
Contrasting ABC and Conventional Product Costs L04−2, L04−3, L04−4
For many years. Thomson Company manufactured a single product called LEC 40. Then three years ago,the company automated a portion of its plant and at the same time introduced a second product called LEC 90 that has become increasingly popular. The LEC 90 is a more complex product, requiring 0.80 hours of direct labor time per unit to manufacture and extensive machining in the automated portion of the plant. The LEC 40 requires only 0.40 hours of direct labor time per unit and only a small amount of machining. Manufacturing
Management estimates that the company will incur $912,000 in manufacturing overhead costs duringthe current year and 60,000 units of the LEC 40 and 20.000 units of the LEC 90 will be produced and sold.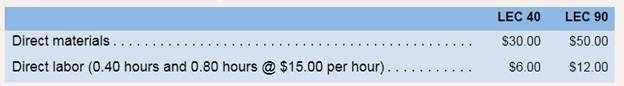
Required:
1. Compute the predetermined overhead rate assuming that the company continues to apply
2. Management is considering using activity-based costing to assign manufacturing overhead page 178cost to products. The activity-based costing system would have the following four activity cost pools: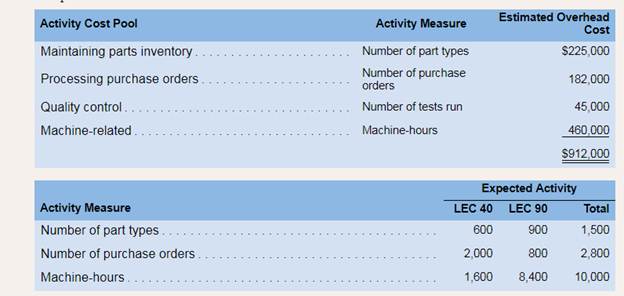
Determine the activity rate for each of the four activity cost pools.
3. Using the activity rates you computed in part (2) above, do the following:
a. Determine the total amount of manufacturing overhead cost that would be assigned to each product using the activity-based costing system. After these totals have been computed, determinethe amount of manufacturing overhead cost per unit of each product.
b. Compute the unit product cost of each product.
4. From the data you have developed in parts (1) through (3) above. Identify factors that may account forthe company’s declining profits.
1
Predetermined overhead rate
It is a rate that is used by a company to allocate its manufacturing overhead cost to all the products. This rate is calculated by using the estimated data (estimated cost and hours).
Unit product cost
Unit product cost is the total cost incurred by a company to produce one unit. It is calculated by the division of total cost and total number of units manufactured.
To calculate: Predetermined overhead rate and unit product cost by using the predetermined overhead rate.
Answer to Problem 16P
Predetermined overhead rate is calculated as $22.8.
Unit product cost for product LEC 40 is $45.12 and for product LEC 90 is $80.24.
Explanation of Solution
Predetermined overhead rate is calculated by the following formula:
Here, total manufacturing overhead cost is given as $912,000 and total direct labor hours will be calculated as:
So, predetermined overhead rate will be,
Unit product cost can be calculated by dividing total cost incurred by the total number of manufactured units or by adding per unit cost of direct material, direct labor and overheads. Here, per unit cost of direct material and direct labor is given and per unit cost of manufacturing overheads will be calculated as follows:
So, unit product cost will be calculated as follows:
| Particulars | LEC 40 (in $) | LEC 90 (in $) |
| Direct material (per unit) | 30 | 50 |
| Direct labor (per unit) | 6 | 12 |
| Manufacturing overheads | 9.12 | 18.24 |
| Unit product cost | 45.12 | 80.24 |
Therefore, predetermined overhead rate is $22.8, unit product cost for product LEC 40 is $45.12 and unit product cost for product LEC 90 is $80.24.
2
Activity rates
Activity rates are calculated when ABC system is used, these rates are used in the process of cost allocation and are calculated by dividing estimated cost and total estimated activity.
To compute: Activity cost rates for the given four cost pools.
Answer to Problem 16P
Activity rates are:
| Maintaining parts inventory | $150 per part |
| Processing purchase orders | $65 per order |
| Quality control | $1.125 per DLH |
| Machine related | $46 per hour |
Explanation of Solution
Activity rates will be calculated as follows:
| Cost pools | Activity measure | Estimated overhead cost (in $) (A) | Estimated activity (B) | Activity rates (A/B) (in $) |
| Maintaining parts inventory | Part types | 225,000 | 1,500 | 150 per part |
| Processing purchase orders | Purchase orders | 182,000 | 2,800 | 65 per order |
| Quality control | Direct labor hours * | 45,000 | 40,000 | 1.125 per hour |
| Machine related | Machine hours | 460,000 | 10,000 | 46 per hour |
Note*: Activity measure of quality control is number of tests run but since information of tests run is not provided in the question, direct labor hours are used to calculate the activity rate. Total direct labor hours are 40,000 (computed in sub part 1).
So, activity rate for maintenance of inventory part is $150 per part, for processing purchase orders is $65 per order, for quality control is $1.125 per DLH and for machine related activity is $46 per machine hour.
3
Manufacturing overheads
It includes all the costs incurred by a company while providing certain manufacturing facilities and does include costs related to direct materials and direct labors. These costs are indirectly related to a product.
To calculate: Amount of variable overhead rate and efficiency variances. To explain the relation between variable overhead efficiency and labor efficiency variances.
Answer to Problem 16P
Total overhead cost allocated to product LEC 40 is $320,600 and to product LEC 90 is $591,400. Per unit overhead cost is $5.34 for product LEC 40 and $29.57 for product LEC 90.
Total per unit cost is $41.34 for product LEC 40 and $91.57 for product LEC 90.
Explanation of Solution
Part a
In the ABC system, manufacturing overhead costs are allocated to each product in the ratio in which products consume different activities. So, that ratio will be calculated first.
Calculation of ratio:
| Particulars | LEC 40 | LEC 90 | RatioLEC 40: LEC 90 |
| Maintaining parts inventory (parts) | 600 | 900 | 6:9 or 2:3 |
| Purchase orders (orders) | 2,000 | 800 | 20:8 or 5:2 |
| Quality control (DLHs) | 24,000 | 16,000 | 24:16 or 3:2 |
| Machine related (Machine hours) | 1,600 | 8,400 | 16:84 or 4:21 |
Now, overhead costs will be allocated as follows:
| Activity cost pool | Overhead expense(in $) | Ratio | LEC 40 (in $) | LEC 90 (in $) |
| Maintaining part inventory | 225,000 | 2:3 | 90,000 | 135,000 |
| Purchase orders | 182,000 | 5:2 | 130,000 | 52,000 |
| Quality control | 45,000 | 3:2 | 27,000 | 18,000 |
| Machine related | 460,000 | 4:21 | 73,600 | 386,400 |
| Total overhead cost | 320,600 | 591,400 | ||
Per unit manufacturing cost will be calculated as follows:
| Particulars | LEC 40 | LEC 90 |
| Total manufacturing overhead cost | 320,600 | 591,400 |
| Total units | 60,000 | 20,000 |
| Manufacturing cost per unit | $5.34 | $29.57 |
Therefore, total manufacturing overhead cost allocated to product LEC 40 is $320,600 and allocated to product $591,400. Per unit manufacturing cost of product LEC 40 is $5.34 and of product LEC 90 is $29.57.
Part b
Unit product cost will be calculated as follows:
| Particulars | LEC 40 (in $) | LEC 90 (in $) |
| Direct material (per unit) | 30 | 50 |
| Direct labor (per unit) | 6 | 12 |
| Manufacturing overheads | 5.34 | 29.57 |
| Unit product cost | 41.34 | 91.57 |
Unit product cost for product LEC 40 is $41.34 and LEC 90 is $91.57.
4
Decline in profits
Profit is calculated by deducting all the expenses from the generated revenue. It starts declining when there is an increase in the expenses or decrease in sales.
To identify: Possible factors for decline in company’s profits.
Answer to Problem 16P
Possible factors for a decrease in profit are increase in cost or decrease in sales.
Explanation of Solution
When the management decided to use ABC system, cost of product LEC 40 is declining by $3.78 (45.12 − 41.34) but cost of product LEC 90 is increasing by $11.33 (91.57-80.24). Therefore, profits of the company are declining. There will be a decrease in the company’s profits because of the following factors-
1 Increase in cost of product LEC 40.
2 There is no increase in the units sold.
Profits of the company are decreasing because cost of the company is increasing but units sold are the same.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Introduction To Managerial Accounting
- Hadley, Inc. manufactures a product that uses $25 in direct materials and $10 in direct labor per unit. Under the traditional costing system Hadley uses, manufacturing overhead applied to each unit is $13. However, Hadley is considering switching to an ABC system. Under the ABC system, the total activity cost would be $30. What is the total manufacturing cost per unit for Hadley under the ABC system? Right Answerarrow_forwardAbcarrow_forwardWhat amount should the bond issue proceeds increase shareholders equity?arrow_forward
- Hadley, Inc. manufactures a product that uses $25 in direct materials and $10 in direct labor per unit. Under the traditional costing system Hadley uses, manufacturing overhead applied to each unit is $13. However, Hadley is considering switching to an ABC system. Under the ABC system, the total activity cost would be $30. What is the total manufacturing cost per unit for Hadley under the ABC system?arrow_forwardPlease provide correct solution for this financial accounting questionarrow_forwardWhat is the full cost of the productarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning





