
College Physics
OER 2016 Edition
ISBN: 9781947172173
Author: OpenStax
Publisher: OpenStax College
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 33, Problem 1PE
A virtual particle having an approximate mass of 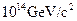 may be associated with the uni?cation of the strong and electroweak forces. For what length of time could this virtual particle exist (in temporary violation of the conservation of mass-energy as allowed by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle)?
may be associated with the uni?cation of the strong and electroweak forces. For what length of time could this virtual particle exist (in temporary violation of the conservation of mass-energy as allowed by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle)?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).
What are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V)
ammeter
I =
simple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart law
Chapter 33 Solutions
College Physics
Ch. 33 - The total energy in the beam of an accelerator is...Ch. 33 - Synchrotron radiation takes energy from an...Ch. 33 - What two major limitations prevent us from...Ch. 33 - What are the advantages of collidingbeam...Ch. 33 - Large quanti?es of antimatter isolated from normal...Ch. 33 - Massless particles are not only neutral, they are...Ch. 33 - Massless particles must travel at the speed of...Ch. 33 - When a stat erupts in a supernova explosion, huge...Ch. 33 - Theorists have had spectacular success in...Ch. 33 - What lifetime do you expect for an antineutron...
Ch. 33 - Why does the meson have such a short lifetime...Ch. 33 - (a) Is a hadron always a baryon? (b) Is a baryon...Ch. 33 - Explain how conservation of baryon number is...Ch. 33 - The quark ?avor change it takes place in decay....Ch. 33 - Explain how the weak force can change strangeness...Ch. 33 - Beta decay is caused by the weak force, as are all...Ch. 33 - Why is it easier to see the properties of the c,...Ch. 33 - How can quarks, which are fermions, combine to...Ch. 33 - What evidence is cited is support the contention...Ch. 33 - Discuss how we know that (mesons are not...Ch. 33 - An antibaryon has three antiquarks with colors...Ch. 33 - Suppose leptons are created in a reaction. Does...Ch. 33 - How can the lifetime of a particle indicate that...Ch. 33 - (a) Do all particles having strangeness also have...Ch. 33 - The sigmazero particle decays mostly via the...Ch. 33 - What do the quark compositions and other quantum...Ch. 33 - Discuss the similarities and differences between...Ch. 33 - Identity evidence for electroweak unification.Ch. 33 - The quarks in a particle are con?ned, meaning...Ch. 33 - If a GUT is proven, and the four forces are...Ch. 33 - If the Higgs boson is discovered and found to have...Ch. 33 - Gluons and the photon are massless. Does this...Ch. 33 - A virtual particle having an approximate mass of...Ch. 33 - Calculate the mass in of a virtual carrier...Ch. 33 - Another component of the strong nuclear force is...Ch. 33 - (a) Find the ratio of the strengths the weak and...Ch. 33 - We ratio of the strong to the weak force and the...Ch. 33 - At full energy, protons in the 2.00kmdiameter...Ch. 33 - Suppose a W created in a bubble chamber lives for...Ch. 33 - What length track does a (+ traveling at 0.100 c...Ch. 33 - The 3.20kmlong SLAC produces a beam of 50.0GeV...Ch. 33 - Because of energy loss due to synchrotron...Ch. 33 - A proton and an antiproton collide headon, with...Ch. 33 - When an electron and positron collide at the SLAC...Ch. 33 - The is its own antiparticle and decays in the...Ch. 33 - The primary decay mode for the negative pion is...Ch. 33 - The mass of a theoretical particle that may be...Ch. 33 - The decay mode of the negative muon is (a) Find...Ch. 33 - The decay mode of the positive tau is (a) What...Ch. 33 - The principal decay mode at the sigma zero is (a)...Ch. 33 - (a) What is the uncertainty in the energy released...Ch. 33 - (a) What is the uncertainty in the energy released...Ch. 33 - (a) Verify from its quark composition that the...Ch. 33 - Accelerators such as the Triangle Universities...Ch. 33 - The reaction (described in the preceding problem)...Ch. 33 - One of the decay modes of the omega minus is (a)...Ch. 33 - Repeat the previous problem for the decay modeCh. 33 - One decay mode for the etazero meson is (a) Find...Ch. 33 - One decay mode for the etazero meson is (a) Write...Ch. 33 - Is the decay possible considering the appropriate...Ch. 33 - Is the decay possible considering the appropriate...Ch. 33 - (a) Is the decay possible considering the...Ch. 33 - (a) Is the decay possible considering the...Ch. 33 - The only combination of quark colors that produces...Ch. 33 - (a) Three quarks form a baryon. How many...Ch. 33 - (a) Show that the conjectured decay of the proton,...Ch. 33 - Verify the quantum numbers given for the + in...Ch. 33 - Verify the quantum numbers given for the proton...Ch. 33 - (a) How much energy would be released if the...Ch. 33 - (a) Find the charge, baryon number, strangeness,...Ch. 33 - There are particles called Dmesons. One of them is...Ch. 33 - There are particles called bottom mesons or...Ch. 33 - (a) What particle has the quark composition u-u-d?...Ch. 33 - (a) Show than all combinations of three quarks...Ch. 33 - Integrated Concepts The intensity of cosmic ray...Ch. 33 - Integrated Concepts Assuming conservation of...Ch. 33 - Integrated Concepts What is the wavelength of a...Ch. 33 - Integrated Concepts Calculate the relativistic...Ch. 33 - Integrated Concepts The primary decay mode for the...Ch. 33 - Integrated Concepts Plans for an accelerator that...Ch. 33 - Integrated Concepts Suppose you are designing a...Ch. 33 - Integrated Concepts In supernovas, neutrinos are...Ch. 33 - Construct Your Own Problem Consider an...Ch. 33 - Construct Your Own Problem Consider a detector...Ch. 33 - Prob. 1TPCh. 33 - Prob. 2TPCh. 33 - Prob. 3TPCh. 33 - Prob. 4TPCh. 33 - Prob. 5TPCh. 33 - Prob. 6TPCh. 33 - Prob. 7TPCh. 33 - Prob. 8TPCh. 33 - Prob. 9TPCh. 33 - Prob. 10TPCh. 33 - Prob. 11TPCh. 33 - Prob. 12TPCh. 33 - Prob. 13TPCh. 33 - Prob. 14TPCh. 33 - Prob. 15TPCh. 33 - Prob. 16TPCh. 33 - Prob. 17TPCh. 33 - Prob. 18TP
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Why is an endospore called a resting structure? Of what advantage is an endospore to a bacterial cell?
Microbiology: An Introduction
Johnny was vigorously exercising the only joints in the skull that are freely movable. What would you guess he ...
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
How do you think a cell performing cellular respiration rids itself of the resulting CO2?
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
25. The 100 kg block in FIGURE EX7.25 takes 6.0 s to reach the floor after being released from rest. What is th...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Define and discuss these terms: (a) synapsis, (b) bivalents, (c) chiasmata, (d) crossing over, (e) chromomeres,...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
What is the difference between cellular respiration and external respiration?
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forwardAn L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forwardA long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forward
- Describe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forwardDiscuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forwardExplain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward
- 3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forwardA 0.850-m-long metal bar is pulled to the right at a steady 5.0 m/s perpendicular to a uniform, 0.650-T magnetic field. The bar rides on parallel metal rails connected through a 25-Ω, resistor (Figure 1), so the apparatus makes a complete circuit. Ignore the resistance of the bar and the rails. Please explain how to find the direction of the induced current.arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted, determine the direction (right, left, or zero) of the current induced to flow through the resistor in the circuit containing the secondary coil. The coils are wrapped around a plastic core. Immediately after the switch is closed, as shown in the figure, (Figure 1) in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? If the switch is then opened, as shown in the figure, in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? I have the answers to the question, but would like to understand the logic behind the answers. Please show steps.arrow_forward
- When violet light of wavelength 415 nm falls on a single slit, it creates a central diffraction peak that is 8.60 cm wide on a screen that is 2.80 m away. Part A How wide is the slit? ΟΙ ΑΣΦ ? D= 2.7.10-8 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 8 attempts remaining marrow_forwardTwo complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all stepsarrow_forwardCalculate the center of mass of the hollow cone shown below. Clearly specify the origin and the coordinate system you are using. Z r Y h Xarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Modern Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781111794378
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning