
Concept explainers
Draw the products of each reaction.
a. 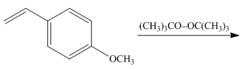 e.
e. 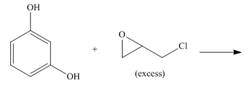
b. 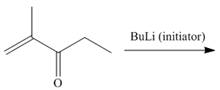 f.
f. 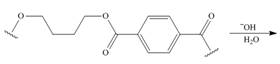
c. 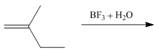 g.
g. 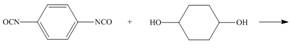
d. 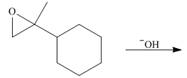 h.
h. 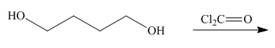
(a)
Interpretation: The product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Radical polymerization takes place via free radical intermediate. The peroxide used in this polymerization forms the free radical
The alkenes which have the substituents that can stabilize the radicals undergo radical polymerization.
Answer to Problem 30.49P
The product for the given reaction is,
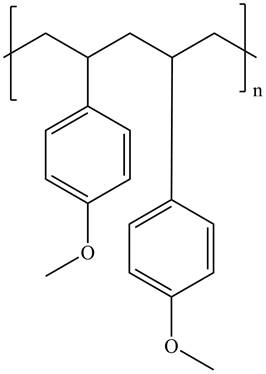
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
The given alkene undergoes radical polymerization in presence of peroxide to form the polymer. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
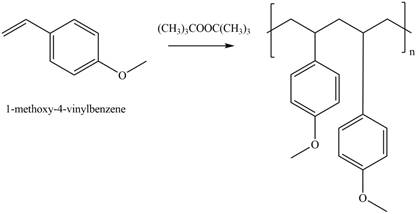
Figure 2
The product for the given reaction is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The anionic polymerization is a chain growth polymerization. Anionic polymerization takes place in alkene substituted with electron withdrawing groups and epoxides. In this polymerization the initator is anion.
Answer to Problem 30.49P
The product for the given reaction is,
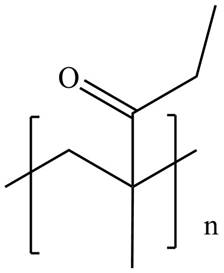
Figure 3
Explanation of Solution
The given alkene undergoes anionic polymerization in presence of
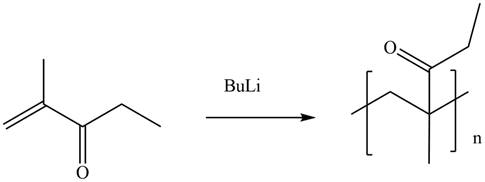
Figure 4
The product for the given reaction is shown in Figure 3.
(c)
Interpretation: The product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The cationic polymerization is a chain growth polymerization. This polymerization occurs in the alkenes with substituents which can stabilize the intermediate carbocation. This is an electrophilc addition reaction that involves the carbocations as intermediates.
Answer to Problem 30.49P
The product for the given reaction is,
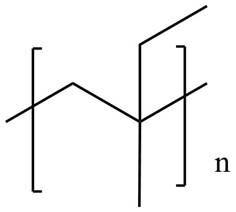
Figure 5
Explanation of Solution
The given alkene undergoes cationic polymerization in presence of boron trifluoride in aqueous medium to form the polymer. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
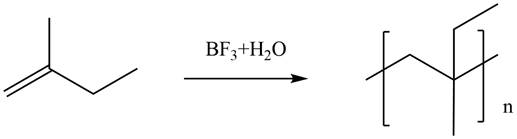
Figure 6
The product for the given reaction is shown in Figure 5.
(d)
Interpretation: The product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The anionic polymerization is a chain growth polymerization. Anionic polymerization takes place in alkene substituted with electron withdrawing groups and epoxides. In this polymerization the initator is anion.
Answer to Problem 30.49P
The product for the given reaction is,
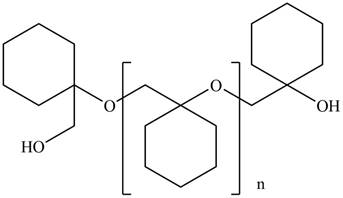
Figure 7
Explanation of Solution
The given epoxide undergoes anionic polymerization in presence base to form the polymer. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
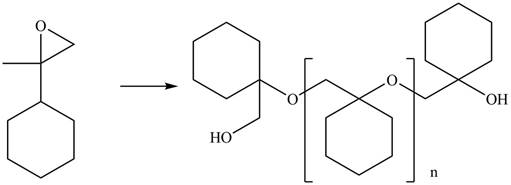
Figure 8
The product for the given reaction is shown in Figure 7.
(e)
Interpretation: The product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: In Step-growth polymerization the monomers with different functional groups combine together to form the polymer with the loss of small molecule such as water. For example polyamides, polyesters, polyurethanes, polycarbonates and epoxy resins.
Prepolymer which is composed of polymeric chain with epoxide rings at the each terminal and cross linked polymers. These two components form epoxy resins.
Answer to Problem 30.49P
The product for the given reaction is,
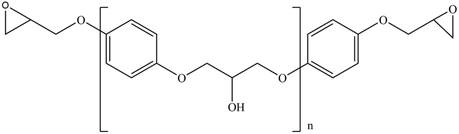
Figure 9
Explanation of Solution
The resorcinol undergoes step growth polymerization in presence of excess epichlorohydrin to form the polymer. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
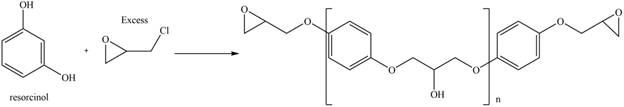
Figure 10
The product for the given reaction is shown in Figure 9.
(f)
Interpretation: The product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: In Step-growth polymerization the monomers with different functional groups combine together to form the polymer with the loss of small molecule such as water. For example polyamides, polyesters, polyurethanes, polycarbonates and epoxy resins.
The polyesters are formed by the reaction of acid and alcohol as monomers.
Answer to Problem 30.49P
The product for the given reaction is,
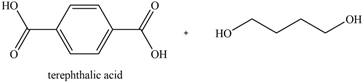
Figure 11
Explanation of Solution
The given polyester on hydrolysis produces its monomers. The ester linkages are cleaved to produce alcohol and acid. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
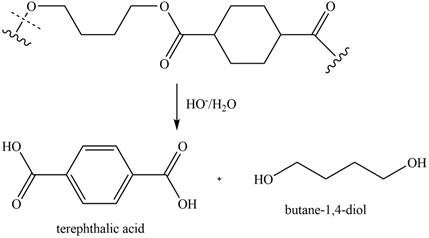
Figure 12
The product for the given reaction is shown in Figure 11.
(g)
Interpretation: The product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: In Step-growth polymerization the monomers with different functional groups combine together to form the polymer with the loss of small molecule such as water. For example polyamides, polyesters, polyurethanes, polycarbonates and epoxy resins.
Polyurethanes contain carbonyl compounds bonded to
Answer to Problem 30.49P
The product for the given reaction is,
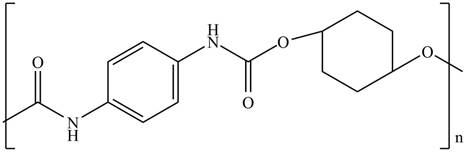
Figure 13
Explanation of Solution
The given diisocyanate reacts with the given diol to undergo step growth polymerization in to form the polyurethane. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
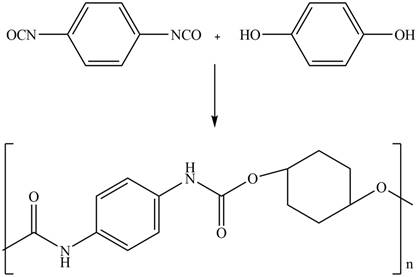
Figure 14
The product for the given reaction is shown in Figure 13.
(g)
Interpretation: The product for the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: In Step-growth polymerization the monomers with different functional groups combine together to form the polymer with the loss of small molecule such as water. For example polyamides, polyesters, polyurethanes, polycarbonates and epoxy resins.
Polycarbonates contain carbonyl compounds bonded to two
Answer to Problem 30.49P
The product for the given reaction is,
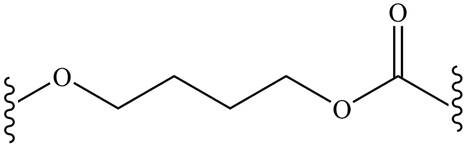
Figure 15
Explanation of Solution
The given diol reacts with phosgene to undergo step growth polymerization to form the polycarbonate. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
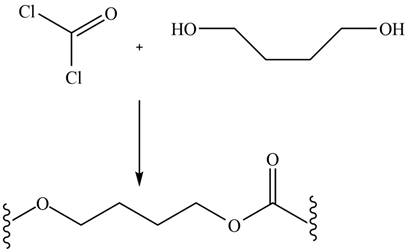
Figure 16
The product for the given reaction is shown in Figure 15.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 30 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Identify the amino acids by name. Illustrate a titration curve for this tetrapeptide indicating the pKa's for each ionizable groups and identify the pI for this tetrapeptide. please helparrow_forward↓ ina xSign x Sign X labs X Intro X Cop Xa chat X My Cx Grac X Laur x Laur xash learning.com/ihub/assessment/f188d950-dd73-11e0-9572-0800200c9a66/d591b3f2-d5f7-4983-843c-0d00c1c0340b/f2b47861-07c4-4d1b-a1ee-e7db2 +949 pts /3400 K Question 16 of 34 > © Macmillan Learning Draw the major E2 reaction product formed when cis-1-chloro-2-ethylcyclohexane (shown) reacts with hydroxide ion in DMSO. H CH2CH3 H H HO- H H H Cl DMSO H H C Select Draw Templates More C H 0 2 Erasearrow_forwardA common buffer for stabilizing antibodies is 100 mM Histidine at pH 7.0. Describe the preparation of this buffer beginning with L-Histidine monohydrochloride monohydrate and 1 M NaOH. Be certain to show the buffering reaction that includes the conjugate acid and base.arrow_forward
- Fina x | Sign X Sign X lab: X Intro X Cop) X a chat x My x Grad xLaur x Laur x a sheg X S Shoj XS SHE X acmillanlearning.com/ihub/assessment/f188d950-dd73-11e0-9572-0800200c9a66/d591b3f2-d5f7-4983-843c-0d00c1c0340b/f2b47861-07c4-4d1b-a1ee-e7db27d6b4ee?actualCourseld=d591b3f2- 5 © Macmillan Learning Organic Chemistry Maxwell presented by Macmillan Learning For the dehydrohalogenation (E2) reaction shown, draw the Zaitsev product, showing the stereochemistry clearly. H H KOH Br EtOH Heat Select Draw Templates More Erase // C H Q Search hp Q2 Q Δ קו Resouarrow_forwardIs the structural form shown possible given the pKa constraints of the side chains?arrow_forwardon x Fina X Sign X Sign x lab X Intro X Cop X chat X My x Grac x Laur x Laur x ashes x S Shox S SHE x a eve.macmillanlearning.com/ihub/assessment/f188d950-dd73-11e0-9572-0800200c9a66/d591b3f2-d5f7-4983-843c-0d00c1c0340b/f2b47861-07c4-4d1b-a1ee-e7db27d6b4ee?actualCourseld=d591b3f2-c stions estion. ct each urces. +95 Macmillan Learning Draw the product formed by the reaction of potassium t-butoxide with (15,25)-1-bromo-2-methyl-1-phenylbutane (shown). Clearly show the stereochemistry of the product. H BH (CH3)3CO-K+ +100 H3CW (CH3)3COH +85 H3CH2C +95 ossible ↓ Q Search Select Draw Templates More C H 0 bp A Erase 2Q 112 Resouarrow_forward
- Identify the structure of the PTH derivative generated after two rounds of Edman degradation.arrow_forwardUse the data below from an electron impact mass spectrum of a pure compound to deduce its structure. Draw your structure in the drawing window. Data selected from the NIST WebBook, https://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/ m/z Relative intensity 31 0.5 30 26 29 22 28 100 27 33 26 23 15 4 • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. 妊 n ? Previous Nextarrow_forwardfor this question. Write the molecular formula for a compound with the possible elements C, H, N and O that exhibits a molecular ion at M+ = 98.1106. Exact Masses of the Most Abundant Isotope of Selected Elements Isotope Natural abundance (%) Exact mass 1H 99.985 1.008 12C 98.90 12.000 14N 99.63 14.003 160 99.76 15.995 Molecular formula (In the order CHNO, with no subscripts)arrow_forward
- PLEASE READ!!! I DONT WANT EXAMPLES, I DONT WANT WORDS OR PARAGRAPHS!!! PLEASE I UNDERSTAND THE BASICS BUT THIS IS AN EXCEPTION THAT EVEN THE INTERNET CANT HELP!!!! THIS IS THE THIRD TIME I'VE SENT THOSE QUESTIONS SO PLEASE DONT RESEND THE SAME STUFF, ITS NOT HELPING ME!!! I ALSO ALREADY TRIED TO DRAW THE MECHANISM MYSELF, SO IF ITS RIGHT PLEASE TELL ME OR TELL ME WHAT I HAVE TO CHANGE!!! First image: I have to SHOW (DRAWING) the mechanism (with arows and structures of molecules) NOT WORDS PLEASE! of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primary Second image: I have to show the mechanism (IMAGE) (with arrows and structures of the molecules) NOT WORDS PLEASE !! for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion HOMEWORK, NOT EXAM!! ALL DETAILS ARE IN THE IMAGES PLEASE LOOK AT THE IMAGES, DONT LOOK AT THE AI GENERATED TEXT!!!arrow_forwardWrite the molecular formula for a compound with the possible elements C, H, N and O that exhibits a molecular ion at M+ = 85.0899. Exact Masses of the Most Abundant Isotope of Selected Elements Isotope Natural abundance (%) Exact mass 1H 99.985 1.008 12C 98.90 12.000 14N 99.63 14.003 160 99.76 15.995 Molecular formula (In the order CHNO, with no subscripts)arrow_forwardUse the data below from an electron impact mass spectrum of a pure compound to deduce its structure. Draw your structure in the drawing window. Data selected from the NIST WebBook, https://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/ m/z Relative intensity 59 3.0 58 64 43 100 15 23 • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. •You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. + n[] 85 // ? CH4 Previous Nextarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





