
Engineering Mechanics: Statics and Modified Mastering Engineering with eText and Access Card (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780134229287
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.4, Problem 8FP
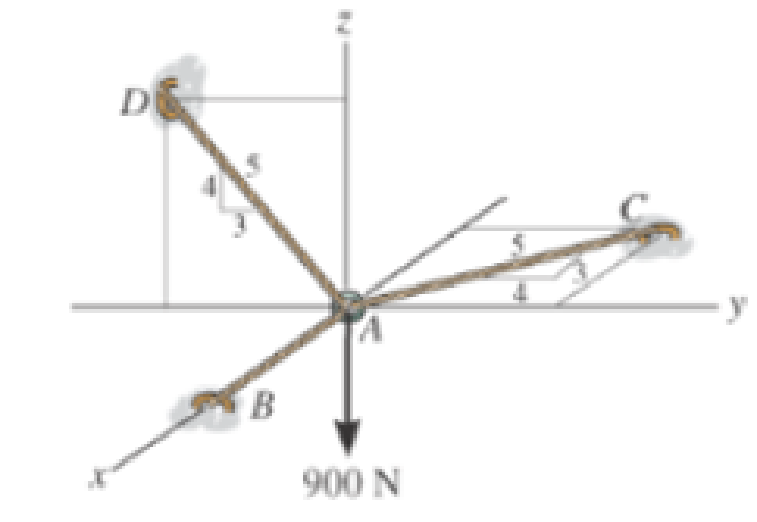
Determine the tension developed in cables AB, AC, and AD.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule05:56
Students have asked these similar questions
4. Determine which of the following flow fields represent a possible
incompressible flow?
(a) u= x²+2y+z; v=x-2y+z;w= -2xy + y² + 2z
a
(b) V=U cose
U coso 1 (9)
[1-9]
Usino |1 (4)]
[+]
V=-Usin 1+1
3. Determine the flow rate through the pipe line show in the figure in ft³/s,
and determine the pressures at A and C, in psi.
5'
B
C
12°
20'
D
6"d
2nd-
Water
A
5. A flow is field given by V = x²₁³+xy, and determine
3
·y³j-
(a) Whether this is a one, two- or three-dimensional flow
(b) Whether it is a possible incompressible flow
(c) Determine the acceleration of a fluid particle at the location (X,Y,Z)=(1,2,3)
(d) Whether the flow is rotational or irrotational flow?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics and Modified Mastering Engineering with eText and Access Card (14th Edition)
Ch. 3.3 - In each case, draw a free-body diagram of the ring...Ch. 3.3 - Do not solve.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the force in each supporting cable.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the shortest cable ABC that can be used...Ch. 3.3 - Neglect the size of the pulley.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the unstretched length of the spring.Ch. 3.3 - If the mass of cylinder C is 40 kg, determine the...Ch. 3.3 - Also, find the angle .Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitudes of F1 and F2 for...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitude of F1 and its angle for...
Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitude and direction of F so...Ch. 3.3 - The bottom one is subjected to a 125-N force at...Ch. 3.3 - If the forces are concurrent at point O, determine...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the tension force in member C and its...Ch. 3.3 - If the tension in AB is 60 lb, determine the...Ch. 3.3 - The cords ABC and BD can each support a maximum...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the maximum force F that can be...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the angle for equilibrium and the force...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 11PCh. 3.3 - Determine the force in each of the cables AB and...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 13PCh. 3.3 - The springs are shown in the equilibrium position.Ch. 3.3 - If the block is held in the equilibrium position...Ch. 3.3 - Note that s = 0 when the cylinders are removed.Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 17PCh. 3.3 - determine the stiffness of the spring to hold the...Ch. 3.3 - Take k = 180 N/m.Ch. 3.3 - If the spring has an unstretched length of 2 ft,...Ch. 3.3 - Cord AB is 2 ft long. Take k = 50 lb/ft.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the horizontal force F applied to the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the displacement d of the cord from the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the distances x and y for equilibrium if...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitude of F1 and the distance y...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the force in each cord for equilibrium.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the largest mass of pipe that can be...Ch. 3.3 - If each light has a weight of 50 lb. determine the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the tension developed in each cord...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the maximum mass of the lamp that the...Ch. 3.3 - If x = 2 m determine the force F and the sag s for...Ch. 3.3 - If F = 80 N. determine the sag s and distance x...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the tension in each cord and the angle ...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the largest weight of the lamp that can...Ch. 3.3 - Also, what is the force in cord AB? Hint: use the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the position x and the tension developed...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 37PCh. 3.3 - Take F = 300 N and d = 1 m.Ch. 3.3 - If a force of F = 100 N is applied horizontally to...Ch. 3.3 - If the cable can be attached at either points A...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the position x and the tension in the...Ch. 3.3 - The cord is fixed to a pin at A and passes over...Ch. 3.3 - Establish appropriate dimensions and use an...Ch. 3.3 - If the maximum tension that can be supported by...Ch. 3.3 - If the angle between AB and BC is 30, determine...Ch. 3.3 - If the distance BC is 1.5 m, and AB can support a...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the magnitude of forces F1, F2, F3, so...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in cables AB, AC,...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in cables AB, AC,...Ch. 3.4 - F310. Determine the tension developed in cables...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension in these wires.Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force developed in each cable for...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the magnitudes of F1, F2, and F3 for...Ch. 3.4 - If the bucket and its contents have a total weight...Ch. 3.4 - Each spring has on unstretched length of 2 m and a...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each cable needed to...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension in the cables in order to...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the maximum mass of the crate so that...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each cable if F = 500 lb.Ch. 3.4 - Determine the greatest force F that can be applied...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tens on developed in cables AB and...Ch. 3.4 - Also, what is the force developed along strut AD?Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in each cable for...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the maximum weight of the crate that can...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 56PCh. 3.4 - If each cord can sustain a maximum tension of 50 N...Ch. 3.4 - which has a mass of 15 kg. Take h = 4 m.Ch. 3.4 - Take h = 3.5 m.Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each chain for equilibrium....Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension in each cable for...Ch. 3.4 - If the maximum force in each rod con not exceed...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in each cable for...Ch. 3.4 - If cable AD is tightened by a turnbuckle and...Ch. 3.4 - If cable AD is tightened by a turnbuckle and...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in cables AB, AC,...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the maximum weight of the crate so that...Ch. 3.4 - If the bolt exerts a force of 50 lb on the pipe in...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 2RPCh. 3.4 - Determine the maximum weight of the flowerpot that...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the magnitude of the applied vertical...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 5RPCh. 3.4 - Determine the magnitudes of F1, F2, and F3 for...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each cable needed to...Ch. 3.4 - If cable AB is subjected to a tension of 700 N,...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The following code creates a small phone book. An array is used to store a list of names and another array is u...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Modify the Product_T table by adding an attribute QtyOnHand that can be used to track the finished goods invent...
Modern Database Management
What is the importance of modeling in engineering? How are the mathematical models for engineering processes pr...
HEAT+MASS TRANSFER:FUND.+APPL.
When displaying a Java applet, the browser invokes the _____ to interpret the bytecode into the appropriate mac...
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
Look at the following pseudocode statement: Input temperature What happens when this statement executes?
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
public class MyClassT { public static void displayValue(T value) { System.out.println(value); } }
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwarddraw the pneumatic circuit to operate a double-acting cylinder with: 1. Extension: Any of two manual conditions plus cylinder fully retracted, → Extension has both meter-in and meter-out, 2. Retraction: one manual conditions plus cylinder fully extended, → Retraction is very fast using quick exhaust valve.arrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you. Expert solution plsarrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only with fbd. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Engineering Basics - Statics & Forces in Equilibrium; Author: Solid Solutions - Professional Design Solutions;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQBvQ2hJZFg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY