
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
15th Edition
ISBN: 9780134261928
Author: Michael T. Madigan, Kelly S. Bender, Daniel H. Buckley, W. Matthew Sattley, David A. Stahl
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.11, Problem 2MQ
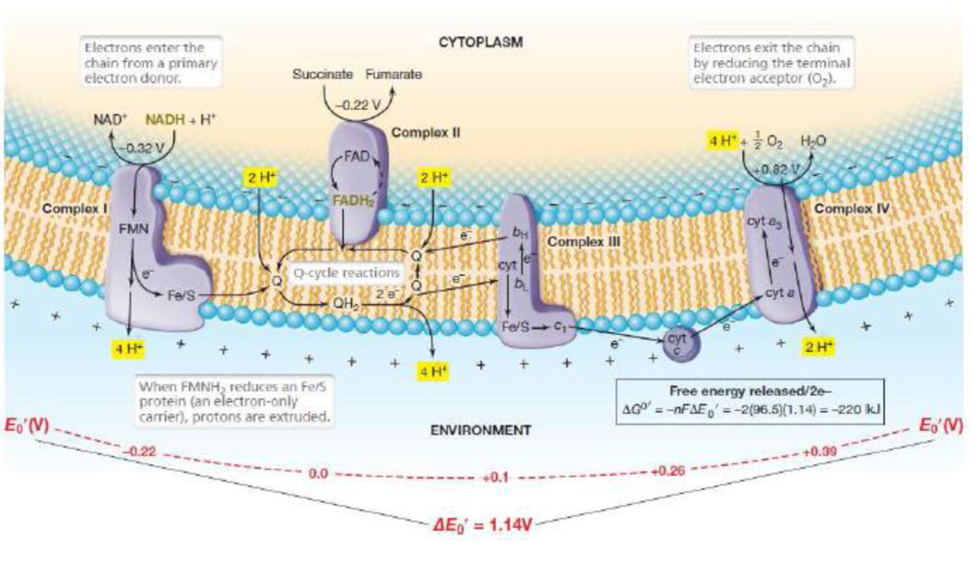
- How much energy is released per NADH oxidized through the electron transport chain of Paracoccus shown in Figure 3 22? At which sites in the chain is the proton motive force being established?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The following table is from Kumar et. al. Highly Selective Dopamine D3 Receptor (DR) Antagonists and Partial Agonists Based on Eticlopride and the D3R Crystal Structure: New Leads for Opioid Dependence Treatment. J. Med Chem 2016.
The following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the
pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin.
You are a chef in a fancy new science-themed restaurant. You have a recipe that calls for 1 teaspoon of resinferatoxin, but you feel uncomfortable serving foods with "toxins" in them. How much capsaicin could you substitute instead?
What protein is necessary for packaging acetylcholine into synaptic vesicles?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Ch. 3.1 - Which four chemical elements make up the bulk of a...Ch. 3.1 - Which two classes of macromolecules contain most...Ch. 3.1 - Differentiate between trace metals and growth...Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 1CRCh. 3.2 - Compare and contrast simple transporters, the...Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 2MQCh. 3.2 - Cells of Escherichia coli transport lactose via...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 1MQCh. 3.3 - Prob. 2MQCh. 3.3 - Prob. 1CR
Ch. 3.4 - What is free energy?Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 2MQCh. 3.4 - Using Table 3.2, calculate G0 for the reaction...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 1CRCh. 3.5 - Prob. 1MQCh. 3.5 - Prob. 2MQCh. 3.5 - Prob. 3MQCh. 3.5 - Prob. 1CRCh. 3.6 - Prob. 1MQCh. 3.6 - Prob. 2MQCh. 3.6 - Prob. 3MQCh. 3.6 - Prob. 1CRCh. 3.7 - How much free energy is released when ATP is...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 2MQCh. 3.7 - Prob. 3MQCh. 3.7 - Prob. 1CRCh. 3.8 - Which reactions in glycolysis are redox steps?Ch. 3.8 - Prob. 2MQCh. 3.8 - Prob. 3MQCh. 3.8 - How is ATP made in fermentation and in...Ch. 3.9 - How many molecules of CO2, NADH, and FADH2 are...Ch. 3.9 - What two major roles do the citric acid cycle and...Ch. 3.9 - Why is the glyoxylate cycle necessary for growth...Ch. 3.9 - Prob. 1CRCh. 3.10 - Prob. 1MQCh. 3.10 - Which electron carriers described in this section...Ch. 3.10 - List some of the key electron carriers found in...Ch. 3.11 - How do electron transport reactions generate the...Ch. 3.11 - How much energy is released per NADH oxidized...Ch. 3.11 - What structure in the cell links the proton motive...Ch. 3.11 - Prob. 1CRCh. 3.12 - Prob. 1MQCh. 3.12 - Prob. 2MQCh. 3.12 - Prob. 3MQCh. 3.12 - What is the major difference between aerobic...Ch. 3.13 - What form of activated glucose is used in the...Ch. 3.13 - Prob. 2MQCh. 3.13 - What functions does the pentose phosphate pathway...Ch. 3.13 - What is the importance of the enzyme...Ch. 3.14 - Prob. 1MQCh. 3.14 - List the steps required for the cell to...Ch. 3.14 - Which nitrogen bases are purines and which are...Ch. 3.14 - Prob. 1CRCh. 3.15 - Prob. 1MQCh. 3.15 - Prob. 2MQCh. 3.15 - Describe the process by which a fatty acid such as...Ch. 3 - Using the data of Figure 3.10, predict the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 2AQ
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Match each vocabulary term to its best descriptor A. affinity B. efficacy C. inert D. mimic E. how drugs move through body F. how drugs bind Kd Bmax Agonist Antagonist Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamicsarrow_forward50 mg dose of a drug is given orally to a patient. The bioavailability of the drug is 0.2. What is the volume of distribution of the drug if the plasma concentration is 1 mg/L? Be sure to provide units.arrow_forwardDetermine Kd and Bmax from the following Scatchard plot. Make sure to include units.arrow_forward
- Choose a catecholamine neurotransmitter and describe/draw the components of the synapse important for its signaling including synthesis, packaging into vesicles, receptors, transporters/degradative enzymes. Describe 2 drugs that can act on this system.arrow_forwardThe following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin. a) Which has a higher potency? b) Which is has a higher efficacy? c) What is the approximate Kd of capsaicin in uM? (you can round to the nearest power of 10)arrow_forwardWhat is the rate-limiting-step for serotonin synthesis?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Biochemical Tests-Part 1; Author: Southern Stacker;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a-i9vANfQWQ;License: Standard Youtube License