
Concept explainers
Classify each terpene and terpenoid in Problem 31.26 (e.g., as a monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.).
(a)
Interpretation: The terpene and terpenoid are to be classified as monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.
Concept introduction: Terpenes are naturally occurring compounds that are present in plants and animals. Terpenes contain one or more isoprene units. Terpenoids are derivatives of terpenes with oxygen containing functional group such as carbonyl groups. Monoterpenes contain two isoprene units, sesquiterpene contain three isoprene units etc.
Answer to Problem 31.27P
Neral is classified as monoterpene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isoprene is,
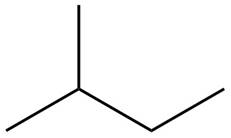
Figure 1
The isoprene unit contains four carbon atoms in the long chain and one carbon atom in branch. Isoprene unit in a terpene consists of carbon-carbon sigma or pi bonds.
The isoprene units in the given compound are shown below.
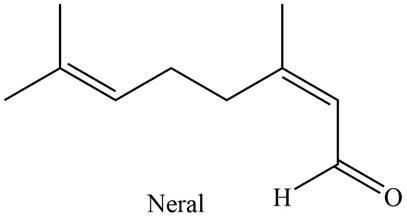
Figure 2
The highlighted bonds represent the isoprene unit. There are two isoprene units present in the given compound. Neral is classified as monoterpene.
Neral is classified as monoterpene.
(b)
Interpretation: The terpene and terpenoid are to be classified as monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.
Concept introduction: Terpenes are naturally occurring compounds that are present in plants and animals. Terpenes contain one or more isoprene units. Terpenoids are derivatives of terpenes with oxygen containing functional group such as carbonyl groups. Monoterpenes contain two isoprene units, sesquiterpene contain three isoprene units etc.
Answer to Problem 31.27P
Carvone is classified as monoterpene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isoprene is,
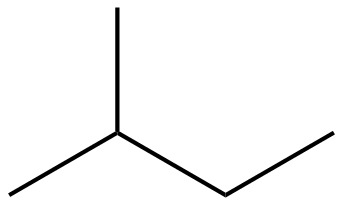
Figure 1
The isoprene unit contains four carbon atoms in the long chain and one carbon atom in branch. Isoprene unit in a terpene consists of carbon-carbon sigma or pi bonds.
The isoprene units in the given compound are shown below.
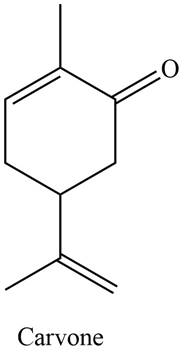
Figure 3
The highlighted bonds represent the isoprene unit. There are two isoprene units present in the given compound. Carvone is classified as monoterpene.
Carvone is classified as monoterpene.
(c)
Interpretation: The terpene and terpenoid are to be classified as monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.
Concept introduction: Terpenes are naturally occurring compounds that are present in plants and animals. Terpenes contain one or more isoprene units. Terpenoids are derivatives of terpenes with oxygen containing functional group such as carbonyl groups. Monoterpenes contain two isoprene units, sesquiterpene contain three isoprene units etc.
Answer to Problem 31.27P
Lycopene is classified as tetraterpene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isoprene is,
Figure 1
The isoprene unit contains four carbon atoms in the long chain and one carbon atom in branch. Isoprene unit in a terpene consists of carbon-carbon sigma or pi bonds.
The isoprene units in the given compound are shown below.
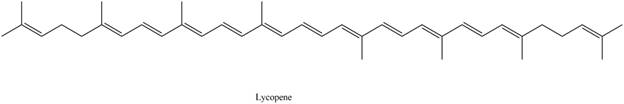
Figure 4
The highlighted bonds represent the isoprene unit. There are eight isoprene units present in the given compound. Lycopene is classified as tetraterpene.
Lycopene is classified as tetraterpene.
(d)
Interpretation: The terpene and terpenoid are to be classified as monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.
Concept introduction: Terpenes are naturally occurring compounds that are present in plants and animals. Terpenes contain one or more isoprene units. Terpenoids are derivatives of terpenes with oxygen containing functional group such as carbonyl groups. Monoterpenes contain two isoprene units, sesquiterpene contain three isoprene units etc.
Answer to Problem 31.27P
The
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isoprene is,

Figure 1
The isoprene unit contains four carbon atoms in the long chain and one carbon atom in branch. Isoprene unit in a terpene consists of carbon-carbon sigma or pi bonds.
The isoprene units in the given compound are shown below.
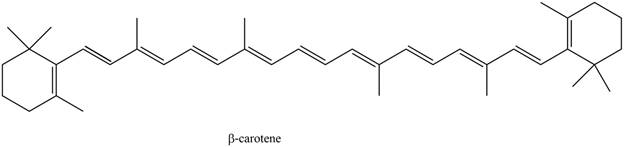
Figure 5
The highlighted bonds represent the isoprene unit. There are eight isoprene units present in the given compound. The
The
(e)
Interpretation: The terpene and terpenoid are to be classified as monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.
Concept introduction: Terpenes are naturally occurring compounds that are present in plants and animals. Terpenes contain one or more isoprene units. Terpenoids are derivatives of terpenes with oxygen containing functional group such as carbonyl groups. Monoterpenes contain two isoprene units, sesquiterpene contain three isoprene units etc.
Answer to Problem 31.27P
Patchouli alcohol is classified as sesquiterpene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isoprene is,

Figure 1
The isoprene unit contains four carbon atoms in the long chain and one carbon atom in branch. Isoprene unit in a terpene consists of carbon-carbon sigma or pi bonds.
The isoprene units in the given compound are shown below.
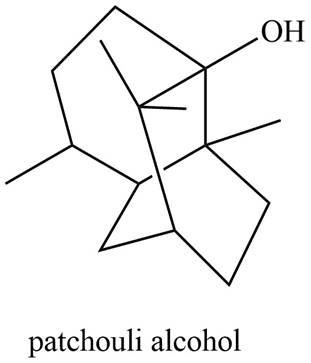
Figure 6
The highlighted bonds represent the isoprene unit. There are three isoprene units present in the given compound. Patchouli alcohol is classified as sesquiterpene.
Patchouli alcohol is classified as sesquiterpene.
(f)
Interpretation: The terpene and terpenoid are to be classified as monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.
Concept introduction: Terpenes are naturally occurring compounds that are present in plants and animals. Terpenes contain one or more isoprene units. Terpenoids are derivatives of terpenes with oxygen containing functional group such as carbonyl groups. Monoterpenes contain two isoprene units, sesquiterpene contain three isoprene units etc.
Answer to Problem 31.27P
Periplanone B is classified as sesquiterpene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isoprene is,
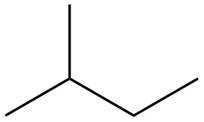
Figure 1
The isoprene unit contains four carbon atoms in the long chain and one carbon atom in branch. Isoprene unit in a terpene consists of carbon-carbon sigma or pi bonds.
The isoprene units in the given compound are shown below.
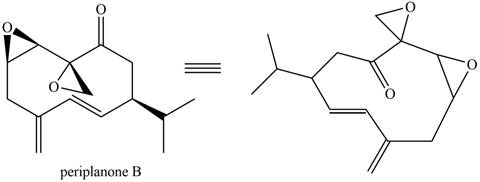
Figure 7
The highlighted bonds represent the isoprene unit. There are three isoprene units present in the given compound. Periplanone B is classified as sesquiterpene.
Periplanone B is classified as sesquiterpene.
(g)
Interpretation: The terpene and terpenoid are to be classified as monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.
Concept introduction: Terpenes are naturally occurring compounds that are present in plants and animals. Terpenes contain one or more isoprene units. Terpenoids are derivatives of terpenes with oxygen containing functional group such as carbonyl groups. Monoterpenes contain two isoprene units, sesquiterpene contain three isoprene units etc.
Answer to Problem 31.27P
Dextropimaric acid is classified as diterpene.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isoprene is,

Figure 1
The isoprene unit contains four carbon atoms in the long chain and one carbon atom in branch. Isoprene unit in a terpene consists of carbon-carbon sigma or pi bonds.
The isoprene units in the given compound are shown below.
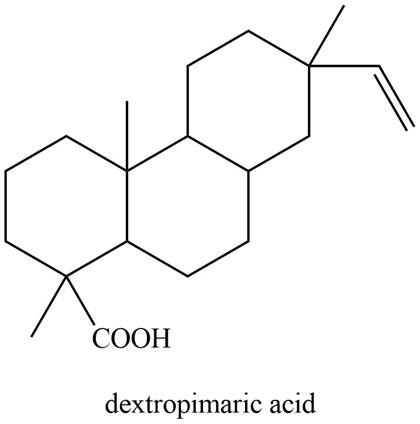
Figure 8
The highlighted bonds represent the isoprene unit. There are four isoprene units present in the given compound. Dextropimaric acid is classified as diterpene.
Dextropimaric acid is classified as diterpene.
(h)
Interpretation: The terpene and terpenoid are to be classified as monoterpene, sesquiterpene, etc.
Concept introduction: Terpenes are naturally occurring compounds that are present in plants and animals. Terpenes contain one or more isoprene units. Terpenoids are derivatives of terpenes with oxygen containing functional group such as carbonyl groups. Monoterpenes contain two isoprene units, sesquiterpene contain three isoprene units etc.
Answer to Problem 31.27P
The
Explanation of Solution
The structure of isoprene is,
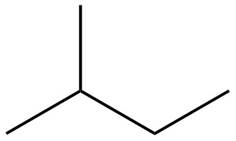
Figure 1
The isoprene unit contains four carbon atoms in the long chain and one carbon atom in branch. Isoprene unit in a terpene consists of carbon-carbon sigma or pi bonds.
The isoprene units in the given compound are shown below.
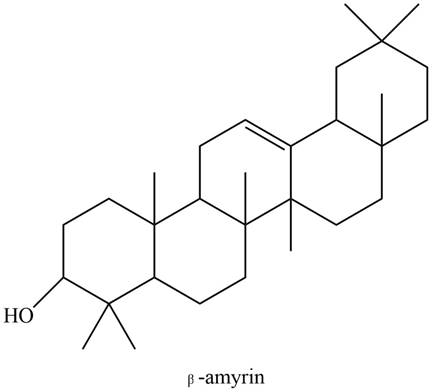
Figure 9
The highlighted bonds represent the isoprene unit. There are four isoprene units present in the given compound. The
The
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 31 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction: HBr (1 equiv) cold ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of this reaction in the drawing area below. • You can draw the products in any arrangement you like. • Pay careful attention to the reaction conditions, and only include the major products. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • Note that there is only 1 equivalent of HBr reactant, so you need not consider the case of multiple additions. dm Re Explanation Check ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Termarrow_forwardb) Use curved arrows to show the reaction of the radical with hydrogen bromide. Br: Br H .. Answer Bankarrow_forwardIndicate the reaction products when CH3COCH2COOCH2COOC2H5 (ethyl acetoacetoacetate) reacts with 1º OH-/H2O and 2º H3O+arrow_forward
- Indicate whether the product of the reaction between Naphthalene and CrO3 in acetic acid at 25ºC is 1,4 naphthoquinone or phthalic anhydride.arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction between CH3COCH2COOC2H5 and Na+-OC2H5.arrow_forwardPrimary, Secondary, and Tertiary Alcohols O-H O-H O-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-R₁ H R₂ R₂ Primary Alcohol Secondary Alcohol ChemistryLearner.com R stands for Carbon group like ethyl methyl propyl Tertiary Alcohol If 1 carbon group with two H attached to alcoholic carbon, then primary If 2 carbon group and 1 H are attached to alcoholic carbon, then secondary IF 3 carbon group and no H attach to alcoholic carbon then tertiary. The bottom line Starting "Weak" oxidant material PCC, DMP, Swern, etc Primary alcohol Aldehyde OH Secondary alcohol Ketone OH "Strong" oxidant KMnO4, H₂CrO4 (or equivalent) OH Carboxylic acid 요 Ketone No reaction No reaction Tertiary alcohol 1. Is ethanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of ethanol and any oxidation products of ethanol. If there is more than one oxidation product, give the structure of each of the products. 2. Is 2-propanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of 2-propanol and any…arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole


