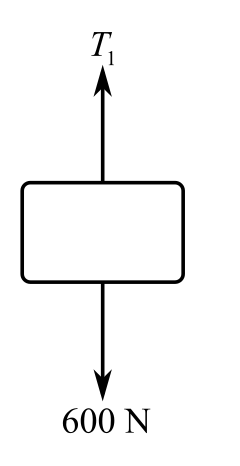
In above the diagram,
Recall the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Consider the direction of the upward forces is positive and the direction of the downward forces is negative. Therefore,
Substitute
Conclusion:
The magnitude of the tension attached in a bottom hook is
(b)
The number of sections of the rope that supports the movable pulleyin the Figure
Answer to Problem 17SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to the figure 4-8.
The load hanging at rest is
Formula used:
Write the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Here,
Explanation:
Refer the schematic diagram from the first part (a).
To observed the free body diagram, there are only three ropes that support the movable pulley.
Conclusion:
A segment of the rope that supports the movable pulley is
(c)
The magnitude of the tension in the long ropein the Figure
Answer to Problem 17SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to the figure 4-8.
The load hanging at rest is
Formula used:
Write the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Here,
Explanation:
Draw the free body diagram of the pulley
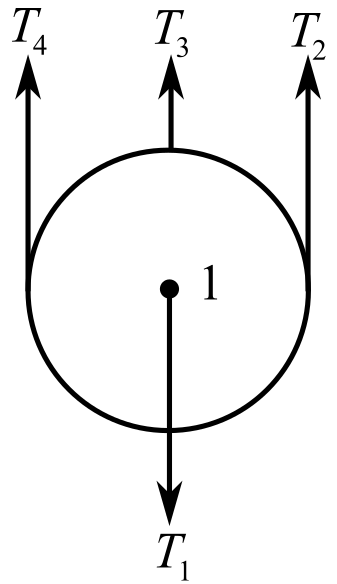
In the above diagram,
Recall the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Consider the direction of the upward forces is positive and the direction of the downward forces is negative. Therefore,
Refer to the equation (1)
Substitute
Conclusion:
The magnitude of the tension in the long rope is
(d)
The maximum force applied by the man to pull the rope in the Figure
Answer to Problem 17SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to the figure 4-8.
The load hanging motionlessly is
Formula used:
Write the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Here,
Explanation:
Draw the free body diagram when a man applied a pulling force on the rope:
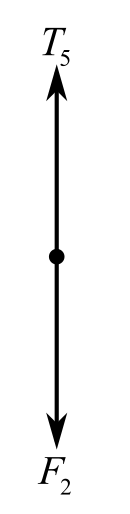
To observed the above diagram,
Recall the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Consider the direction of the upward forces is positive and the direction of the downward forces is negative. Therefore,
Since the same rope is passing over the pulley, the tension
Substitute
Conclusion:
The magnitude of the force applied by the man is
(e)
The maximum force that is acting downward on the ceilingin the Figure 4.8.
Answer to Problem 17SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to the figure 4-8.
The load hanging motionlessly is
Formula used:
Write the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Here,
Explanation:
Consider both the pulley 3 and pulley 3 as a system and draw theirfree body diagram:
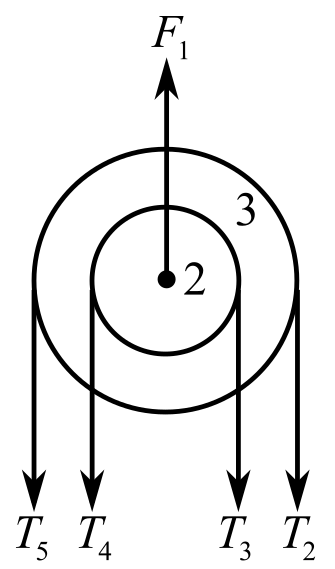
In the above diagram,
Recall the expression for the first condition of the force’s equilibrium:
Consider the direction of the upward forces is positive and the direction of the downward forces is negative. Therefore,
Refer to the equation (1)
Substitute
Since
Conclusion:
The maximum force acting on the ceiling is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Schaum's Outline of College Physics, Twelfth Edition (Schaum's Outlines)
- Correct answer please. I will upvote.arrow_forwardDefine operational amplifierarrow_forwardA bungee jumper plans to bungee jump from a bridge 64.0 m above the ground. He plans to use a uniform elastic cord, tied to a harness around his body, to stop his fall at a point 6.00 m above the water. Model his body as a particle and the cord as having negligible mass and obeying Hooke's law. In a preliminary test he finds that when hanging at rest from a 5.00 m length of the cord, his body weight stretches it by 1.55 m. He will drop from rest at the point where the top end of a longer section of the cord is attached to the bridge. (a) What length of cord should he use? Use subscripts 1 and 2 respectively to represent the 5.00 m test length and the actual jump length. Use Hooke's law F = KAL and the fact that the change in length AL for a given force is proportional the length L (AL = CL), to determine the force constant for the test case and for the jump case. Use conservation of mechanical energy to determine the length of the rope. m (b) What maximum acceleration will he…arrow_forward
- 9 V 300 Ω www 100 Ω 200 Ω www 400 Ω 500 Ω www 600 Ω ww 700 Ω Figure 1: Circuit symbols for a variety of useful circuit elements Problem 04.07 (17 points). Answer the following questions related to the figure below. A What is the equivalent resistance of the network of resistors in the circuit below? B If the battery has an EMF of 9V and is considered as an ideal batter (internal resistance is zero), how much current flows through it in this circuit? C If the 9V EMF battery has an internal resistance of 2 2, would this current be larger or smaller? By how much? D In the ideal battery case, calculate the current through and the voltage across each resistor in the circuit.arrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardIf the block does reach point B, how far up the curved portion of the track does it reach, and if it does not, how far short of point B does the block come to a stop? (Enter your answer in m.)arrow_forward
- Truck suspensions often have "helper springs" that engage at high loads. One such arrangement is a leaf spring with a helper coil spring mounted on the axle, as shown in the figure below. When the main leaf spring is compressed by distance yo, the helper spring engages and then helps to support any additional load. Suppose the leaf spring constant is 5.05 × 105 N/m, the helper spring constant is 3.50 × 105 N/m, and y = 0.500 m. Truck body yo Main leaf spring -"Helper" spring Axle (a) What is the compression of the leaf spring for a load of 6.00 × 105 N? Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. m (b) How much work is done in compressing the springs? ☑ Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. Jarrow_forwardA spring is attached to an inclined plane as shown in the figure. A block of mass m = 2.71 kg is placed on the incline at a distance d = 0.285 m along the incline from the end of the spring. The block is given a quick shove and moves down the incline with an initial speed v = 0.750 m/s. The incline angle is = 20.0°, the spring constant is k = 505 N/m, and we can assume the surface is frictionless. By what distance (in m) is the spring compressed when the block momentarily comes to rest? m m 0 k wwwwarrow_forwardA block of mass m = 2.50 kg situated on an incline at an angle of k=100 N/m www 50.0° is connected to a spring of negligible mass having a spring constant of 100 N/m (Fig. P8.54). The pulley and incline are frictionless. The block is released from rest with the spring initially unstretched. Ө m i (a) How far does it move down the frictionless incline before coming to rest? m (b) What is its acceleration at its lowest point? Magnitude m/s² Direction O up the incline down the inclinearrow_forward
- (a) A 15.0 kg block is released from rest at point A in the figure below. The track is frictionless except for the portion between points B and C, which has a length of 6.00 m. The block travels down the track, hits a spring of force constant 2,100 N/m, and compresses the spring 0.250 m from its equilibrium position before coming to rest momentarily. Determine the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the rough surface between points B and C. -A 3.00 m B C -6.00 m i (b) What If? The spring now expands, forcing the block back to the left. Does the block reach point B? Yes No If the block does reach point B, how far up the curved portion of the track does it reach, and if it does not, how far short of point B does the block come to a stop? (Enter your answer in m.) marrow_forwardA ball of mass m = 1.95 kg is released from rest at a height h = 57.0 cm above a light vertical spring of force constant k as in Figure [a] shown below. The ball strikes the top of the spring and compresses it a distance d = 7.80 cm as in Figure [b] shown below. Neglecting any energy losses during the collision, find the following. т m a d T m b i (a) Find the speed of the ball just as it touches the spring. 3.34 m/s (b) Find the force constant of the spring. Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. kN/marrow_forwardI need help with questions 1-10 on my solubility curve practice sheet. I tried to my best ability on the answers, however, i believe they are wrong and I would like to know which ones a wrong and just need help figuring it out.arrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning





