
Engineering Mechanics: Statics and Modified Mastering Engineering with eText and Access Card (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780134229287
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.4, Problem 63P
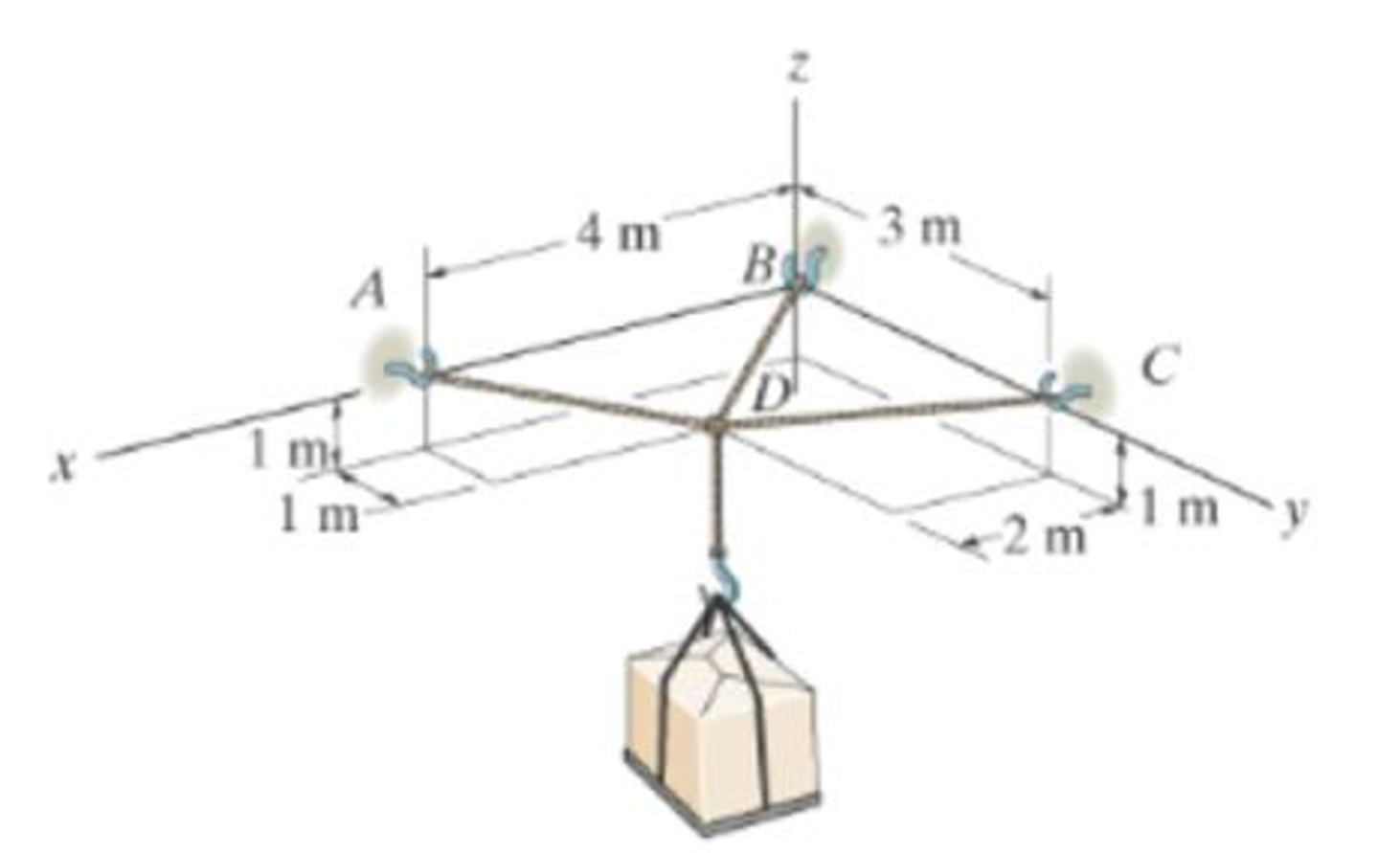
Determine the tension developed in each cable for equilibrium.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule12:46
Students have asked these similar questions
Please draw the front top and side view for the following object
Draw the top view
Suppose that a steel of eutectoid composition is cooled to 675°C (1250°F) from 760°C (1400°F)
in less than 0.5 s and held at this temperature.
(a) How long will it take for the austenite-topearlite reaction to go to 50% completion? To 100%
completion?
(b) Estimate the hardness of the alloy that has completely transformed to pearlite.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics and Modified Mastering Engineering with eText and Access Card (14th Edition)
Ch. 3.3 - In each case, draw a free-body diagram of the ring...Ch. 3.3 - Do not solve.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the force in each supporting cable.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the shortest cable ABC that can be used...Ch. 3.3 - Neglect the size of the pulley.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the unstretched length of the spring.Ch. 3.3 - If the mass of cylinder C is 40 kg, determine the...Ch. 3.3 - Also, find the angle .Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitudes of F1 and F2 for...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitude of F1 and its angle for...
Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of F so...Ch. 3.3 - The bottom one is subjected to a 125-N force at...Ch. 3.3 - If the forces are concurrent at point O, determine...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the tension force in member C and its...Ch. 3.3 - If the tension in AB is 60 lb, determine the...Ch. 3.3 - The cords ABC and BD can each support a maximum...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the maximum force F that can be...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the angle for equilibrium and the force...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 11PCh. 3.3 - Determine the force in each of the cables AB and...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 13PCh. 3.3 - The springs are shown in the equilibrium position.Ch. 3.3 - If the block is held in the equilibrium position...Ch. 3.3 - Note that s = 0 when the cylinders are removed.Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 17PCh. 3.3 - determine the stiffness of the spring to hold the...Ch. 3.3 - Take k = 180 N/m.Ch. 3.3 - If the spring has an unstretched length of 2 ft,...Ch. 3.3 - Cord AB is 2 ft long. Take k = 50 lb/ft.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the horizontal force F applied to the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the displacement d of the cord from the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the distances x and y for equilibrium if...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitude of F1 and the distance y...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the force in each cord for equilibrium.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the largest mass of pipe that can be...Ch. 3.3 - If each light has a weight of 50 lb. determine the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the tension developed in each cord...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the maximum mass of the lamp that the...Ch. 3.3 - If x = 2 m determine the force F and the sag s for...Ch. 3.3 - If F = 80 N. determine the sag s and distance x...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the tension in each cord and the angle ...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the largest weight of the lamp that can...Ch. 3.3 - Also, what is the force in cord AB? Hint: use the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the position x and the tension developed...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 37PCh. 3.3 - Take F = 300 N and d = 1 m.Ch. 3.3 - If a force of F = 100 N is applied horizontally to...Ch. 3.3 - If the cable can be attached at either points A...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the position x and the tension in the...Ch. 3.3 - The cord is fixed to a pin at A and passes over...Ch. 3.3 - Establish appropriate dimensions and use an...Ch. 3.3 - If the maximum tension that can be supported by...Ch. 3.3 - If the angle between AB and BC is 30, determine...Ch. 3.3 - If the distance BC is 1.5 m, and AB can support a...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the magnitude of forces F1, F2, F3, so...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in cables AB, AC,...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in cables AB, AC,...Ch. 3.4 - F310. Determine the tension developed in cables...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension in these wires.Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force developed in each cable for...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the magnitudes of F1, F2, and F3 for...Ch. 3.4 - If the bucket and its contents have a total weight...Ch. 3.4 - Each spring has on unstretched length of 2 m and a...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each cable needed to...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension in the cables in order to...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the maximum mass of the crate so that...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each cable if F = 500 lb.Ch. 3.4 - Determine the greatest force F that can be applied...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tens on developed in cables AB and...Ch. 3.4 - Also, what is the force developed along strut AD?Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in each cable for...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the maximum weight of the crate that can...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 56PCh. 3.4 - If each cord can sustain a maximum tension of 50 N...Ch. 3.4 - which has a mass of 15 kg. Take h = 4 m.Ch. 3.4 - Take h = 3.5 m.Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each chain for equilibrium....Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension in each cable for...Ch. 3.4 - If the maximum force in each rod con not exceed...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in each cable for...Ch. 3.4 - If cable AD is tightened by a turnbuckle and...Ch. 3.4 - If cable AD is tightened by a turnbuckle and...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in cables AB, AC,...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the maximum weight of the crate so that...Ch. 3.4 - If the bolt exerts a force of 50 lb on the pipe in...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 2RPCh. 3.4 - Determine the maximum weight of the flowerpot that...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the magnitude of the applied vertical...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 5RPCh. 3.4 - Determine the magnitudes of F1, F2, and F3 for...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each cable needed to...Ch. 3.4 - If cable AB is subjected to a tension of 700 N,...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
This project requires that you complete Programming Project 7 from this chapter and Programming Project 8 from ...
Problem Solving with C++ (10th Edition)
You can use a lambda expression to instantiate an object that __________. a. that has no constructor. b. extend...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
What is the difference between operating system software and application software?
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Average Number of Letters Modify the program you wrote for Programming Challenge 3 (Word Counter), so it also d...
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
In Exercises 39 through 44, write a program to carry out the stated task. Cost of Electricity The cost of the e...
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 2: Determine the components of the reaction at point B (Please use paper sheet + FBD ,don't use chatgpt) MECHANICAL ENGGarrow_forwardARL040_AE_Kn_2of3... Dor Question 4. A two-throw crankshaft has masses distributed as shown: RAH 90 rpm A TRAV B Re Rev M₁ = 15kg; M₂ = 12kg L = 950mm; 1, 350mm; 1₁ = 600mm; 0₁ = 90°; 02=0°; r₁ = 300mm; r250mm The crankshaft is to be balanced by attaching masses at radii of 300 mm and rotating in planes 150 mm outside the planes of number one and number two cranks. Determine the magnitude and angular position of the balance masses. Answer 4.arrow_forwardFEAarrow_forward
- Finite Element Analysisarrow_forwardan experimental research station is constructed on a concrete slab floor. The heat loss from the floor slab is significant, given the cold environment, and is measured to be 5 kW. The edges of the floor slab are insulated with a 60 mm thickness of cellular glass insulation. The width of this insulation at the floor slab is 0.9 m. To avoid excessive fuel consumption, the station air temperature is maintained at a slightly cool temperature of 18ºC. The station is constructed in a square shape, to keep the surface area to volume ratio low; the horizontal dimensions of the floor of the station are 20 m by 20 m. The number of occupants in the research station varies between 5 and 20, depending on the research workload.a) Determine the design outdoor temperature that was used in designing the research station.b) If the floor dimensions of the station are changed to 15 m by 25 m, would the design outdoor temperature that was used in designing the research station from part (a) change? If so,…arrow_forwardFinite element analysisarrow_forward
- a station is constructed on a concrete slab floor. The heat loss from the floor slab is significant, given the cold environment, and is measured to be 5 kW. The edges of the floor slab are insulated with a 60 mm thickness of cellular glass insulation. The width of this insulation at the floor slab is 0.9 m. To avoid excessive fuel consumption, the station air temperature is maintained at a slightly cool temperature of 18ºC. The station is constructed in a square shape, to keep the surface area to volume ratio low; the horizontal dimensions of the floor of the station are 20 m by 20 m. The number of occupants in the research station varies between 5 and 20, depending on the research workload.a) Determine the design outdoor temperature that was used in designing the research station.b) If the floor dimensions of the station are changed to 15 m by 25 m, would the design outdoor temperature that was used in designing the research station from part (a) change? If so, what would it be?…arrow_forwardFinite Element Analysisarrow_forwardFinite Element Analysisarrow_forward
- A small auditorium that can accommodate 30 people allows smoking. The design engineers of the auditorium assume that the smokers each are responsible for an average of 50 micrograms per minute of tobacco smoke being added to the auditorium space. The volumetric flow rate of recirculated room air is 200 cfm. Outdoor air is also supplied, and is mixed with the recirculated room air. The system has a ventilation effectiveness of 80%. In an effort to maintain the level of particulate matter from the tobacco smoke in the auditorium to no more than 5.5 micrograms per cubic foot, filters with an effective efficiency of 90% are added to the ventilation system downstream of the point in the system where outdoor air and recirculated room air are mixed. a) What is the necessary volumetric flow rate (in cfm) for the supply outdoor air? Assume the outdoor air is clean. b) The outdoor air taken into the system becomes contaminated with tobacco smoke due to a leak in an adjacent building’s…arrow_forwardroom to be maintained with a dry-bulb temperature of 72ºF and 30% relative humidity. The room has a sensible heat factor of 0.8 and a total hourly heating load of 200,000 Btu. A flow rate of 1000 cfm of outdoor air (at 20% relative humidity and a dry-bulb temperature of 40ºF) is used. In order to maintain adequate comfort, the supply air to the room is set to a dry-bulb temperature of 120ºF. To humidify the air, steam with a specific enthalpy of 1150 Btu per pound is utilized.Determine the wet bulb temperature, specific enthalpy, and volumetric flow rate of the supply air to the room. Evaluate the increase in dry-bulb temperature as the air is sensibly heated, and the mass flow rate (in lb/hr) of steam required during the latent heating of the air. Calculate the heat added to the room during sensible heating (i.e., excluding humidification).arrow_forwardPlease can you help with the attached question? Many thanksarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Engineering Basics - Statics & Forces in Equilibrium; Author: Solid Solutions - Professional Design Solutions;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQBvQ2hJZFg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY