
Concept explainers
Draw the products of each reaction.
a. 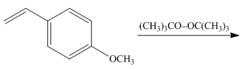 e.
e. 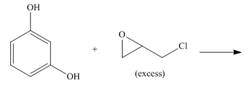
b. 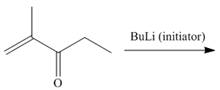 f.
f. 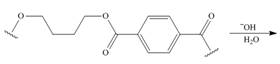
c. 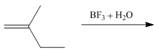 g.
g. 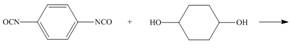
d. 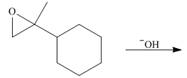 h.
h. 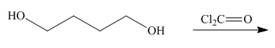
(a)
Interpretation: The product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Radical polymerization takes place via free radical intermediate. The peroxide used in this polymerization forms the free radical
The alkenes which have the substituents that can stabilize the radicals undergo radical polymerization.
Answer to Problem 30.49P
The product for the given reaction is,
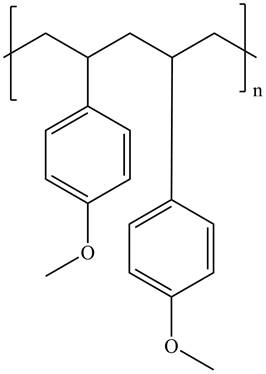
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
The given alkene undergoes radical polymerization in presence of peroxide to form the polymer. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
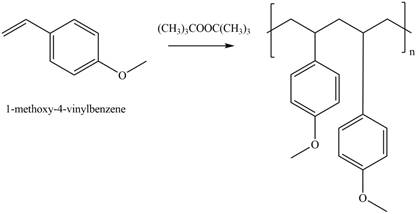
Figure 2
The product for the given reaction is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The anionic polymerization is a chain growth polymerization. Anionic polymerization takes place in alkene substituted with electron withdrawing groups and epoxides. In this polymerization the initator is anion.
Answer to Problem 30.49P
The product for the given reaction is,
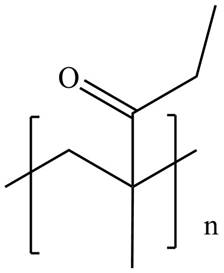
Figure 3
Explanation of Solution
The given alkene undergoes anionic polymerization in presence of
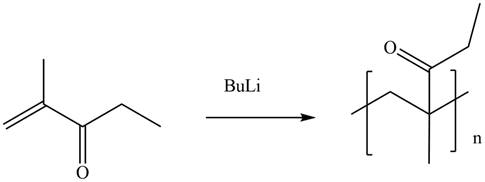
Figure 4
The product for the given reaction is shown in Figure 3.
(c)
Interpretation: The product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The cationic polymerization is a chain growth polymerization. This polymerization occurs in the alkenes with substituents which can stabilize the intermediate carbocation. This is an electrophilc addition reaction that involves the carbocations as intermediates.
Answer to Problem 30.49P
The product for the given reaction is,
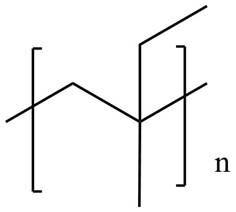
Figure 5
Explanation of Solution
The given alkene undergoes cationic polymerization in presence of boron trifluoride in aqueous medium to form the polymer. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
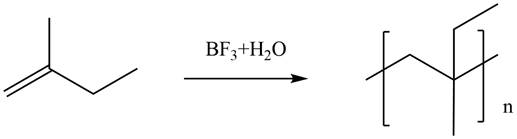
Figure 6
The product for the given reaction is shown in Figure 5.
(d)
Interpretation: The product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The anionic polymerization is a chain growth polymerization. Anionic polymerization takes place in alkene substituted with electron withdrawing groups and epoxides. In this polymerization the initator is anion.
Answer to Problem 30.49P
The product for the given reaction is,
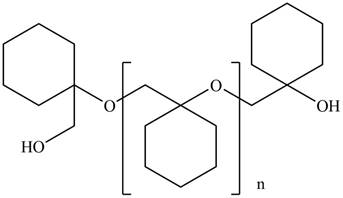
Figure 7
Explanation of Solution
The given epoxide undergoes anionic polymerization in presence base to form the polymer. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
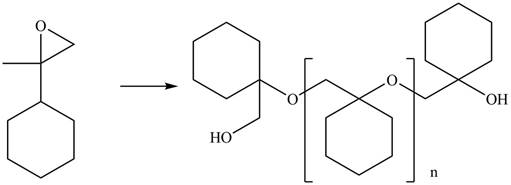
Figure 8
The product for the given reaction is shown in Figure 7.
(e)
Interpretation: The product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: In Step-growth polymerization the monomers with different functional groups combine together to form the polymer with the loss of small molecule such as water. For example polyamides, polyesters, polyurethanes, polycarbonates and epoxy resins.
Prepolymer which is composed of polymeric chain with epoxide rings at the each terminal and cross linked polymers. These two components form epoxy resins.
Answer to Problem 30.49P
The product for the given reaction is,
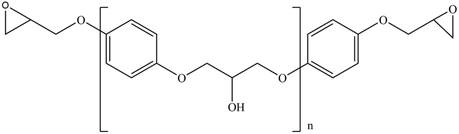
Figure 9
Explanation of Solution
The resorcinol undergoes step growth polymerization in presence of excess epichlorohydrin to form the polymer. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
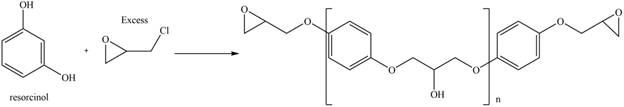
Figure 10
The product for the given reaction is shown in Figure 9.
(f)
Interpretation: The product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: In Step-growth polymerization the monomers with different functional groups combine together to form the polymer with the loss of small molecule such as water. For example polyamides, polyesters, polyurethanes, polycarbonates and epoxy resins.
The polyesters are formed by the reaction of acid and alcohol as monomers.
Answer to Problem 30.49P
The product for the given reaction is,
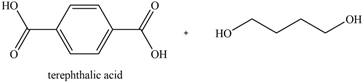
Figure 11
Explanation of Solution
The given polyester on hydrolysis produces its monomers. The ester linkages are cleaved to produce alcohol and acid. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
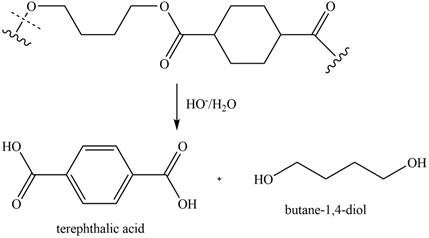
Figure 12
The product for the given reaction is shown in Figure 11.
(g)
Interpretation: The product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: In Step-growth polymerization the monomers with different functional groups combine together to form the polymer with the loss of small molecule such as water. For example polyamides, polyesters, polyurethanes, polycarbonates and epoxy resins.
Polyurethanes contain carbonyl compounds bonded to
Answer to Problem 30.49P
The product for the given reaction is,
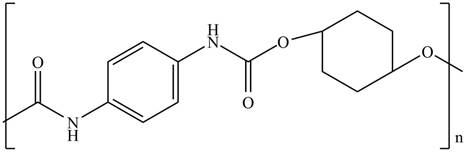
Figure 13
Explanation of Solution
The given diisocyanate reacts with the given diol to undergo step growth polymerization in to form the polyurethane. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
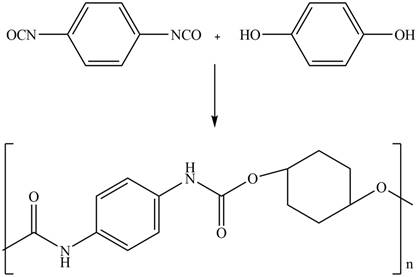
Figure 14
The product for the given reaction is shown in Figure 13.
(g)
Interpretation: The product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: In Step-growth polymerization the monomers with different functional groups combine together to form the polymer with the loss of small molecule such as water. For example polyamides, polyesters, polyurethanes, polycarbonates and epoxy resins.
Polycarbonates contain carbonyl compounds bonded to two
Answer to Problem 30.49P
The product for the given reaction is,
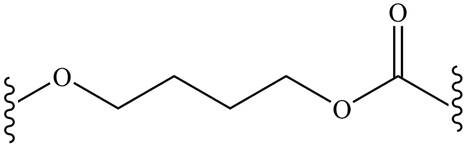
Figure 15
Explanation of Solution
The given diol reacts with phosgene to undergo step growth polymerization to form the polycarbonate. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
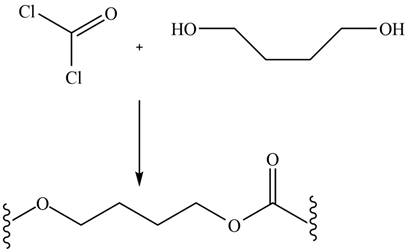
Figure 16
The product for the given reaction is shown in Figure 15.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 30 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





