
PHYSICS F./SCI... W/MOD V.II W/KIT
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134819884
Author: GIANCOLI
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 32, Problem 4P
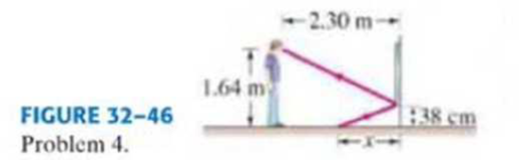
(II) A person whose eyes are 1.64 m above the floor stands 2.30 m in front of a vertical plane mirror whose bottom edge is 38 cm above the floor, Fig. 32–46. What is the horizontal distance x to the base of the wall supporting the mirror of the nearest point on the floor that can be seen reflected in the mirror?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A ball is thrown with an initial speed v, at an angle 6, with the horizontal. The horizontal range of the ball is R, and the ball reaches a maximum height R/4. In terms of R and g, find the following.
(a) the time interval during which the ball is in motion
2R
(b) the ball's speed at the peak of its path
v=
Rg 2
√ sin 26, V 3
(c) the initial vertical component of its velocity
Rg
sin ei
sin 20
(d) its initial speed
Rg
√ sin 20
×
(e) the angle 6, expressed in terms of arctan of a fraction.
1
(f) Suppose the ball is thrown at the same initial speed found in (d) but at the angle appropriate for reaching the greatest height that it can. Find this height.
hmax
R2
(g) Suppose the ball is thrown at the same initial speed but at the angle for greatest possible range. Find this maximum horizontal range.
Xmax
R√3
2
An outfielder throws a baseball to his catcher in an attempt to throw out a runner at home plate. The ball bounces once before reaching the catcher. Assume the angle at which the bounced ball leaves the ground is the same as the angle at which the outfielder threw it as shown in the figure, but that the ball's speed after the bounce is one-half of what it was before the bounce.
8
(a) Assuming the ball is always thrown with the same initial speed, at what angle & should the fielder throw the ball to make it go the same distance D with one bounce (blue path) as a ball thrown upward at 35.0° with no bounce (green path)?
24
(b) Determine the ratio of the time interval for the one-bounce throw to the flight time for the no-bounce throw.
Cone-bounce
no-bounce
0.940
A rocket is launched at an angle of 60.0° above the horizontal with an initial speed of 97 m/s. The rocket moves for 3.00 s along its initial line of motion with an acceleration of 28.0 m/s². At this time, its engines fail and the rocket proceeds to move as a projectile.
(a) Find the maximum altitude reached by the rocket.
1445.46
Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. m
(b) Find its total time of flight.
36.16
x
Your response is within 10% of the correct value. This may be due to roundoff error, or you could have a mistake in your calculation. Carry out all intermediate results to at least four-digit accuracy to minimize roundoff error. s
(c) Find its horizontal range.
1753.12
×
Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. m
Chapter 32 Solutions
PHYSICS F./SCI... W/MOD V.II W/KIT
Ch. 32.1 - Does the result of Example 322 depend on your...Ch. 32.1 - Return to the Chapter-Opening Question, page 837,...Ch. 32.1 - Suppose you are standing about 3 m in front of a...Ch. 32.5 - Light passes from a medium with n = 1.3 into a...Ch. 32.7 - Fill a sink with water. Place a waterproof watch...Ch. 32.7 - It 45.0 plastic lenses are used in binoculars,...Ch. 32 - What would be the appearance of the Moon if it had...Ch. 32 - Archimedes is said to have burned the whole Roman...Ch. 32 - What is the focal length of a plane mirror? What...Ch. 32 - An object is placed along the principal axis of a...
Ch. 32 - Using the rules for the three rays discussed with...Ch. 32 - Prob. 6QCh. 32 - If a concave mirror produces a real image, is the...Ch. 32 - Prob. 8QCh. 32 - When you look at the Moons reflection from a...Ch. 32 - How can a spherical mirror have a negative object...Ch. 32 - Prob. 11QCh. 32 - When you look down into a swimming pool or a lake,...Ch. 32 - Draw a ray diagram to show why a stick looks bent...Ch. 32 - Prob. 14QCh. 32 - You look into an aquarium and view a fish inside....Ch. 32 - Prob. 16QCh. 32 - A ray of light is refracted through three...Ch. 32 - Can a light ray traveling in air be totally...Ch. 32 - When you look up at an object in air from beneath...Ch. 32 - What type of mirror is shown in Fig. 3244?Ch. 32 - Light rays from stars (including our Sun) always...Ch. 32 - (I) When you look at yourself in a 60-cm-tall...Ch. 32 - (I) Suppose that you want to take a photograph of...Ch. 32 - (II) Two plane mirrors meet at a 135 angle, Fig....Ch. 32 - (II) A person whose eyes are 1.64 m above the...Ch. 32 - (II) Show that if two plane mirrors meet at an...Ch. 32 - (II) Suppose you are 88 cm from a plane mirror....Ch. 32 - (II) Stand up two plane minors so they form a 90.0...Ch. 32 - (III) Suppose a third mirror is placed beneath the...Ch. 32 - (I) A solar cooker, really a concave mirror...Ch. 32 - (I) How far from a concave mirror (radius 24.0cm)...Ch. 32 - (I) When walking toward a concave mirror you...Ch. 32 - (II) A small candle is 35 cm from a concave mirror...Ch. 32 - (II) You look at yourself in a shiny...Ch. 32 - (II) A mirror at an amusement park shows an...Ch. 32 - (II) A dentist wants a small mirror that, when...Ch. 32 - (II) Some rearview mirrors produce images of cars...Ch. 32 - (II) You are standing 3.0 m from a convex security...Ch. 32 - (II) An object 3.0 mm high is placed 18 cm from a...Ch. 32 - (II) The image of a distant tree is virtual and...Ch. 32 - (II) Use two techniques, (a) a ray diagram, and...Ch. 32 - (II) Show, using a ray diagram, that the...Ch. 32 - (II) Use ray diagrams to show that the mirror...Ch. 32 - (II) The magnification of a convex mirror is +0.55...Ch. 32 - (II) (a) Where should an object be placed in front...Ch. 32 - (II) A 4.5-cm tall object is placed 26 cm in front...Ch. 32 - (II) A shaving or makeup mirror is designed to...Ch. 32 - (II) Let the focal length of a convex mirror be...Ch. 32 - (II) A spherical mirror of focal length f produces...Ch. 32 - Prob. 30PCh. 32 - (III) A short thin object (like a short length of...Ch. 32 - (I) The speed of light in ice is 2.29 108 m/s....Ch. 32 - (I) What is the speed of light in (a) ethyl...Ch. 32 - (I) Our nearest star (other than the Sun) is 4.2...Ch. 32 - (I) How long does it take light to reach us from...Ch. 32 - (II) The speed of light in a certain substance is...Ch. 32 - (II) Light is emitted from an ordinary lightbulb...Ch. 32 - (I) A diver shines a flashlight upward from...Ch. 32 - (I) A flashlight beam strikes the surface of a...Ch. 32 - Prob. 40PCh. 32 - (I) A light beam coming from an underwater...Ch. 32 - (II) A beam of light in air strikes a slab of...Ch. 32 - (II) A light beam strikes a 2.0-cm-thick piece of...Ch. 32 - (II) An aquarium filled with water has flat glass...Ch. 32 - (II) In searching the bottom of a pool at night, a...Ch. 32 - (II) The block of glass (n = 1.5) shown in cross...Ch. 32 - (II) A laser beam of diameter d1 = 3.0 mm in air...Ch. 32 - (II) Light is incident on an equilateral glass...Ch. 32 - (II) A triangular prism made of crown glass (n =...Ch. 32 - (II) Show in general that for a light beam...Ch. 32 - (III) A light ray is incident on a flat piece of...Ch. 32 - (I) By what percent is the speed of blue light...Ch. 32 - (I) A light beam strikes a piece of glass at a...Ch. 32 - (II) A parallel beam of light containing two...Ch. 32 - (III) A ray of light with wavelength is incident...Ch. 32 - (III) For visible light, the index of refraction n...Ch. 32 - (I) What is the critical angle for the interlace...Ch. 32 - (I) The critical angle for a certain liquidair...Ch. 32 - (II) A beam of light is emitted in a pool of water...Ch. 32 - (II) A ray of light, after entering a light fiber,...Ch. 32 - (II) A beam of light is emitted 8.0cm beneath the...Ch. 32 - (II) Figure 3257 shows a liquid-detecting prism...Ch. 32 - (II) Two rays A and B travel down a cylindrical...Ch. 32 - (II) (a) What is the minimum index of refraction...Ch. 32 - (III) Suppose a ray strikes the left face of the...Ch. 32 - (III) A beam of light enters the end of an optic...Ch. 32 - (II) A 13.0-cm-thick plane piece of glass (n =...Ch. 32 - (II) A fish is swimming in water inside a thin...Ch. 32 - (III) In Section 32-8, we derived Eq. 32-8 for a...Ch. 32 - Two identical concave mirrors are set facing each...Ch. 32 - A slab of thickness D, whose two faces are...Ch. 32 - Two plane mirrors are facing each other 2.2 m...Ch. 32 - We wish to determine the depth of a swimming pool...Ch. 32 - A 1.80-m-tall person stands 3.80 m from a convex...Ch. 32 - Prob. 76GPCh. 32 - Each student in a physics lab is assigned to find...Ch. 32 - A kaleidoscope makes symmetric patterns with two...Ch. 32 - When light passes through a prism, the angle that...Ch. 32 - If the apex angle of a prism is = 72 (see Fig....Ch. 32 - Fermats principle slates that light travels...Ch. 32 - Suppose Fig. 3236 shows a cylindrical rod whose...Ch. 32 - An optical fiber is a long transparent cylinder of...Ch. 32 - An object is placed 15 cm from a certain mirror....Ch. 32 - The end faces of a cylindrical glass rod (n =...Ch. 32 - The paint used or highway signs often contains...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
15. You have a collection of six 1.0 k? resistors. What is the smallest resistance you can make by combining th...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Predict how many electrons each element will most likely gain or lose. a. l b. Ba c. Cs d. Se
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Why is petroleum jelly used in the hanging-drop procedure?
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Which culture uses NAD+? Use the following choices to answer questions. a. E. coli growing in glucose broth at ...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Why is living epithelial tissue limited to a certain thickness?
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
A mixed culture of Escherichia coli and Penicillium chrysogenum is inoculated onto the following culture media....
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Race car driver is cruising down the street at a constant speed of 28.9 m/s (~65 mph; he has a “lead” foot) when the traffic light in front of him turns red. a) If the driver’s reaction time is 160 ms, how far does he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he begins to slow down? b) If the driver’s combined reaction and movement time is 750 ms, how far do he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he slams on her brakes and car begins to slow down? Please answer parts a-B. Show all work. For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places. DONT FORGET TO DRAW VECTORS! ONLY USE BASIC FORMULAS TAUGHT IN PHYSICS. distance = speed * time.arrow_forwardRace car driver is cruising down the street at a constant speed of 28.9 m/s (~65 mph; he has a “lead” foot) when the traffic light in front of him turns red. a) If the driver’s reaction time is 160 ms, how far does he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he begins to slow down? b) If the driver’s combined reaction and movement time is 750 ms, how far do he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he slams on her brakes and car begins to slow down? c) If the driver’s average rate of acceleration is -9.5 m/s2 as he slows down, how long does it take him to come to a stop (use information about his speed of 28.9 m/s but do NOT use his reaction and movement time in this computation)? Please answer parts a-c. Show all work. For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.…arrow_forwardHow is it that part a is connected to part b? I can't seem to solve either part and don't see the connection between the two.arrow_forward
- Hello, please help with inputing trial one into the equation, I just need a model for the first one so I can answer the rest. Also, does my data have the correct sigfig? Thanks!arrow_forwardFind the current in the R₁ resistor in the drawing (V₁=16.0V, V2=23.0 V, V₂ = 16.0V, R₁ = 2005, R₂ = and R₂ = 2.705) 2.3052 VIT A www R www R₂ R₂ Vaarrow_forwardWhich of the following laws is true regarding tensile strength? • tensile strength T ①Fbreak = Wtfest Piece thickness rate (mm) ②T = test piece width rabe (mm) Fbreak break watarrow_forward
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forwardYou hold a spherical salad bowl 85 cm in front of your face with the bottom of the bowl facing you. The salad bowl is made of polished metal with a 40 cm radius of curvature. Where is the image of your 2.0 cm tall nose located? What is image's size, orientation, and nature. I keep getting the answer -26.2, but it keeps saying it is wrong. I just want to know what i'm doing wrong.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College
Convex and Concave Lenses; Author: Manocha Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CJ6aB5ULqa0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY