
Concept explainers
Complete this concept map on animal movement.
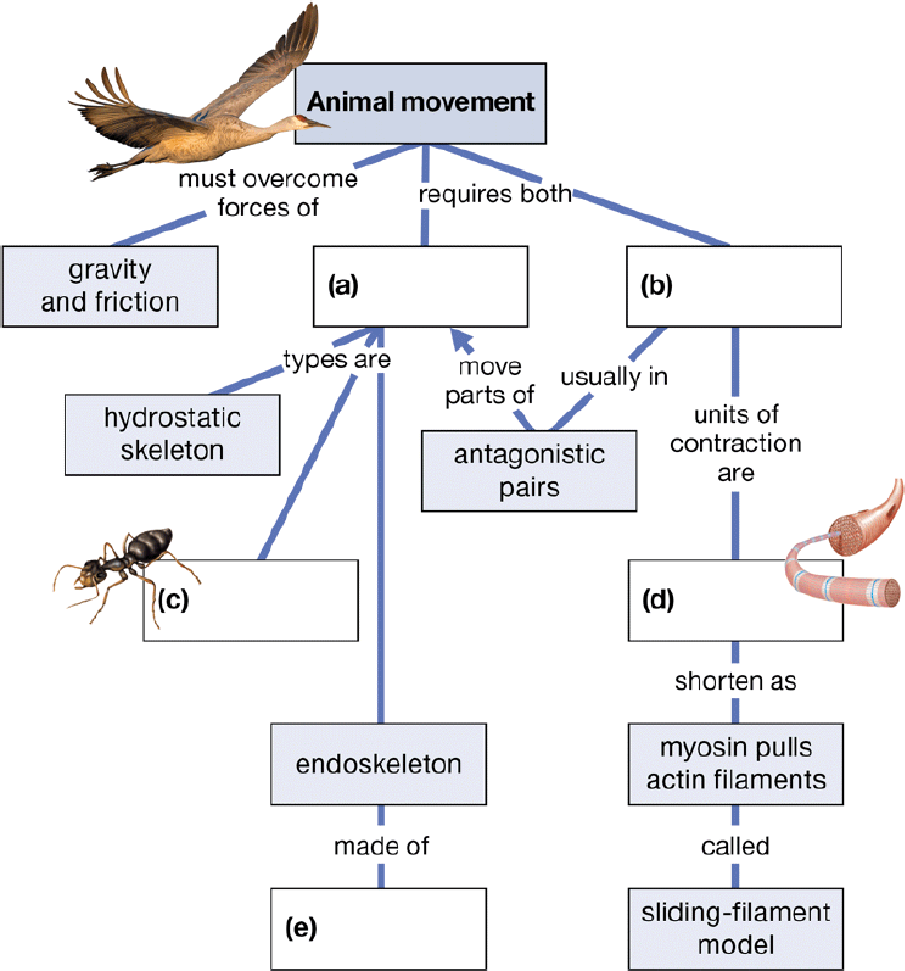
To complete: The given map showing the animal movement.
Introduction:
Movement is a distinguishing characteristic of animals. Even animals that are attached to a substrate move their body parts. All types of animal movement have underlying similarities. At the cellular level, every form of movement involves protein strands moving against one another, an energy-consuming process.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
Fig. 1 shows the completed map of the animal movement.
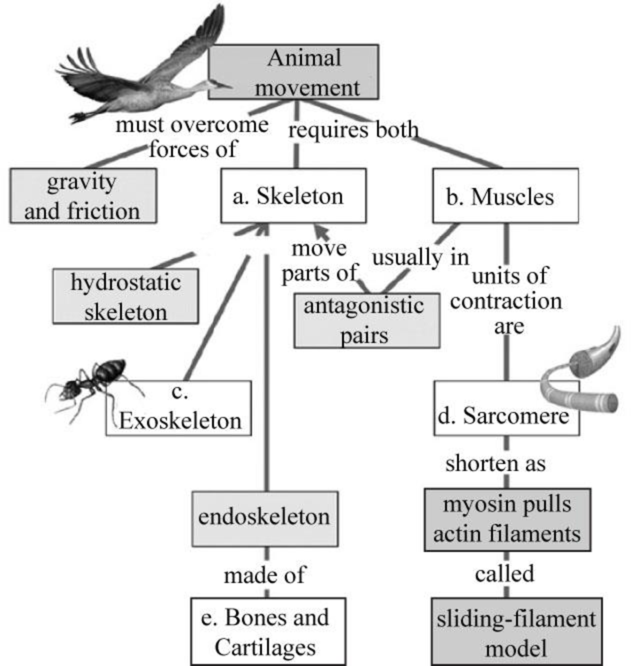
Fig. 1: Completed map of the animal movement
(a)
Correct answer: Skeleton.
Movement in animals requires both the skeleton as well as the muscle. There are many types of skeletons present among the various organisms, which include the endoskeleton, exoskeleton, and hydrostatic skeleton. Each skeleton is associated with different types of movement, such as, flying, walking, running, crawling, and others. Hence, the correct answer is skeleton.
(b)
Correct answer: Muscles.
In every organism, muscles are required to generate a required amount of energy, whether walking, running, swimming, or flying. Hence, the correct answer is muscles.
(c)
Correct answer: Exoskeleton.
The skeletons found among the diverse group of organisms are categorized into three types, which include the endoskeleton, hydrostatic skeleton, and exoskeleton. The exoskeleton is primarily found in the insects. Hence, the correct answer is exoskeleton.
(d)
Correct answer: Sarcomere.
Sarcomeres are the units of muscle contraction; they are found in the striated muscles and are present between 2-Z lines as a repeating unit. Hence, the correct answer is sarcomere.
(e)
Correct answer: Bones and Cartilages.
Endoskeletons are present inside the body and made up of bones and cartilages. Usually, all the vertebrates have a skeleton type as an endoskeleton. Hence, the correct answer is bones and cartilages.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 30 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Books a la Carte Plus Mastering Biology with eText -- Access Card Package (8th Edition)
- answer questions 1-10arrow_forwardAnswer Question 1-9arrow_forwardEx: Mr. Mandarich wanted to see if the color of light shined on a planthad an effect on the number of leaves it had. He gathered a group ofthe same species of plants, gave them the same amount of water, anddid the test for the same amount of time. Only the color of light waschanged. IV:DV:Constants:Control Gr:arrow_forward
- ethical considerations in medical imagingarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward2. In one of the reactions of the citric acid cycle, malate is oxidized to oxaloacetate. When this reaction is considered in isolation, a small amount of malate remains and is not oxidized. The best term to explain this is a. enthalpy b. entropy c. equilibrium d. free energy e. loss of energyarrow_forward
- 18. The citric acid cycle takes place in a. the chloroplasts b. the cytosol c. the inner mitochondrial membrane d. between the two mitochondrial membranes e. the mitochondrial matrix 40 WILarrow_forward8. Most reactions of anaerobic respiration are similar to a. aerobic respiration b. photosynthesis c. lactic acid fermentation d. alcoholic fermentation e. both c and darrow_forward12. Which of the following molecules can absorb light? a. Pigments b. Chlorophyll c. Rhodopsin d. Carotenoids e. All of the abovearrow_forward
- Which of the following proteins or protein complexes is directly required for the targeting of mitochondrial inner membrane multipass proteins, such as metabolite transporters, whose signal sequence is normally not cleaved after import? OA. TIM22 OB. TIM23 C. OXA OD. Mia40 OE SAMarrow_forwardQUESTION 9 An animal cell has been wounded and has a small rupture in its plasma membrane. Which of the following is more likely to happen next? OA. The cell rapidly cleaves by cytokinesis. OB. The rate of receptor-mediati endocytosis is increased. OC. The rate of exocytosis is increased. OD. The rate of pinocytosis is increased.arrow_forwardFor the a subunit of a trimeric G protein, A. a G-protein-coupled receptor GPCR) acts as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF), whereas a regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) can act as a GTPase-activating protein (GAP). B. a GPCR acts as a GAP, whereas an RGS can act as a GEF. C. both a GPCR and an RGS can act as a GEF. O D. both a GPCR and an RGS can act as a GAP OE. None of the above.arrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





