
Finite Mathematics & Its Applications (12th Edition)
12th Edition
ISBN: 9780134437767
Author: Larry J. Goldstein, David I. Schneider, Martha J. Siegel, Steven Hair
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.3, Problem 21E
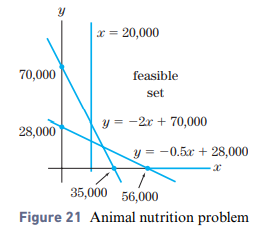
Nutrition—-Dairy Cows Refer to Exercises 3.2, Problem 13. How many pounds of each food should be purchased in order to meet the nutritional requirements at the least cost? (See the graph of the feasible set in Fig. 21.)
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
12:25 AM Sun Dec 22
uestion 6- Week 8: QuX
Assume that a company X +
→ C
ezto.mheducation.com
Week 8: Quiz i
Saved
6
4
points
Help
Save & Exit
Submit
Assume that a company is considering purchasing a machine for $50,000 that will have a five-year useful life and a $5,000 salvage value. The
machine will lower operating costs by $17,000 per year. The company's required rate of return is 15%. The net present value of this investment
is closest to:
Click here to view Exhibit 12B-1 and Exhibit 12B-2, to determine the appropriate discount factor(s) using the tables provided.
00:33:45
Multiple Choice
О
$6,984.
$11,859.
$22,919.
○ $9,469,
Mc
Graw
Hill
2
100-
No chatgpt pls will upvote
7. [10 marks]
Let G
=
(V,E) be a 3-connected graph. We prove that for every x, y, z Є V, there is a
cycle in G on which x, y, and z all lie.
(a) First prove that there are two internally disjoint xy-paths Po and P₁.
(b) If z is on either Po or P₁, then combining Po and P₁ produces a cycle on which
x, y, and z all lie. So assume that z is not on Po and not on P₁. Now prove that
there are three paths Qo, Q1, and Q2 such that:
⚫each Qi starts at z;
• each Qi ends at a vertex w; that is on Po or on P₁, where wo, w₁, and w₂ are
distinct;
the paths Qo, Q1, Q2 are disjoint from each other (except at the start vertex
2) and are disjoint from the paths Po and P₁ (except at the end vertices wo,
W1, and w₂).
(c) Use paths Po, P₁, Qo, Q1, and Q2 to prove that there is a cycle on which x, y, and
z all lie. (To do this, notice that two of the w; must be on the same Pj.)
Chapter 3 Solutions
Finite Mathematics & Its Applications (12th Edition)
Ch. 3.1 - Graph the inequality 3xy3.Ch. 3.1 - Graph the feasible set for the system of...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 1-4, state whether the inequality is...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 1-4, state whether the inequality is...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 1-4, state whether the inequality is...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 1-4, state whether the inequality is...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 5-7, solve for x, 2x53Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 6ECh. 3.1 - In Exercises 5-7, solve for x,
7.
Ch. 3.1 - Which of the following results from solving x+13...
Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 9ECh. 3.1 - In Exercises 9-14, write the linear inequality in...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 9-14, write the linear inequality in...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 9-14, write the linear inequality in...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 9-14, write the linear inequality in...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 9-14, write the linear inequality in...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 15-22, determine whether or not the...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 15-22, determine whether or not the...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 15-22, determine whether or not the...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 15-22, determine whether or not the...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 15-22, determine whether or not the...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 15-22, determine whether or not the...Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 21ECh. 3.1 - Prob. 22ECh. 3.1 - In Exercises 23-26, graph the given inequality by...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 23-26, graph the given inequality by...Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 25ECh. 3.1 - In Exercises 23-26, graph the given inequality by...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 27-30, give the linear inequality...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 27-30, give the linear inequality...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 27-30, give the linear inequality...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 27-30, give the linear inequality...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 31-42, graph the given inequality....Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 31-42, graph the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 31-42, graph the given inequality. x2Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 31-42, graph the given inequality. x0Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 31-42, graph the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 31-42, graph the given inequality....Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 31-42, graph the given inequality....Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 31-42, graph the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 31-42, graph the given inequality....Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 31-42, graph the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 31-42, graph the given inequality....Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 31-42, graph the given inequality....Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 43-48, graph the feasible set for the...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 43-48, graph the feasible set for the...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 43-48, graph the feasible set for the...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 43-48, graph the feasible set for the...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 43-48, graph the feasible set for the...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 43-48, graph the feasible set for the...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 49-52, determine whether the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 49-52, determine whether the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 49-52, determine whether the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 49-52, determine whether the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 52-56, determine whether the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 52-56, determine whether the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 52-56, determine whether the given...Ch. 3.1 - In Exercises 52-56, determine whether the given...Ch. 3.1 - Give a system of inequalities for which the graph...Ch. 3.1 - The shaded region in Fig. 9 is bounded by four...Ch. 3.1 - The shaded region in Fig. 10 is bounded by four...Ch. 3.1 - Which quadrant if Fig. 11 contains no points that...Ch. 3.1 - Graph the line 4x2y=7. (a) Locate the point on the...Ch. 3.1 - 62. Graph the line
(a) Locate the point on the...Ch. 3.1 - Display the feasible set in Exercise 47.Ch. 3.1 - Display the feasible set in Exercise 48.Ch. 3.2 - 1. Determine whether the following points are in...Ch. 3.2 - A physical fitness enthusiast decides to devote...Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 1ECh. 3.2 - Prob. 2ECh. 3.2 - In Exercises 14, determine whether the given point...Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 4ECh. 3.2 - Manufacturing Consider the furniture manufacturing...Ch. 3.2 - 6. Manufacturing Consider the furniture...Ch. 3.2 - Packaging Joes Confectionary puts together two...Ch. 3.2 - Nutrition-Animal Mr. Holloway decides to feed his...Ch. 3.2 - Shipping A truck traveling from New York to...Ch. 3.2 - 10. Mining A coal company owns mines in two...Ch. 3.2 - 11. Exam Strategy A student is taking an exam...Ch. 3.2 - 12. Political Campaign—Resource Allocation A local...Ch. 3.2 - Nutrition-Dairy Cows A dairy farmer concludes that...Ch. 3.2 - Manufacturing-Resource Allocation A clothing...Ch. 3.3 - The feasible set for the nutrition problem of...Ch. 3.3 - 2. Rework the nutrition problem, assuming that...Ch. 3.3 - For each of the feasible sets in Exercises 1–4,...Ch. 3.3 - For each of the feasible sets in Exercises 14,...Ch. 3.3 - For each of the feasible sets in Exercises 14,...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 4ECh. 3.3 - In Exercises 58, find the values of x and y that...Ch. 3.3 - In Exercises 58, find the values of x and y that...Ch. 3.3 - In Exercises 58, find the values of x and y that...Ch. 3.3 - In Exercises 5–8, find the values of x and y that...Ch. 3.3 - In Exercises 9–12, find the values of x and y that...Ch. 3.3 - In Exercises 9–12, find the values of x and y that...Ch. 3.3 - In Exercises 9–12, find the values of x and y that...Ch. 3.3 - In Exercises 9–12, find the values of x and y that...Ch. 3.3 - 13. Nutrition—People Consider the nutrition...Ch. 3.3 - 14. Nutrition—People Consider the nutrition...Ch. 3.3 - 15. Packaging Refer to Exercises 3.2, Problem 7....Ch. 3.3 - Nutrition-Animal Refer to Exercises 3.2, Problem...Ch. 3.3 - 17. Shipping Refer to Exercises 3.2, Problem 9....Ch. 3.3 - 18. Mining Refer to Exercises 3.2, Problem 10....Ch. 3.3 - Exam Strategy Refer to Exercises 3.2, Problem 11....Ch. 3.3 - Political Campaign-Resource Allocation Refer to...Ch. 3.3 - 21. Nutrition—Dairy Cows Refer to Exercises 3.2,...Ch. 3.3 - Manufacturing-Resource Allocation Refer to...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 23ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 24ECh. 3.3 - In Exercises 25–32, find the optimal value for the...Ch. 3.3 - In Exercises 25–32, find the optimal value for the...Ch. 3.3 - In Exercises 2532, find the optimal value for the...Ch. 3.3 - In Exercises 25–32, find the optimal value for the...Ch. 3.3 - In Exercises 25–32, find the optimal value for the...Ch. 3.3 - In Exercises 25–32, find the optimal value for the...Ch. 3.3 - In Exercises 2532, find the optimal value for the...Ch. 3.3 - In Exercises 25–32, find the optimal value for the...Ch. 3.3 - 33. Manufacturing—Resource Allocation Infotron,...Ch. 3.3 - 34. Manufacturing—Production Planning An...Ch. 3.3 - Agriculture-Crop Planning A farmer has 100 acres...Ch. 3.3 - 36. Manufacturing—Resource Allocation A company...Ch. 3.3 - 37. Manufacturing The E-JEM Company produces two...Ch. 3.3 - Refining A refinery has two smelters that extract...Ch. 3.3 - 39. Nutrition—People A nutritionist, working for...Ch. 3.3 - 40. Construction—Resource Allocation A contractor...Ch. 3.3 - 41. Packaging—Product Mix The Beautiful Day Fruit...Ch. 3.3 - 42. Manufacturing—Resource Allocation The Bluejay...Ch. 3.3 - Agriculture-Crop Planning Suppose that the farmer...Ch. 3.3 - 44. Nutrition Pavan wants to add a sliced carrot...Ch. 3.3 - Packaging A small candy shop makes a special Cupid...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 46ECh. 3.3 - 47. Packaging A bath shop sells two different gift...Ch. 3.3 - Packaging A florist offers two types of Thank You...Ch. 3.3 - Consider the following linear programming problem:...Ch. 3.3 - Consider the following linear programming problem:...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 51ECh. 3.3 - Use Excel or Wolfram| Alpha to solve Exercise 26.Ch. 3.4 - Problems 1–3 refer to Example 1. Translate the...Ch. 3.4 - Problems 13 refer to Example 1. Translate the...Ch. 3.4 - Problems 13 refer to Example 1. Translate the...Ch. 3.4 - A linear programming problem has objective...Ch. 3.4 - 1. Figure 10(a) shows the feasible set of the...Ch. 3.4 - Figure 10(b) shows the feasible set of the...Ch. 3.4 - Consider the feasible set in Fig. 11, where three...Ch. 3.4 - Consider the feasible set in Fig. 11, where three...Ch. 3.4 - Consider the feasible set in Fig. 11, where three...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 6ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 7ECh. 3.4 - Consider the feasible set in Fig. 12, where three...Ch. 3.4 - Consider the feasible set in Fig. 12, where three...Ch. 3.4 - Consider the feasible set in Fig. 12, where three...Ch. 3.4 - Consider the feasible set in Fig. 13. For what...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 12ECh. 3.4 - Nutrition-Animal Mr. Smith decides to feed his pet...Ch. 3.4 - Oil Production An oil company owns two refineries....Ch. 3.4 - Investment Planning Mr. Jones has $9000 to invest...Ch. 3.4 - Shipping-Product Mix A produce dealer in Florida...Ch. 3.4 - 17. Transportation—Shipping A foreign-car...Ch. 3.4 - Transportation-Shipping Consider the foreign-car...Ch. 3.4 - Manufacturing-Production Planning An oil refinery...Ch. 3.4 - 20. Manufacturing—Production Planning Suppose that...Ch. 3.4 - 21. Shipping—Resource Allocation A shipping...Ch. 3.4 - Shipping-Resource Allocation Suppose that the...Ch. 3.4 - 23. Transportation—Shipping A major coffee...Ch. 3.4 - Transportation-Shipping Consider the coffee...Ch. 3.4 - 25. Packaging—Product Mix A pet store sells three...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 26ECh. 3.4 - 27. Refer to Fig. 6. As the lines of constant...Ch. 3.4 - Figure 16 shows the feasible set for the nutrition...Ch. 3.4 - Consider the feasible set in Fig. 17(a). In...Ch. 3.4 - Consider the feasible set in Fig. 17(a). In...Ch. 3.4 - Consider the feasible set in Fig. 17(a). In...Ch. 3.4 - Consider the feasible set in Fig. 17(a). In...Ch. 3.4 - Consider the feasible set in Fig. 17(a). In...Ch. 3.4 - Consider the feasible set in Fig. 17(a). In...Ch. 3.4 - Consider the feasible set in Fig. 17(a). In...Ch. 3.4 - Consider the feasible set in Fig. 17(a). In...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 37ECh. 3 - State the inequality properties for addition,...Ch. 3 - What are the general forms of a linear inequality...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3FCCECh. 3 - 4. What is meant by the feasible set of a system...Ch. 3 - Prob. 5FCCECh. 3 - Prob. 6FCCECh. 3 - Prob. 7FCCECh. 3 - Prob. 8FCCECh. 3 - 9. Give a procedure for solving a linear...Ch. 3 - Prob. 1RECh. 3 - 2. Graph the linear inequality.
Ch. 3 - 3. Write the inequality whose graph is the...Ch. 3 - 4. Travel—Resource Allocation Terrapin Airlines...Ch. 3 - Nutrition-People A nutritionist is designing a new...Ch. 3 - Prob. 6RECh. 3 - Packaging-Product Mix A confectioner makes two...Ch. 3 - Prob. 8RECh. 3 - Packaging-Resource Allocation A computer company...Ch. 3 - Transportation-Shipping An appliance company has...Ch. 3 - Prob. 11RECh. 3 - Prob. 12RECh. 3 - Prob. 13RECh. 3 - Prob. 14RECh. 3 - Prob. 15RECh. 3 - Prob. 16RECh. 3 - When mathematicians are presented with a linear...Ch. 3 - When mathematicians are presented with a linear...Ch. 3 - When mathematicians are presented with a linear...Ch. 3 - When mathematicians are presented with a linear...Ch. 3 - When mathematicians are presented with a linear...Ch. 3 - When mathematicians are presented with a linear...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, subject and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 6. [10 marks] Let T be a tree with n ≥ 2 vertices and leaves. Let BL(T) denote the block graph of T. (a) How many vertices does BL(T) have? (b) How many edges does BL(T) have? Prove that your answers are correct.arrow_forward4. [10 marks] Find both a matching of maximum size and a vertex cover of minimum size in the following bipartite graph. Prove that your answer is correct. ย ພarrow_forward5. [10 marks] Let G = (V,E) be a graph, and let X C V be a set of vertices. Prove that if |S||N(S)\X for every SCX, then G contains a matching M that matches every vertex of X (i.e., such that every x X is an end of an edge in M).arrow_forward
- Q/show that 2" +4 has a removable discontinuity at Z=2i Z(≥2-21)arrow_forwardRefer to page 100 for problems on graph theory and linear algebra. Instructions: • Analyze the adjacency matrix of a given graph to find its eigenvalues and eigenvectors. • Interpret the eigenvalues in the context of graph properties like connectivity or clustering. Discuss applications of spectral graph theory in network analysis. Link: [https://drive.google.com/file/d/1wKSrun-GlxirS3IZ9qoHazb9tC440 AZF/view?usp=sharing]arrow_forwardRefer to page 110 for problems on optimization. Instructions: Given a loss function, analyze its critical points to identify minima and maxima. • Discuss the role of gradient descent in finding the optimal solution. . Compare convex and non-convex functions and their implications for optimization. Link: [https://drive.google.com/file/d/1wKSrun-GlxirS31Z9qo Hazb9tC440 AZF/view?usp=sharing]arrow_forward
- Refer to page 140 for problems on infinite sets. Instructions: • Compare the cardinalities of given sets and classify them as finite, countable, or uncountable. • Prove or disprove the equivalence of two sets using bijections. • Discuss the implications of Cantor's theorem on real-world computation. Link: [https://drive.google.com/file/d/1wKSrun-GlxirS31Z9qoHazb9tC440 AZF/view?usp=sharing]arrow_forwardRefer to page 120 for problems on numerical computation. Instructions: • Analyze the sources of error in a given numerical method (e.g., round-off, truncation). • Compute the error bounds for approximating the solution of an equation. • Discuss strategies to minimize error in iterative methods like Newton-Raphson. Link: [https://drive.google.com/file/d/1wKSrun-GlxirS31Z9qo Hazb9tC440 AZF/view?usp=sharing]arrow_forwardRefer to page 145 for problems on constrained optimization. Instructions: • Solve an optimization problem with constraints using the method of Lagrange multipliers. • • Interpret the significance of the Lagrange multipliers in the given context. Discuss the applications of this method in machine learning or operations research. Link: [https://drive.google.com/file/d/1wKSrun-GlxirS31Z9qo Hazb9tC440 AZF/view?usp=sharing]arrow_forward
- Only 100% sure experts solve it correct complete solutions okarrow_forwardGive an example of a graph with at least 3 vertices that has exactly 2 automorphisms(one of which is necessarily the identity automorphism). Prove that your example iscorrect.arrow_forward3. [10 marks] Let Go (Vo, Eo) and G₁ = (V1, E1) be two graphs that ⚫ have at least 2 vertices each, ⚫are disjoint (i.e., Von V₁ = 0), ⚫ and are both Eulerian. Consider connecting Go and G₁ by adding a set of new edges F, where each new edge has one end in Vo and the other end in V₁. (a) Is it possible to add a set of edges F of the form (x, y) with x € Vo and y = V₁ so that the resulting graph (VUV₁, Eo UE₁ UF) is Eulerian? (b) If so, what is the size of the smallest possible F? Prove that your answers are correct.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:9781305652231
Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Graph Theory: Euler Paths and Euler Circuits; Author: Mathispower4u;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5M-m62qTR-s;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
WALK,TRIAL,CIRCUIT,PATH,CYCLE IN GRAPH THEORY; Author: DIVVELA SRINIVASA RAO;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iYVltZtnAik;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY