
Concept explainers
a)
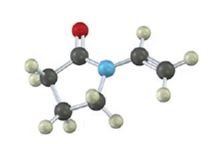
Interpretation:
Draw the structures of the
Concept introduction:
The term “polymer” is derived from the two words poly+mer. Where poly means ‘many’ and mer means ‘unit’, when combined known as polymer. The
The reaction mechanism may be classified into two categories:
Chain growth polymerization:
Chain growth polymers are produced by chain growth polymerization or addition polymerization. In this process an initiator is added to the reaction mixture. This initiator gets added to the carbon-carbon double bond and yields a reactive monomer (intermediate). This reactive intermediate reacts with the monomer and this process keeps on repeating to give rise to final polymeric product.
Step growth polymerization:
Step growth polymers are produced by step growth polymerization or condensation polymerization. In this process, each bond is formed in a step wise manner. In this the product of each is again a bi-
b)
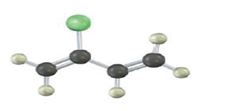
Interpretation:
Draw the structures of the polymers formed by the given monomer units.
Concept introduction:
The term “polymer” is derived from the two words poly+mer. Where poly means ‘many’ and mer means ‘unit’, when combined known as polymer. The polymerization is the process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to give rise to a polymer. If the reacting units are same then this type of polymer is known as homopolymer and if the reaction takes place between different molecules then it is called copolymer.
The reaction mechanism may be classified into two categories:
Chain growth polymerization:
Chain growth polymers are produced by chain growth polymerization or addition polymerization. In this process an initiator is added to the reaction mixture. This initiator gets added to the carbon-carbon double bond and yields a reactive monomer (intermediate). This reactive intermediate reacts with the monomer and this process keeps on repeating to give rise to final polymeric product.
Step growth polymerization:
Step growth polymers are produced by step growth polymerization or condensation polymerization. In this process, each bond is formed in a step wise manner. In this the product of each is again a bi-functional group and the condensation goes on.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 31 Solutions
Bundle: Organic Chemistry, 9th, Loose-Leaf + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- 32. Consider a two-state system in which the low energy level is 300 J mol 1 and the higher energy level is 800 J mol 1, and the temperature is 300 K. Find the population of each level. Hint: Pay attention to your units. A. What is the partition function for this system? B. What are the populations of each level? Now instead, consider a system with energy levels of 0 J mol C. Now what is the partition function? D. And what are the populations of the two levels? E. Finally, repeat the second calculation at 500 K. and 500 J mol 1 at 300 K. F. What do you notice about the populations as you increase the temperature? At what temperature would you expect the states to have equal populations?arrow_forward30. We will derive the forms of the molecular partition functions for atoms and molecules shortly in class, but the partition function that describes the translational and rotational motion of a homonuclear diatomic molecule is given by Itrans (V,T) = = 2πmkBT h² V grot (T) 4π²IKBT h² Where h is Planck's constant and I is molecular moment of inertia. The overall partition function is qmolec Qtrans qrot. Find the energy, enthalpy, entropy, and Helmholtz free energy for the translational and rotational modes of 1 mole of oxygen molecules and 1 mole of iodine molecules at 50 K and at 300 K and with a volume of 1 m³. Here is some useful data: Moment of inertia: I2 I 7.46 x 10- 45 kg m² 2 O2 I 1.91 x 101 -46 kg m²arrow_forwardK for each reaction step. Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. HI HaC Drawing Arrows! H3C OCH3 H 4 59°F Mostly sunny H CH3 HO O CH3 'C' CH3 Select to Add Arrows CH3 1 L H&C. OCH3 H H H H Select to Add Arrows Q Search Problem 30 of 20 H. H3C + :0: H CH3 CH3 20 H2C Undo Reset Done DELLarrow_forward
- Draw the principal organic product of the following reaction.arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided structures, draw the curved arrows that epict the mechanistic steps for the proton transfer between a hydronium ion and a pi bond. Draw any missing organic structures in the empty boxes. Be sure to account for all lone-pairs and charges as well as bond-breaking and bond-making steps. 2 56°F Mostly cloudy F1 Drawing Arrows > Q Search F2 F3 F4 ▷11 H. H : CI: H + Undo Reset Done DELLarrow_forwardCalculate the chemical shifts in 13C and 1H NMR for 4-chloropropiophenone ? Write structure and label hydrogens and carbons. Draw out the benzene ring structure when doing itarrow_forward
- 1) Calculate the longest and shortest wavelengths in the Lyman and Paschen series. 2) Calculate the ionization energy of He* and L2+ ions in their ground states. 3) Calculate the kinetic energy of the electron emitted upon irradiation of a H-atom in ground state by a 50-nm radiation.arrow_forwardCalculate the ionization energy of He+ and Li²+ ions in their ground states. Thannnxxxxx sirrr Ahehehehehejh27278283-4;*; shebehebbw $+$;$-;$-28283773838 hahhehdvaarrow_forwardPlleeaasseee solllveeee question 3 andd thankss sirr, don't solve it by AI plleeaasseee don't use AIarrow_forward
- Calculate the chemical shifts in 13C and 1H NMR for 4-chloropropiophenone ? Write structure and label hydrogens and carbonsarrow_forwardPlease sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forwardPlease sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuu, don't solve it by AI plleeaasseeearrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





