
Concept explainers
Human Adaptation to a Starchy Diet The human AMY-1 gene encodes salivary amylase, an enzyme that breaks down starch. The number of copies of this gene varies, and people who have more copies generally make more enzyme. In addition, the average number of AMY-1 copies differs among cultural groups.
George Perry and his colleagues hypothesized that duplications of the AMY-1 gene would be selectively advantageous in cultures in which starch is a large part of the diet. To test this hypothesis, the scientists compared the number of copies of the AMY-1 gene among members of seven cultural groups that differed in their traditional diets. FIGURE 39.9 shows their results.
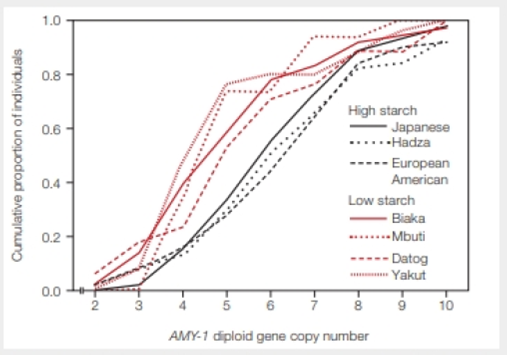
FIGURE 39.9 Number of copies of the AMY-1 gene among members of cultures with traditional high-starch or low-starch diets. The Hadza, Biaka, Mbuti, and Datog are tribes in Africa. The Yakut live in Siberia.
Starchy tubers are a mainstay of Hadza hunter–gatherers in Africa, whereas fishing sustains Siberia's Yakut. Almost 60 percent of Yakut had fewer than 5 copies of the AMY1 gene. What percentage of the Hadza had fewer than 5 copies?
To determine: The percentage of Hadza people who had fewer than five copies of AMY1 gene.
Introduction: An enzyme present in the saliva that initiates or mediates the hydrolysis of starch into simpler sugar molecules is called as salivary amylase. AMY-1 is the gene that encodes for the salivary amylase enzyme. Humans possess this gene, but copy number of that particular gene highly depends on their dietary habits. Varied number of the copy numbers of AMY1 genes is observed among the people. The people consuming high starchy diets have more copies of AMY1 gene when compared those with less starchy diets.
Explanation of Solution
Refer figure 39.9 “Number of copies of AMY-1 gene among members of cultures with high-starch or low-starch diets” in the textbook. It gives the information about cumulative proportion of individuals versus AMY-1 diploid gene copy number found in them. The variations in copy numbers of the salivary amylase (AMY-1) gene was tested among peoples of seven traditional groups that differ in their traditional food habits. They chose individuals with high starchy diet (Hadza, European American, and Japanese) and with low starchy diet (Yakut, Mbuti, Biaka, and Datog). Researchers observed a great difference in the enzyme copy number in the individuals of different populations.
Hadza are the hunter-gatherers (the people who follow hunting patterns for living instead of farming) in Africa. Their dietary habits include nuts, fruits, roots, berries, grasses, honey, seasonal vegetables, and also meat from animals. Because of high starch consumption, Hadza people possess high copy number of salivary enzyme, whereas, the Yakut tribes from Siberia mostly consume proteinaceous foods such as meat, fish, and milk. Therefore, most probably the salivary enzyme copy numbers will be lesser in the population of Yakut people.
From the given data shown in figure 39.9, almost 60% of Yakut had fewer than five copies of gene because they consume less starchy food. From the given graph, it can be materialized that approximately 30% of the Hadza population had fewer than 5 copies of the AMY-1 gene. The rest of the Hadza population about 70% of people had above 5 copies of AMY-1 gene. This is because of the high starch consumption habits followed among the Hadza population.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 39 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
- What did the Cre-lox system used in the Kikuchi et al. 2010 heart regeneration experiment allow researchers to investigate? What was the purpose of the cmlc2 promoter? What is CreER and why was it used in this experiment? If constitutively active Cre was driven by the cmlc2 promoter, rather than an inducible CreER system, what color would you expect new cardiomyocytes in the regenerated area to be no matter what? Why?arrow_forwardWhat kind of organ size regulation is occurring when you graft multiple organs into a mouse and the graft weight stays the same?arrow_forwardWhat is the concept "calories consumed must equal calories burned" in regrads to nutrition?arrow_forward
- You intend to insert patched dominant negative DNA into the left half of the neural tube of a chick. 1) Which side of the neural tube would you put the positive electrode to ensure that the DNA ends up on the left side? 2) What would be the internal (within the embryo) control for this experiment? 3) How can you be sure that the electroporation method itself is not impacting the embryo? 4) What would you do to ensure that the electroporation is working? How can you tell?arrow_forwardDescribe a method to document the diffusion path and gradient of Sonic Hedgehog through the chicken embryo. If modifying the protein, what is one thing you have to consider in regards to maintaining the protein’s function?arrow_forwardThe following table is from Kumar et. al. Highly Selective Dopamine D3 Receptor (DR) Antagonists and Partial Agonists Based on Eticlopride and the D3R Crystal Structure: New Leads for Opioid Dependence Treatment. J. Med Chem 2016.arrow_forward
- The following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin. You are a chef in a fancy new science-themed restaurant. You have a recipe that calls for 1 teaspoon of resinferatoxin, but you feel uncomfortable serving foods with "toxins" in them. How much capsaicin could you substitute instead?arrow_forwardWhat protein is necessary for packaging acetylcholine into synaptic vesicles?arrow_forward1. Match each vocabulary term to its best descriptor A. affinity B. efficacy C. inert D. mimic E. how drugs move through body F. how drugs bind Kd Bmax Agonist Antagonist Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamicsarrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning- Nutritional Sciences: From Fundamentals to Food, ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337486415Author:McGuirePublisher:Cengage
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





