
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305116399
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 31, Problem 31.10CQ
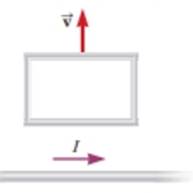
A loop of wire is moving near a long, straight wire carrying a constant current I as shown in Figure CQ31.10. (a) Determine the direction of the induced current in the loop as it moves away from the wire. (b) What would be the direction of the induced current in the loop if it were moving toward the wire?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
a)
What is the minimum tension in N that the cable must be able to support without breaking? Assume the cable is massless.
T =
b)
If the cable can only support a tension of 10,000 N what is the highest mass the ball can have in kg?
mm =
Curve Fitter
CURVE FITTER
Open
Update Fit
Save
New
Exclusion Rules
Select Validation Data
Polynomial Exponential Logarithmic
Auto
Fourier
Fit
Fit
Duplicate Data
Manual
FILE
DATA
FIT TYPE
FIT
Harmonic Motion X
us
0.45
mi
ce
0.4
0.35
0.3
0.25
0.2
Residuals Plot
Contour Plot
Plot Prediction Bounds None
VISUALIZATION
Colormap Export
PREFERENCES EXPORT
Fit Options
COA Fourier
Equation
Fit Plot
x vs. t
-Harmonic Motion
a0+ a1*cos(x*w) +
b1*sin(x*w)
Number of terms
Center and scale
1
▸ Advanced Options
Read about fit options
Results
Value
Lower
Upper
0.15
a0
0.1586
0.1551
0.1620
a1
0.0163
0.0115
0.0211
0.1
b1
0.0011
-0.0093
0.0115
W
1.0473
0.9880
1.1066
2
8
10
t
12
14
16
18
20
Goodness of Fit
Value
Table of Fits
SSE
0.2671
Fit State Fit name
Data
Harmonic Motion x vs. t
Fit type
fourier1
R-square
0.13345
SSE
DFE
0.26712
296
Adj R-sq
0.12467
RMSE
0.030041
# Coeff
Valic
R-square
0.1335
4
DFE
296.0000
Adj R-sq
0.1247
RMSE
0.0300
What point on the spring or different masses should be the place to measure the displacement of the spring? For instance, should you measure to the bottom of the hanging masses?
Chapter 31 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
Ch. 31 - A circular loop of wire is held in a uniform...Ch. 31 - In Figure 30.8a, a given applied force of...Ch. 31 - Figure 30.12 Figure 30.12 shows a circular loop of...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.4QQCh. 31 - In an equal-arm balance from the early 20th...Ch. 31 - Figure OQS1.I is a graph of the magnetic flux...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.2OQCh. 31 - A rectangular conducting loop is placed near a...Ch. 31 - A circular loop of wire with a radius of 4.0 cm is...Ch. 31 - A square, flat loop of wire is pulled at constant...
Ch. 31 - The bar in Figure OQ31.6 moves on rails to the...Ch. 31 - A bar magnet is held in a vertical orientation...Ch. 31 - What happens to the amplitude of the induced emf...Ch. 31 - Two coils are placed near each other as shown in...Ch. 31 - A circuit consists of a conducting movable bar and...Ch. 31 - Two rectangular loops of wire lie in the same...Ch. 31 - In Section 7.7, we defined conservative and...Ch. 31 - A spacecraft orbiting the Earth has a coil of wire...Ch. 31 - In a hydroelectric dam, how is energy produced...Ch. 31 - A bar magnet is dropped toward a conducting ring...Ch. 31 - A circular loop of wire is located in a uniform...Ch. 31 - A piece of aluminum is dropped vertically downward...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.7CQCh. 31 - When the switch in Figure CQ31.8a is closed, a...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.9CQCh. 31 - A loop of wire is moving near a long, straight...Ch. 31 - A flat loop of wire consisting of a single turn of...Ch. 31 - An instrument based on induced emf has been used...Ch. 31 - Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a...Ch. 31 - A 25-turn circular coil of wire has diameter 1.00...Ch. 31 - A circular loop of wire of radius 12.0 cm is...Ch. 31 - A circular loop of wire of radius 12.0 cm is...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.7PCh. 31 - A strong electromagnet produces a uniform magnetic...Ch. 31 - A 30-turn circular coil of radius 4.00 cm and...Ch. 31 - Scientific work is currently under way to...Ch. 31 - An aluminum ring of radius r1 = 5.00 cm and...Ch. 31 - An aluminum ring of radius r1 and resistance R is...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.13PCh. 31 - A coil of 15 turns and radius 10.0 cm surrounds a...Ch. 31 - A square, single-turn wire loop = 1.00 cm on a...Ch. 31 - A long solenoid has n = 400 turns per meter and...Ch. 31 - A coil formed by wrapping 50 turns of wire in the...Ch. 31 - When a wire carries an AC current with a known...Ch. 31 - A toroid having a rectangular cross section (a =...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.20PCh. 31 - A helicopter (Fig. P30.11) has blades of length...Ch. 31 - Use Lenzs law 10 answer the following questions...Ch. 31 - A truck is carrying a steel beam of length 15.0 in...Ch. 31 - A small airplane with a wingspan of 14.0 m is...Ch. 31 - A 2.00-m length of wire is held in an eastwest...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.26PCh. 31 - Figure P31.26 shows a lop view of a bar that can...Ch. 31 - A metal rod of mass m slides without friction...Ch. 31 - A conducting rod of length moves on two...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.30PCh. 31 - Review. Figure P31.31 shows a bar of mass m =...Ch. 31 - Review. Figure P31.31 shows a bar of mass m that...Ch. 31 - The homopolar generator, also called the Faraday...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.34PCh. 31 - Review. Alter removing one string while...Ch. 31 - A rectangular coil with resistance R has N turns,...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.37PCh. 31 - An astronaut is connected to her spacecraft by a...Ch. 31 - Within the green dashed circle show in Figure...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.40PCh. 31 - Prob. 31.41PCh. 31 - 100-turn square coil of side 20.0 cm rotates about...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.43PCh. 31 - Figure P30.24 (page 820) is a graph of the induced...Ch. 31 - In a 250-turn automobile alternator, the magnetic...Ch. 31 - In Figure P30.26, a semicircular conductor of...Ch. 31 - A long solenoid, with its axis along the x axis,...Ch. 31 - A motor in normal operation carries a direct...Ch. 31 - The rotating loop in an AC generator is a square...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.50PCh. 31 - Prob. 31.51APCh. 31 - Suppose you wrap wire onto the core from a roll of...Ch. 31 - A circular coil enclosing an area of 100 cm2 is...Ch. 31 - A circular loop of wire of resistance R = 0.500 ...Ch. 31 - A rectangular loop of area A = 0.160 m2 is placed...Ch. 31 - A rectangular loop of area A is placed in a region...Ch. 31 - Strong magnetic fields are used in such medical...Ch. 31 - Consider the apparatus shown in Figure P30.32: a...Ch. 31 - A guitars steel string vibrates (see Fig. 30.5)....Ch. 31 - Why is the following situation impossible? A...Ch. 31 - The circuit in Figure P3 1.61 is located in a...Ch. 31 - Magnetic field values are often determined by...Ch. 31 - A conducting rod of length = 35.0 cm is free to...Ch. 31 - Review. A particle with a mass of 2.00 1016 kg...Ch. 31 - The plane of a square loop of wire with edge...Ch. 31 - In Figure P30.38, the rolling axle, 1.50 m long,...Ch. 31 - Figure P30.39 shows a stationary conductor whose...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.68APCh. 31 - A small, circular washer of radius a = 0.500 cm is...Ch. 31 - Figure P30.41 shows a compact, circular coil with...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.71APCh. 31 - Review. In Figure P30.42, a uniform magnetic field...Ch. 31 - An N-turn square coil with side and resistance R...Ch. 31 - A conducting rod of length moves with velocity v...Ch. 31 - The magnetic flux through a metal ring varies with...Ch. 31 - A rectangular loop of dimensions and w moves with...Ch. 31 - A long, straight wire carries a current given by I...Ch. 31 - A thin wire = 30.0 cm long is held parallel to...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.79CPCh. 31 - An induction furnace uses electromagnetic...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.81CPCh. 31 - A betatron is a device that accelerates electrons...Ch. 31 - Review. The bar of mass m in Figure P30.51 is...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Let's assume that the brightness of a field-emission electron gun is given by β = 4iB π² d²α² a) Assuming a gun brightness of 5x108 A/(cm²sr), if we want to have an electron beam with a semi-convergence angle of 5 milliradian and a probe current of 1 nA, What will be the effective source size? (5 points) b) For the same electron gun, plot the dependence of the probe current on the parameter (dpa) for α = 2, 5, and 10 milliradian, respectively. Hint: use nm as the unit for the electron probe size and display the three plots on the same graph. (10 points)arrow_forwardi need step by step clear answers with the free body diagram clearlyarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- Review the data in Data Table 1 and examine the standard deviations and 95% Margin of Error calculations from Analysis Questions 3 and 4 for the Acceleration of the 1st Based on this information, explain whether Newton’s Second Law of Motion, Equation 1, was verified for your 1st Angle. Equation: SF=ma Please help with explaining the information I collected from a lab and how it relates to the equation and Newton's Second Law. This will help with additional tables in the lab. Thanks!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the problem step by step with explanations along side each step stating what's been done correctly please. Thank you!! ( preferably type out everything)arrow_forwardAnswer thisarrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote instantarrow_forwardKirchoff's Laws. A circuit contains 3 known resistors, 2 known batteries, and 3 unknown currents as shown. Assume the current flows through the circuit as shown (this is our initial guess, the actual currents may be reverse). Use the sign convention that a potential drop is negative and a potential gain is positive. E₂ = 8V R₁₁ = 50 R₂ = 80 b с w 11 www 12 13 E₁ = 6V R3 = 20 a) Apply Kirchoff's Loop Rule around loop abefa in the clockwise direction starting at point a. (2 pt). b) Apply Kirchoff's Loop Rule around loop bcdeb in the clockwise direction starting at point b. (2 pt). c) Apply Kirchoff's Junction Rule at junction b (1 pt). d) Solve the above 3 equations for the unknown currents I1, 12, and 13 and specify the direction of the current around each loop. (5 pts) I1 = A 12 = A 13 = A Direction of current around loop abef Direction of current around loop bcde (CW or CCW) (CW or CCW)arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward4.) The diagram shows the electric field lines of a positively charged conducting sphere of radius R and charge Q. A B Points A and B are located on the same field line. A proton is placed at A and released from rest. The magnitude of the work done by the electric field in moving the proton from A to B is 1.7×10-16 J. Point A is at a distance of 5.0×10-2m from the centre of the sphere. Point B is at a distance of 1.0×10-1 m from the centre of the sphere. (a) Explain why the electric potential decreases from A to B. [2] (b) Draw, on the axes, the variation of electric potential V with distance r from the centre of the sphere. R [2] (c(i)) Calculate the electric potential difference between points A and B. [1] (c(ii)) Determine the charge Q of the sphere. [2] (d) The concept of potential is also used in the context of gravitational fields. Suggest why scientists developed a common terminology to describe different types of fields. [1]arrow_forward3.) The graph shows how current I varies with potential difference V across a component X. 904 80- 70- 60- 50- I/MA 40- 30- 20- 10- 0+ 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 VIV Component X and a cell of negligible internal resistance are placed in a circuit. A variable resistor R is connected in series with component X. The ammeter reads 20mA. 4.0V 4.0V Component X and the cell are now placed in a potential divider circuit. (a) Outline why component X is considered non-ohmic. [1] (b(i)) Determine the resistance of the variable resistor. [3] (b(ii)) Calculate the power dissipated in the circuit. [1] (c(i)) State the range of current that the ammeter can measure as the slider S of the potential divider is moved from Q to P. [1] (c(ii)) Describe, by reference to your answer for (c)(i), the advantage of the potential divider arrangement over the arrangement in (b).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What is Electromagnetic Induction? | Faraday's Laws and Lenz Law | iKen | iKen Edu | iKen App; Author: Iken Edu;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3HyORmBip-w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY