
Concept explainers
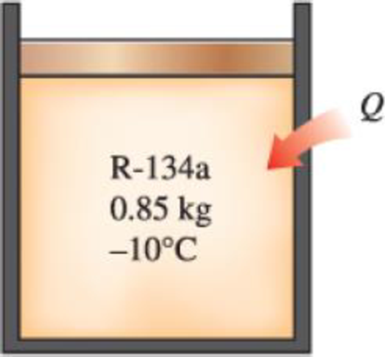
A piston–cylinder device contains 0.85 kg of refrigerant-134a at −10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 88 kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Determine (a) the final pressure, (b) the change in the volume of the cylinder, and (c) the change in the enthalpy of the refrigerant-134a.
FIGURE P3–30
(a)
The final pressure of the refrigerant R-134a.
Answer to Problem 30P
The final pressure of the refrigerant R-134a is
Explanation of Solution
The final pressure is equal to the initial pressure of the refrigerant R-134a.
Here, atmospheric pressure is
Conclusion:
Substitute 88 kPa for
Thus, the final pressure of the refrigerant R-134a is
(b)
The change in the volume of the cylinder.
Answer to Problem 30P
The change in the volume of the cylinder is
Explanation of Solution
Convert the unit of initial pressure from kPa to MPa.
Write the formula of interpolation method of two variables at
Here, the variables denote by x and y are pressure and specific volume.
Calculate the initial volume of cylinder.
Here, the initial state specific volume is
Calculate the final volume of cylinder.
Here, the final state specific volume is
Calculate the change in the volume of cylinder.
Conclusion:
Refer to Table A-13, obtain the values of below variables as in Table (I) at
| Pressure, MPa | Specific volume, |
| 0.06 | 0.35048 |
| 0.0904 | ? |
| 0.10 | 0.20743 |
Substitute 0.06 for
Thus, the specific volume of refrigerant R-134a at the initial state of 90.4 kPa and
Refer to Table A-13, obtain the values of below variables as in Table (II) at
| Pressure, MPa | Enthalpy, |
| 0.06 | 248.60 |
| 0.0904 | ? |
| 0.10 | 247.51 |
Substitute 0.06 for
Thus, the enthalpy of refrigerant R-134a at the initial state of 90.4 kPa and
Apply spreadsheet and solve the final state specific volume at
Refer to Table A-13, obtain the values of below variables as in Table (III) at
| Temperature, | Specific volume, |
| 10 | 0.37893 |
| 15 | ? |
| 20 | 0.39302 |
Substitute 10 for
Similarly, solve final state specific volume at
Now use interpolation method again to solve the final state specific volume at
| Pressure, MPa | Specific volume, |
| 0.06 | 0.386 |
| 0.0904 | ? |
| 0.10 | 0.2294 |
Substitute 0.06 for
Thus, the final state specific volume at
Apply the above steps to calculate the enthalpy at
Substitute 0.85 kg for m and
Substitute 0.85 kg for m and
Substitute
Thus, the change in the volume of the cylinder is
(c)
The change in the enthalpy of the refrigerant R-134a.
Answer to Problem 30P
The change in the enthalpy of the refrigerant R-134a is
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the total enthalpy change of refrigerant R-134a.
Here, enthalpy at initial state and final state are
Conclusion:
Substitute 0.85 kg for m,
Thus, the change in the enthalpy of the refrigerant R-134a is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
CONNECT FOR THERMODYNAMICS: AN ENGINEERI
- A spring package with two springs and an external force, 200N. The short spring has a loin of 35 mm. Constantly looking for spring for short spring so that total compression is 35 mm (d). Known values: Long spring: Short spring:C=3.98 N/mm Lo=65mmLo=87.4mmF=c·fTotal compression is same for both spring. 200 = (3.98(c1) × 35) + (c₂ × 35) 200 = 139.3 + 35c₂ 200 - 139.3 = 35c₂ 60.7 = 35c₂ c₂ = 60.7/35 Short spring (c₂) = 1.73 N/mm According to my study book, the correct answer is 4.82N/mm What is wrong with the calculating?arrow_forwardWhat is the reason for this composition?arrow_forwardHomework: ANOVA Table for followed design B AB Dr -1 -1 1 (15.18,12) 1 -1 -1 (45.48.51) -1 1 -1 (25,28,19) 1 1 (75.75,81)arrow_forward
- 20. [Ans. 9; 71.8 mm] A semi-elliptical laminated spring is made of 50 mm wide and 3 mm thick plates. The length between the supports is 650 mm and the width of the band is 60 mm. The spring has two full length leaves and five graduated leaves. If the spring carries a central load of 1600 N, find: 1. Maximum stress in full length and graduated leaves for an initial condition of no stress in the leaves. 2. The maximum stress if the initial stress is provided to cause equal stress when loaded. [Ans. 590 MPa ; 390 MPa ; 450 MPa ; 54 mm] 3. The deflection in parts (1) and (2).arrow_forwardQ6/ A helical square section spring is set inside another, the outer spring having a free length of 35 mm greater than the inner spring. The dimensions of each spring are as follows: Mean diameter (mm) Side of square section (mm) Active turns Outer Inner Spring Spring 120 70 8 7 20 15 Determine the (1) Maximum deflection of the two springs and (2) Equivalent spring rate of the two springs after sufficient load has been applied to deflect the outer spring 60 mm. Use G = 83 GN/m².arrow_forwardQ2/ The bumper springs of a railway carriage are to be made of rectangular section wire. The ratio of the longer side of the wire to its shorter side is 1.5, and the ratio of mean diameter of spring to the longer side of wire is nearly equal to 6. Three such springs are required to bring to rest a carriage weighing 25 kN moving with a velocity of 75 m/min with a maximum deflection of 200 mm. Determine the sides of the rectangular section of the wire and the mean diameter of coils when the shorter side is parallel to the axis of the spring. The allowable shear stress is not to exceed 300 MPa and G = 84 kN/mm². Q6/ A belicalarrow_forward
- 11. A load of 2 kN is dropped axially on a close coiled helical spring, from a height of 250 mm. The spring has 20 effective turns, and it is made of 25 mm diameter wire. The spring index is 8. Find the maximum shear stress induced in the spring and the amount of compression produced. The modulus of rigidity for the material of the spring wire is 84 kN/mm². [Ans. 287 MPa; 290 mm]arrow_forwardWhat is the reason for this composition?arrow_forwardHomework: ANOVA Table for followed design B AB Dr -1 -1 1 (15.18,12) 1 -1 -1 (45.48.51) -1 1 -1 (25,28,19) 1 1 (75.75,81)arrow_forward
- S B Pin 6 mm Garrow_forwardMid-Term Exam 2024/2025 Post graduate/Applied Mechanics- Metallurgy Q1/ State the type of fault in the following case, and state the structure in which it will appear. АВСАВСВАСВАСАВСАВСarrow_forwardالثانية Babakt Momentum equation for Boundary Layer S SS -Txfriction dray Momentum equation for Boundary Layer What laws are important for resolving issues 2 How to draw. 3 What's Point about this.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





