
Concept explainers
The circuit in Figure P3 1.61 is located in a magnetic field whose magnitude varies with lime according to the expression B = 1.00 × 10-3 t, where B is in teslas and f is in seconds. Assume the resistance per length of the wire is 0.100 Ω/m. Find the current in section PQ of length a = 65.0 cm.
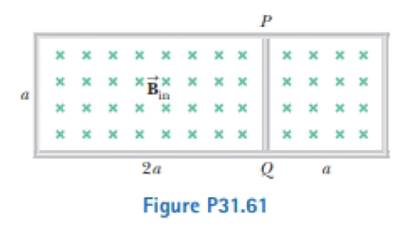
The current in the section PQ.
Answer to Problem 31.61AP
The current in the section PQ is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The time varying magnetic field is
The circuit diagram is as shown below.
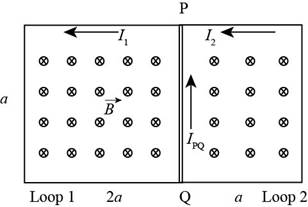
Figure (1)
For loop 1:
The resistance of the loop is,
Here,
The length of PQ is
The area of the loop is,
Thus, the area of the loop 1 is
The flux induced in the loop is,
Here,
The angle between the normal component of the area and the magnetic field is,
Substitute
The emf induced in the loop is,
Substitute
Thus, the induced emf in the loop 1 is
The current in the loop is
Apply Kirchhoff’s loop rule in loop 1.
Substitute
For loop (2):
The resistance of the loop is,
The area of the loop is,
Thus, the area of the loop 2 is
The flux induced in the loop is,
The angle between the normal component of the area and the magnetic field is,
Substitute
Thus, the flux induced in the loop is
The emf induced in the loop is,
Substitute
Thus, the induced emf in the loop 2 is
The current in the loop is
Apply Kirchhoff’s loop rule in loop 2.
Substitute
From the figure (1) the current in the arm PQ is,
Substitute
Rearrange the equation (2) for
Substitute
Substitute
Rearrange the above equation for
Substitute
Further solve the above equation.
The current in PQ is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the current in the PQ arm is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 31 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
- Race car driver is cruising down the street at a constant speed of 28.9 m/s (~65 mph; he has a “lead” foot) when the traffic light in front of him turns red. a) If the driver’s reaction time is 160 ms, how far does he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he begins to slow down? b) If the driver’s combined reaction and movement time is 750 ms, how far do he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he slams on her brakes and car begins to slow down? Please answer parts a-B. Show all work. For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places. DONT FORGET TO DRAW VECTORS! ONLY USE BASIC FORMULAS TAUGHT IN PHYSICS. distance = speed * time.arrow_forwardRace car driver is cruising down the street at a constant speed of 28.9 m/s (~65 mph; he has a “lead” foot) when the traffic light in front of him turns red. a) If the driver’s reaction time is 160 ms, how far does he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he begins to slow down? b) If the driver’s combined reaction and movement time is 750 ms, how far do he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he slams on her brakes and car begins to slow down? c) If the driver’s average rate of acceleration is -9.5 m/s2 as he slows down, how long does it take him to come to a stop (use information about his speed of 28.9 m/s but do NOT use his reaction and movement time in this computation)? Please answer parts a-c. Show all work. For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.…arrow_forwardHow is it that part a is connected to part b? I can't seem to solve either part and don't see the connection between the two.arrow_forward
- Hello, please help with inputing trial one into the equation, I just need a model for the first one so I can answer the rest. Also, does my data have the correct sigfig? Thanks!arrow_forwardFind the current in the R₁ resistor in the drawing (V₁=16.0V, V2=23.0 V, V₂ = 16.0V, R₁ = 2005, R₂ = and R₂ = 2.705) 2.3052 VIT A www R www R₂ R₂ Vaarrow_forwardWhich of the following laws is true regarding tensile strength? • tensile strength T ①Fbreak = Wtfest Piece thickness rate (mm) ②T = test piece width rabe (mm) Fbreak break watarrow_forward
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forwardYou hold a spherical salad bowl 85 cm in front of your face with the bottom of the bowl facing you. The salad bowl is made of polished metal with a 40 cm radius of curvature. Where is the image of your 2.0 cm tall nose located? What is image's size, orientation, and nature. I keep getting the answer -26.2, but it keeps saying it is wrong. I just want to know what i'm doing wrong.arrow_forward

 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning





