
Concept explainers
Cervical Cancer Incidence In HPV-Positive Women In 2003, Michelle Khan and her coworkers published their findings on a 10-year study in which they followed cervical cancer incidence and HPV status in 20,514 women. All women who participated in the study were free of cervical cancer when the test began. Pap tests were taken at regular intervals, and the researchers used a DMA probe hybridization test (Section 15.3) to detect specific types of HPV in the women's cervical cells.
The results are shown in FIGURE 37.26 as a graph of the incidence rate of cervical cancer by HPV type. HPV- positive women are often infected by more than one type, so the data were sorted into groups based on the women's HPV status ranked by type: either positive for HPV16; or negative for HPV16 and positive for HPV18; or negative for HPV16 and HPV18 and positive for any other cancer-causing HPV; or negative for all cancer-causing HPV.
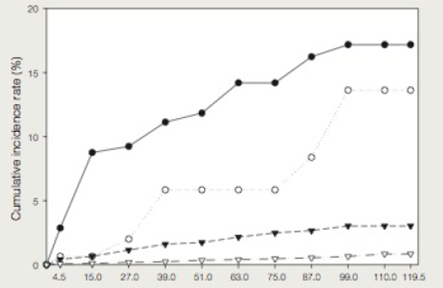
Follow-up time (months)
FIGURE 37.26 Cumulative incidence rate of cervical cancer correlated with HPV status in, 20,514 women aged 16 years and cider.
The data were grouped as follows:
● HPV16 positive
○ HFV16 negative and HPV18 positive
▼ All other cancer-causing HPV Types combined
∇ No cancer-causing HPV type was detected.
3. Is it possible to estimate from this graph the overall risk of cervical cancer that is associated with infection of cancer-causing HPV of any type?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 37 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
- a. What percentage of a drug is eliminated after 4 half-lives? Please round to the nearest percent. b. What will happen to elimination of the drug in the previous question if the system is saturated? explain and show any math involvedarrow_forwardIf you wanted to reduce the difference between peak and trough levels that occur with repeated administration of a drug, how would you adjust the dose and dose interval without changing the plateau concentration (plateau is the average of peak and trough levels)? Select your answers for both dose and interval. Hint: It may be helpful to think about this problem using an example such as food. How would you eat if you wanted to maintain very steady hunger/satiety levels without changing your total caloric intake? Options: A. Dose; Increase dose B. Dose; Decrease dose C. Dose; Do not change dose D. Interval; Increase the interval between doses (give the drug less frequently) E. Interval; Decrease the interval between doses (give the drug more frequently) F. Interval; Do not change the intervalarrow_forwardWhat percentage of a drug is eliminated after 4 half-lives? Please round to the nearest percent. Show the matharrow_forward
- Briefly explain the 6 domain of interprofessional collaboration: Role clarification, Team functioning, Interprofessional communication, Patient/client/family/community-centered care, Interprofessional conflict resolution, Collaborative leadership. Provide a specific negative events that nursing student would observe in a clinical setting for each domain.arrow_forwardwhat is an intermittent water course and what kind of fish habitat it would providearrow_forwardwhy are native freshwater mussels are an important part of great lakes ecosystemarrow_forward
- what morphological features differentiate the lamprey species and other species in the great lakesarrow_forwardThere are a wide range of therapeutic applications available as options for patients. Medical professionals should be aware of these applications so they can make informed recommendations to patients. To gain a better understanding of some therapeutic applications and how they are related to RNA and mRNA, research long non-coding RNA. Respond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: What is lncRNA and what does it do? How does IncRNA differ from mRNA? What are some therapeutic applications associated with lncRNA? Think about possible future uses of this application. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this application and its continued use?arrow_forwardfour fish or mussel species that are native to the great lakesarrow_forward
- There are a wide range of therapeutic applications available as options for patients. Medical professionals should be aware of these applications so they can make informed recommendations to patients. To gain a better understanding of some therapeutic applications and how they are related to RNA and mRNA, research long non-coding RNA. Respond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: What is lncRNA and what does it do? How does IncRNA differ from mRNA? What are some therapeutic applications associated with lncRNA? Think about possible future uses of this application. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this application and its continued use?arrow_forwardfour physial characteristics of a fish or a mussel that would help you identify it to a speciesarrow_forwarddescribe what you would do in this situation, you are working ona. river and it will take 20 minutes by boat to get back to the field truck, you are 1 hour from finishing the field work on the last day of field trip. you hear thunder int he dsitnace, what did you do?arrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning





