
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781118807330
Author: James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.4, Problem 63P
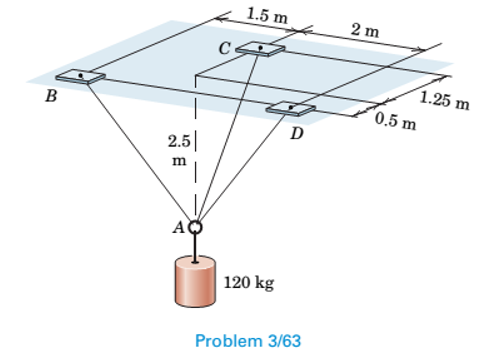
Determine the tensions in cables AB, AC, and AD.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question.
I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor.
No AI-generated responses, please.
Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question.
I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor.
No AI-generated responses, please.
Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question.
I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor.
No AI-generated responses, please.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Ch. 3.3 - In the side view of a 50-lb flat-screen television...Ch. 3.3 - The mass center G of the 1400-kg rear-engine car...Ch. 3.3 - A carpenter carries a 12-lb 2-in. by 4-in. board...Ch. 3.3 - The 450-kg uniform I-beam supports the load shown....Ch. 3.3 - Determine the force P required to maintain the...Ch. 3.3 - The 20-kg homogeneous smooth sphere rests on the...Ch. 3.3 - The 600-lb drum is being hoisted by the lifting...Ch. 3.3 - If the screw B of the wood clamp is tightened so...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the reactions at A and E if P=500 N....Ch. 3.3 - What horizontal force P must a worker exert on the...
Ch. 3.3 - The 20-kg uniform rectangular plate is supported...Ch. 3.3 - The 500-kg uniform beam is subjected to the three...Ch. 3.3 - A former student of mechanics wishes to weigh...Ch. 3.3 - The uniform rectangular body of mass m is placed...Ch. 3.3 - What weight WB will cause the system to be in...Ch. 3.3 - The pair of hooks is designed for the hanging of...Ch. 3.3 - The winch takes in cable at the constant rate of...Ch. 3.3 - To accommodate the rise and fall of the tide, a...Ch. 3.3 - When the 0.05-kg body is in the position shown,...Ch. 3.3 - When the 0.05-kg body is in the position shown,...Ch. 3.3 - When on level ground, the car is placed on four...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitude P of the force required to...Ch. 3.3 - The 180-lb exerciser is beginning to execute some...Ch. 3.3 - Three cables are joined at the junction ring C...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the moment M which the motor must exert...Ch. 3.3 - A bicyclist applies a 40-N force to the brake...Ch. 3.3 - Find the angle of tilt with the horizontal so...Ch. 3.3 - The rack has a mass m=75kg. What moment M must be...Ch. 3.3 - The elements of a wheel-height adjuster for a lawn...Ch. 3.3 - The right-angle uniform slender bar AOB has mass...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the minimum cylinder mass m1 required to...Ch. 3.3 - Cable AB passes over the small ideal pulley C...Ch. 3.3 - A pipe P is being bent by the pipe bender as...Ch. 3.3 - The small slider A is moved along the circular...Ch. 3.3 - The asymmetric simple truss is loaded as shown....Ch. 3.3 - The tailgate OBC is attached to the rear of a...Ch. 3.3 - The indicated location of the center of gravity of...Ch. 3.3 - A uniform ring of mass m and radius r carries an...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the force T required to hold the uniform...Ch. 3.3 - A block placed under the head of the claw hammer...Ch. 3.3 - The uniform slender bar of length 2r and mass m...Ch. 3.3 - The chain binder is used to secure loads of logs,...Ch. 3.3 - In a procedure to evaluate the strength of the...Ch. 3.3 - A woman is holding a 3.6-kg sphere in her hand...Ch. 3.3 - A person is performing slow arm curls with a 10-kg...Ch. 3.3 - The exercise machine is designed with a...Ch. 3.3 - For a given value m1 for the cart mass, determine...Ch. 3.3 - The device shown is used to test automobile-engine...Ch. 3.3 - The portable floor crane in the automotive shop is...Ch. 3.3 - The torsional spring of constant kT=50Nm/rad is...Ch. 3.3 - A torque (moment) of 24Nm is required to turn the...Ch. 3.3 - During an engine test on the ground, a propeller...Ch. 3.3 - To test the deflection of the uniform 200-lb beam...Ch. 3.3 - The pin A, which connects the 200-kg steel beam...Ch. 3.3 - A portion of the shifter mechanism for a manual...Ch. 3.3 - The cargo door for an airplane of circular...Ch. 3.3 - It is desired that a person be able to begin...Ch. 3.3 - Certain elements of an in-refrigerator ice-cube...Ch. 3.3 - The lumbar portion of the human spine supports the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine and plot the moment M which much be...Ch. 3.4 - A uniform steel plate 18 in. square weighing 68 lb...Ch. 3.4 - The uniform I-beam has a mass of 60 kg per meter...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tensions in cables AB, AC, and AD.Ch. 3.4 - An 80-lb sheet of plywood rests on two small...Ch. 3.4 - The vertical and horizontal poles at the...Ch. 3.4 - The body is constructed of uniform slender rod...Ch. 3.4 - In order to make an adjustment, engineering...Ch. 3.4 - The rectangular solid is loaded by a force which...Ch. 3.4 - When on level ground, the car is placed on four...Ch. 3.4 - The uniform rectangular plate of mass m is...Ch. 3.4 - A uniform right-circular cylinder of mass m is...Ch. 3.4 - The uniform square plate is suspended by three...Ch. 3.4 - A three-legged stool is subjected to the load L as...Ch. 3.4 - The uniform slender rod of mass m is suspended by...Ch. 3.4 - One of the vertical walls supporting end B of the...Ch. 3.4 - The light right-angle boom which supports the...Ch. 3.4 - The mass center of the 30-kg door is in the center...Ch. 3.4 - The two I-beams are welded together and are...Ch. 3.4 - The 50-kg uniform triangular plate is supported by...Ch. 3.4 - The large bracket is constructed of heavy plate...Ch. 3.4 - The 800-lb tree trunk is known to have insect...Ch. 3.4 - The smooth homogeneous sphere rests in the 120...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the magnitudes of the force R and couple...Ch. 3.4 - The 25-kg rectangular access door is held in the...Ch. 3.4 - As part of a check on its design, a lower A-arm...Ch. 3.4 - The shaft, lever, and handle are welded together...Ch. 3.4 - During a test, the left engine of the twin-engine...Ch. 3.4 - The bent rod ACDB is supported by a sleeve at A...Ch. 3.4 - Turnbuckle T1 is tightened to a tension of 750 N...Ch. 3.4 - The spring of modulus k=900N/m is stretched a...Ch. 3.4 - A homogeneous door of mass m, height h, and width...Ch. 3.4 - Consider the rudder assembly of a radio-controlled...Ch. 3.4 - The upper ends of the vertical coil springs in the...Ch. 3.4 - The uniform 30- by 40-in. trap door weighs 200 lb...Ch. 3.4 - A uniform bar of length b and mass m is suspended...Ch. 3.4 - A rectangular sign over a store has a mass of 100...Ch. 3.4 - The uniform rectangular panel ABCD has a mass of...Ch. 3.4 - Determine and plot the moment M required to rotate...Ch. 3.5 - The rack for storing automobile wheels consists of...Ch. 3.5 - The positioning device locks the sliding panel C...Ch. 3.5 - The light bracket ABC is freely hinged at A and is...Ch. 3.5 - The uniform bar with end rollers weighs 60 lb and...Ch. 3.5 - The mass of the uniform right-triangular tabletop...Ch. 3.5 - The device shown in the figure is useful for...Ch. 3.5 - Magnetic tape under a tension of 10 N at D passes...Ch. 3.5 - The tool shown is used for straightening twisted...Ch. 3.5 - A freeway sign measuring 12 ft by 6 ft is...Ch. 3.5 - A slender rod of mass m1 is welded to the...Ch. 3.5 - The curved arm BC and attached cables AB and AC...Ch. 3.5 - The device shown in section can support the load L...Ch. 3.5 - A large symmetrical drum for drying sand is...Ch. 3.5 - Determine the force P required to begin rolling...Ch. 3.5 - The small tripod like stepladder is useful for...Ch. 3.5 - Each of the three uniform 1200-mm bars has a mass...Ch. 3.5 - The uniform 15-kg plate is welded to the vertical...Ch. 3.5 - A vertical force P on the foot pedal of the bell...Ch. 3.5 - The drum and shaft are welded together and have a...Ch. 3.5 - Determine and plot the tension ratio Timg required...Ch. 3.5 - Two traffic signals are attached to the 36-ft...Ch. 3.5 - The two traffic signals of Prob. 3/119 are now...Ch. 3.5 - In executing the biceps-curl exercise, the man...Ch. 3.5 - All the conditions of Prob. 3/121 are repeated...Ch. 3.5 - The basic features of a small backhoe are shown in...Ch. 3.5 - The mass center of the 1.5-kg link OC is located...Ch. 3.5 - The system of Prob. 3/60 is repeated here, but now...Ch. 3.5 - The 125-kg homogeneous rectangular solid is held...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Explain how each of the following types of integrity constraints is enforced in the SQL CREATE TABLE commands: ...
Modern Database Management
Write a definition of a method isEmpty for the class StringLinkedList that returns true if the list is empty, t...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
For the circuit shown, use the node-voltage method to find v1, v2, and i1.
How much power is delivered to the c...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
ICA 8-20
A eutectic alloy of two metals contains the specific percentage of each metal that gives the lowest po...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
What does the following program print? 1. // Exercise 4.16: Mystery.java 2. public class Mystery { 3. public st...
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- [Q2]: The cost information supplied by the cost accountant is as follows:Sales 20,00 units, $ 10 per unitCalculate the (a/ newsale guantity and (b) new selling price to earn the sameVariable cost $ 6 per unit, Fixed Cost $ 30,000, Profit $ 50,000profit ifi) Variable cost increases by $ 2 per unitil) Fixed cost increase by $ 10,000Ili) Variable cost increase by $ 1 per unit and fixed cost reduces by $ 10,000arrow_forwardcan you please help me perform Visual Inspection and Fractography of the attatched image: Preliminary examination to identify the fracture origin, suspected fatigue striation, and corrosion evidences.arrow_forwardcan you please help[ me conduct Causal Analysis (FTA) on the scenario attatched: FTA diagram which is a fault tree analysis diagram will be used to gain an overview of the entire path of failure from root cause to the top event (i.e., the swing’s detachment) and to identify interactions between misuse, material decay and inspection errors.arrow_forward
- hi can you please help me in finding the stress intensity factor using a k-calcluator for the scenario attathced in the images.arrow_forwardHi, can you please help me .Identify and justify suitable analytical techniques of the scenario below, bearing in mind the kinds of information being handled to reach a conclusion (methodology). A child swing set was discovered to have failed at the fixing at the top of the chains connecting the seat to the top of the swing set. A 12 mm threaded steel bolt, connecting the shackle to the top beam, failed at the start of the threaded region on the linkage closest to the outside side of the swing set . The linkage and bolts were made of electro galvanised mild steel . The rigid bar chain alternatives and fixings were of the same material and appeared to be fitted in accordance with guidelines. The yield strength of the steel used is 260 MPa and the UTS is 380 MPa. The bolt that failed was threaded using a standard thread with a pitch (distance between threads) of 1.75 mm and a depth of approximately 1.1 mm. The swing set in question had been assigned to ‘toddlers’ with the application of…arrow_forwardHi, can you please define and calculate the failure mode of the linkage that failed on the swing (images added) : A child swing set was discovered to have failed at the fixing at the top of the chains connecting the seat to the top of the swing set. A 12 mm threaded steel bolt, connecting the shackle to the top beam, failed at the start of the threaded region on the linkage closest to the outside side of the swing set . The linkage and bolts were made of electro galvanised mild steel . The rigid bar chain alternatives and fixings were of the same material and appeared to be fitted in accordance with guidelines. The yield strength of the steel used is 260 MPa and the UTS is 380 MPa. The bolt that failed was threaded using a standard thread with a pitch (distance between threads) of 1.75 mm and a depth of approximately 1.1 mm. The swing set in question had been assigned to ‘toddlers’ with the application of a caged-type seat. However, the location was within the play area not…arrow_forward
- Page 11-68. The rectangular plate shown is subjected to a uniaxial stress of 2000 psi. Compute the shear stress and the tensile developed on a plane forming an angle of 30° with the longitud axis of the member. (Hint: Assume a cross-sectional area of unity) 2000 psi 2000 psi hparrow_forward11-70. A shear stress (pure shear) of 5000 psi exists on an element. (a) Determine the maximum tensile and compressive stresses caused in the element due to this shear. (b) Sketch the element showing the planes on which the maximum tensile and compressive stresses act.arrow_forward11-20. An aluminum specimen of circular cross section, 0.50 in. in diameter, ruptured under a tensile load of 12,000 lb. The plane of failure was found to be at 48° with a plane perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the specimen. (a) Compute the shear stress on the failure plane. (b) Compute the maximum tensile stress. (c) Compute the tensile stress on the failure plane. hparrow_forward
- A long flat steel bar 13 mm thick and 120 mm wide has semicircular grooves as shown and carries a tensile load of 50 kN Determine the maximum stress if plate r= 8mm r=21mm r=38mmarrow_forwardProblem 13: F₁ = A =250 N 30% Determine the moment of each of the three forces about point B. F₂ = 300 N 60° 2 m -3 m B 4 m F3=500 Narrow_forward3 kN 3 kN 1.8 kN/m 80 mm B 300 mm D an 1.5 m-1.5 m--1.5 m- PROBLEM 5.47 Using the method of Sec. 5.2, solve Prob. 5.16 PROBLEM 5.16 For the beam and loading shown, determine the maximum normal stress due to bending on a transverse section at C.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Engineering Basics - Statics & Forces in Equilibrium; Author: Solid Solutions - Professional Design Solutions;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQBvQ2hJZFg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY