
PHYSICS F/SCI.+ENGINEERS W/MOD.PHYSICS
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780321992277
Author: GIANCOLI
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 13P
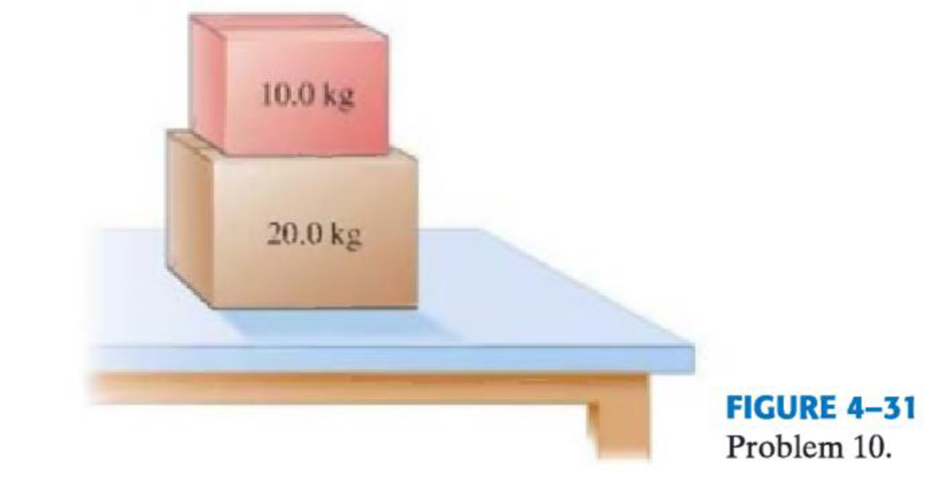
(II) A 20.0-kg box rests on a table. (a) What is the weight of the box and the normal force acting on it? (b) A 10.0-kg box is placed on top of the 20.0-kg box, as shown in Fig. 4–31. Determine the normal force that the table exerts on the 20.0-kg box and the normal force that the 20.0-kg box exerts on the 10.0-kg box.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule05:07
Students have asked these similar questions
It is not possible to see very small objects, such as viruses, using an ordinary light microscope. An electron microscope can view such objects using an electron beam instead of a light beam. Electron microscopy has proved invaluable for investigations of viruses, cell membranes and subcellular structures, bacterial surfaces, visual receptors, chloroplasts, and the contractile properties of muscles. The "lenses" of an
electron microscope consist of electric and magnetic fields that control the electron beam.
As an example of the manipulation of an electron beam, consider an electron traveling away from the origin along the x axis in the xy plane with initial velocity ₁ = vi. As it passes through the region x = 0 to x=d, the electron experiences acceleration a = ai +a, where a and a, are constants. For the case v, = 1.67 x 107 m/s, ax = 8.51 x 1014 m/s², and a = 1.50 x 10¹5 m/s², determine the following at
x = d = 0.0100 m.
(a) the position of the electron
y, = 2.60e1014
m
(b) the…
No chatgpt pls
need help with the first part
Chapter 4 Solutions
PHYSICS F/SCI.+ENGINEERS W/MOD.PHYSICS
Ch. 4.4 - Suppose you watch a cup slide on the (smooth)...Ch. 4.5 - Prob. 1BECh. 4.5 - If you push on a heavy desk, does it always push...Ch. 4.5 - Return to the first Chapter-Opening Question, page...Ch. 4.7 - Prob. 1FECh. 4.7 - Prob. 1GECh. 4.7 - Prob. 1HECh. 4 - Why does a child in a wagon seem to fall backward...Ch. 4 - If an object is moving, is it possible for the net...Ch. 4 - If the acceleration of an object is zero, are no...
Ch. 4 - Only one force acts on an object. Can the object...Ch. 4 - When a golf ball is dropped to the pavement, it...Ch. 4 - If you walk along a log floating on a lake, why...Ch. 4 - (a) Why do you push down harder on the pedals of a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 9QCh. 4 - The force of gravity on a 2-kg rock is twice as...Ch. 4 - Prob. 11QCh. 4 - When an object falls freely under the influence of...Ch. 4 - Compare the effort (or force) needed to lift a...Ch. 4 - When you stand still on the ground, how large a...Ch. 4 - Whiplash sometimes results from an automobile...Ch. 4 - Mary exerts an upward force of 40N to hold a bag...Ch. 4 - A father and his young daughter are ice skating....Ch. 4 - Prob. 19QCh. 4 - Which of the following objects weighs about 1 N:...Ch. 4 - Why might your foot hurt if you kick a heavy desk...Ch. 4 - When you are running and want to slop quickly, you...Ch. 4 - Suppose that you are standing on a cardboard...Ch. 4 - Prob. 2MCQCh. 4 - Prob. 3MCQCh. 4 - Prob. 4MCQCh. 4 - Prob. 5MCQCh. 4 - Prob. 7MCQCh. 4 - Prob. 9MCQCh. 4 - Prob. 10MCQCh. 4 - Prob. 11MCQCh. 4 - Prob. 12MCQCh. 4 - Prob. 13MCQCh. 4 - Prob. 1PCh. 4 - Prob. 2PCh. 4 - Prob. 3PCh. 4 - Prob. 4PCh. 4 - Prob. 5PCh. 4 - Prob. 6PCh. 4 - (II) Superman must stop a 120-km/h train in 150 m...Ch. 4 - Prob. 8PCh. 4 - Prob. 9PCh. 4 - Prob. 10PCh. 4 - (II) A fisherman yanks a fish vertically out of...Ch. 4 - Prob. 12PCh. 4 - (II) A 20.0-kg box rests on a table. (a) What is...Ch. 4 - (II) A particular race car can cover a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 15PCh. 4 - Prob. 16PCh. 4 - Prob. 17PCh. 4 - (II) Can cars stop on a dime? Calculate the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 19PCh. 4 - (II) Using focused laser light, optical tweezers...Ch. 4 - Prob. 21PCh. 4 - Prob. 22PCh. 4 - Prob. 23PCh. 4 - (II) An exceptional standing jump would raise a...Ch. 4 - (II) High-speed elevators function under two...Ch. 4 - Prob. 26PCh. 4 - Prob. 27PCh. 4 - Prob. 28PCh. 4 - (I) Draw the free-body diagram for a basketball...Ch. 4 - (I) A 650-N force acts in a northwesterly...Ch. 4 - (I) Sketch the tree body diagram of a baseball (a)...Ch. 4 - Prob. 32PCh. 4 - Prob. 33PCh. 4 - Prob. 34PCh. 4 - (II) The cords accelerating the buckets in Problem...Ch. 4 - Prob. 36PCh. 4 - (II) A train locomotive is pulling two cars of the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 38PCh. 4 - (II) A skateboarder, with an initial speed of...Ch. 4 - (II) At the instant a race began, a 65-kg sprinter...Ch. 4 - (II) A mass m is at rest on a horizontal...Ch. 4 - Prob. 42PCh. 4 - (II) A 27-kg chandelier hangs from a ceiling on a...Ch. 4 - (II) Redo Example 413 but (a) set up the equations...Ch. 4 - (II) The block shown in Fig. 4-43 has mass m = 7.0...Ch. 4 - Prob. 46PCh. 4 - Prob. 47PCh. 4 - Prob. 48PCh. 4 - Prob. 49PCh. 4 - (II) As shown in Fig. 4-41, five balls (masses...Ch. 4 - A super high-speed 14-car Italian train has a mass...Ch. 4 - Prob. 52PCh. 4 - Prob. 53PCh. 4 - (II) A child on a sled reaches the bottom of a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 55PCh. 4 - Prob. 56PCh. 4 - (III) Determine a formula for the acceleration of...Ch. 4 - (III) Suppose the pulley in Fig. 446 is suspended...Ch. 4 - Prob. 59PCh. 4 - (II) Three blocks on a frictionless horizontal...Ch. 4 - Prob. 61PCh. 4 - (III) A small block of mass m rests on the sloping...Ch. 4 - (III) The double Atwood machine shown in Fig. 4-48...Ch. 4 - (III) Determine a formula for the magnitude of the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 65PCh. 4 - Prob. 66PCh. 4 - Prob. 67GPCh. 4 - Prob. 69GPCh. 4 - Prob. 70GPCh. 4 - Prob. 71GPCh. 4 - Prob. 72GPCh. 4 - Prob. 73GPCh. 4 - Prob. 74GPCh. 4 - Prob. 75GPCh. 4 - A block (mass mA) lying on a fixed frictionless...Ch. 4 - Prob. 77GPCh. 4 - Prob. 78GPCh. 4 - (a) What minimum force F is needed to lift the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 80GPCh. 4 - A jet aircraft is accelerating at 3.8m/s2 as it...Ch. 4 - Prob. 82GPCh. 4 - Prob. 83GPCh. 4 - A fisherman in a boat is using a 10-lb test...Ch. 4 - Prob. 85GPCh. 4 - Prob. 86GPCh. 4 - Prob. 87GPCh. 4 - Prob. 88GPCh. 4 - Prob. 90GPCh. 4 - Prob. 91GPCh. 4 - Prob. 92GPCh. 4 - Prob. 93GPCh. 4 - Prob. 94GP
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Low-pressure centers are also referred to as ______, while high-pressure centers are called ______.
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Explain the role of gene flow in the biological species concept.
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
What is the difference between cellular respiration and external respiration?
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
10.71 Identify each of the following as an acid or a base: (10.1)
H2SO4
RbOH
Ca(OH)2
HI
...
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
89. Determine the volume of 0.150 M NaOH solution required to neutralize each sample of hydrochloric acid. The ...
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Sketch the following spectra that would be obtained for 2-chloroethanol: a. The 1H NMR spectrum for an anhydrou...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A ball is thrown with an initial speed v, at an angle 6, with the horizontal. The horizontal range of the ball is R, and the ball reaches a maximum height R/4. In terms of R and g, find the following. (a) the time interval during which the ball is in motion 2R (b) the ball's speed at the peak of its path v= Rg 2 √ sin 26, V 3 (c) the initial vertical component of its velocity Rg sin ei sin 20 (d) its initial speed Rg √ sin 20 × (e) the angle 6, expressed in terms of arctan of a fraction. 1 (f) Suppose the ball is thrown at the same initial speed found in (d) but at the angle appropriate for reaching the greatest height that it can. Find this height. hmax R2 (g) Suppose the ball is thrown at the same initial speed but at the angle for greatest possible range. Find this maximum horizontal range. Xmax R√3 2arrow_forwardAn outfielder throws a baseball to his catcher in an attempt to throw out a runner at home plate. The ball bounces once before reaching the catcher. Assume the angle at which the bounced ball leaves the ground is the same as the angle at which the outfielder threw it as shown in the figure, but that the ball's speed after the bounce is one-half of what it was before the bounce. 8 (a) Assuming the ball is always thrown with the same initial speed, at what angle & should the fielder throw the ball to make it go the same distance D with one bounce (blue path) as a ball thrown upward at 35.0° with no bounce (green path)? 24 (b) Determine the ratio of the time interval for the one-bounce throw to the flight time for the no-bounce throw. Cone-bounce no-bounce 0.940arrow_forwardA rocket is launched at an angle of 60.0° above the horizontal with an initial speed of 97 m/s. The rocket moves for 3.00 s along its initial line of motion with an acceleration of 28.0 m/s². At this time, its engines fail and the rocket proceeds to move as a projectile. (a) Find the maximum altitude reached by the rocket. 1445.46 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. m (b) Find its total time of flight. 36.16 x Your response is within 10% of the correct value. This may be due to roundoff error, or you could have a mistake in your calculation. Carry out all intermediate results to at least four-digit accuracy to minimize roundoff error. s (c) Find its horizontal range. 1753.12 × Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. marrow_forward
- Race car driver is cruising down the street at a constant speed of 28.9 m/s (~65 mph; he has a “lead” foot) when the traffic light in front of him turns red. a) If the driver’s reaction time is 160 ms, how far does he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he begins to slow down? b) If the driver’s combined reaction and movement time is 750 ms, how far do he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he slams on her brakes and car begins to slow down? Please answer parts a-B. Show all work. For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places. DONT FORGET TO DRAW VECTORS! ONLY USE BASIC FORMULAS TAUGHT IN PHYSICS. distance = speed * time.arrow_forwardRace car driver is cruising down the street at a constant speed of 28.9 m/s (~65 mph; he has a “lead” foot) when the traffic light in front of him turns red. a) If the driver’s reaction time is 160 ms, how far does he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he begins to slow down? b) If the driver’s combined reaction and movement time is 750 ms, how far do he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he slams on her brakes and car begins to slow down? c) If the driver’s average rate of acceleration is -9.5 m/s2 as he slows down, how long does it take him to come to a stop (use information about his speed of 28.9 m/s but do NOT use his reaction and movement time in this computation)? Please answer parts a-c. Show all work. For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.…arrow_forwardHow is it that part a is connected to part b? I can't seem to solve either part and don't see the connection between the two.arrow_forward
- Hello, please help with inputing trial one into the equation, I just need a model for the first one so I can answer the rest. Also, does my data have the correct sigfig? Thanks!arrow_forwardFind the current in the R₁ resistor in the drawing (V₁=16.0V, V2=23.0 V, V₂ = 16.0V, R₁ = 2005, R₂ = and R₂ = 2.705) 2.3052 VIT A www R www R₂ R₂ Vaarrow_forwardWhich of the following laws is true regarding tensile strength? • tensile strength T ①Fbreak = Wtfest Piece thickness rate (mm) ②T = test piece width rabe (mm) Fbreak break watarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Newton's First Law of Motion: Mass and Inertia; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1XSyyjcEHo0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY