
Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781118539293
Author: J. David Irwin, R. Mark Nelms
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 9P
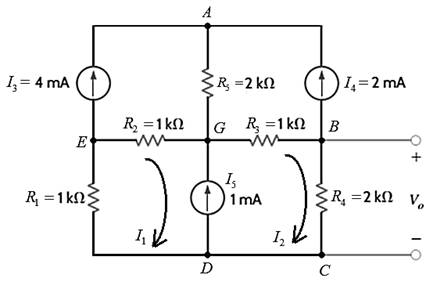
Find
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Don't use ai to answer I will report you answer
Don't use ai to answer I will report you answer
Answer all the questions
What is the minimum value of capacitor C1 required such that Vfiltered does not drop below 8 V? Use the design equation(but make sure you use the right “frequency” and the correct ripple voltage). Show your calculations. Display your circuit in circuit js.
Display Vsecondary (can use the voltage across the added 100 kΩ resistor) and Vfiltered in a “Combined Scope”. Display VDC in a separate scope: a) Turn on “Max Scale”, “Show Peak Value” and “Show Negative Peak Value”: b) Run the simulator and adjust the window and simulation speed and time step to be able to see a couple of cycles. Include a screen capture
Document the minimum and maximum values for Vfiltered in your lab report. Is Vfiltered maintained to be above 8 V? By how much? Why? Explain the waveform shape captured Vfiltered. It may help your understanding to rerun the simulation with C1 removed and compare that waveform for Vfiltered to that captured
Chapter 3 Solutions
Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis
Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find V1 in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Find both Io and Vo in the network in Fig. P3.2...Ch. 3 - Find I1 in the network in Fig. P3.3.Ch. 3 - Find I1 in the circuit in Fig. P3.4.Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find V1 in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Find V1 and V2 in the circuit in Fig. P3.6 using...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find both V1 and Vo in the...Ch. 3 - Write the node equations for the circuit in Fig....Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P3.9.Ch. 3 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P3.10 using nodal...
Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Io in the network in...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P3.13 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P3.15 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in the network in...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P3.19 using...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P3.20 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P3.21 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P3.22 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to determine the node voltages...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in the network in...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to solve for the node voltages...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P3.27 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P3.28 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P3.30 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P3.31 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Using analysis, find Vo in the network in Fig....Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P3.34 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P3.35 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P3.36 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P3.38 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P3.39 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P3.41.Ch. 3 - Find I0 in the network in Fig. P3.42 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P3.43 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P3.44 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P3.45 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P3.46 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P3.47 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P3.49 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P3.50 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P3.51.Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Determine Vo in the network in Fig. P3.53 using...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. B3.56 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to solve for IA in the network...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find V1,V2,V3, and V4 in the...Ch. 3 - Determine Vo in the network in Fig. P3.60 using...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find V1,V2,V3, and V4 in the...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to determine the node voltages...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to determine the node voltages...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to determine the node voltages...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P3.65 using mesh...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P3.66 using mesh...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P3.67 using mesh...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P3.68 using mesh...Ch. 3 - Use mesh analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P3.70 using mesh...Ch. 3 - Use mesh analysis to find Vo in the network in...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P3.72.Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P3.73 using mesh...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in Fig. P3.74 using mesh analysis.Ch. 3 - Use loop analysis to find Vo in the network in...Ch. 3 - Find Io in Fig. P3.76 using mesh analysis.Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P3.77 using loop...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P3.78 using loop...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P3.79 using mesh...Ch. 3 - Use mesh analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Use mesh analysis to find Io in the network in...Ch. 3 - Use loop analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Use loop analysis to calculate the power supplied...Ch. 3 - Use loop analysis to find Io and I1 in the network...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P3.85 using loop...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P3.86 using...Ch. 3 - Find Io in network in Fig. P3.87 using loop...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P3.88 using loop...Ch. 3 - Use loop analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Using loop analysis, find Vo in the network in...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P3.91 using mesh...Ch. 3 - Use analysis to find Io in the network in Fig....Ch. 3 - Using loop analysis, find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Find the mesh currents in the network in Fig....Ch. 3 - Using loop analysis, find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Using loop analysis, find Vo in the network in...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P3.97 using loop...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P3.98 using loop...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P3.99 using loop...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in Fig. P3.100.Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P3.101 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Use loop analysis to find Vo in the network in...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in the network in...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. P3.104 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find the power supplied by the 2-A current source...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P3.106 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P3.107 using loop...Ch. 3 - Use mesh analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Using mesh analysis, find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P3.110 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find Vx in the circuit in Fig. P3.111.Ch. 3 - Find Io in the circuit in Fig. P3.112.Ch. 3 - Write mesh equations for the circuit in Fig....Ch. 3 - Find Ix in the circuit in Fig. P3.114 using loop...Ch. 3 - Solve for the mesh currents defined in the circuit...Ch. 3 - Solve for the assigned mesh currents in the...Ch. 3 - Using the assigned mesh currents shown in Fig....Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the network in Fig. B3.118.Ch. 3 - Using loop analysis, find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Using loop analysis, find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Using loop analysis, find Vo in the network in...Ch. 3 - Using loop analysis, find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Using loop analysis, find Io in the network in...Ch. 3 - Use analysis to find Io in the circuit in Fig....Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. P3.125 using loop...Ch. 3 - Using loop analysis, find Io in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Use mesh analysis to determine the power delivered...Ch. 3 - Use mesh analysis to find the power delivered by...Ch. 3 - Use nodal analysis to find Vo in the circuit in...Ch. 3 - Find Io in the network in Fig. P3.130 using nodal...Ch. 3 - Find Vo in the circuit in Fig. 3PFE-l. a. 3.33 Vc....Ch. 3 - Determine the power dissipated in the 6-ohm...Ch. 3 - Find the current Ix in the 4-ohm resistor in the...Ch. 3 - Determine the voltage Vo in the circuit in Fig....Ch. 3 - What is the voltage V1 in the circuit in Fig....
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A Three-phase, 3.3 kV, Y connected, 500 kVA, 16 salient pole rotor alternator. The direct and quadrature axis synchronous reactance are 8 and 50/ph respectively. The machine is supplying a load of 350 kVA at 0.8 power factor lagging, Determine: 1. Power angle. 2. Percentage Voltage regulation. 3. Developed power. 4. Reluctance powerarrow_forwardA Three-phase, 12 pole, Y-connected alternator has 108 slots and 14 conductors per slot. The windings are (5/6th) pitched. The flux per pole is 57 mWb distributed sinusoidally over the pole. If the machine runs at 500 r.p.m., determine the following: (a) The frequency of the generated e.m.f., (b) The distribution factor, (c) The pitch factor, and (d) The phase and line values of the generated e.m.f.?arrow_forwardMany machines, such as lathes, milling machines, and grinders, are equipped with tracers to reproduce the contours of templates. The figure is a schematic diagram of a hydraulic tracer in which the tool duplicates the shape of the template on the workpiece. a) Explain how the system works. b) Draw a block diagram and identify the system's elements. c) Classify the control system. Oil under pressure Template Style Tool Piece of workarrow_forward
- 2. Refrigerators to maintain the product at a given temperature have a control system. a) Explain how the control system is or how you think it should be (Make a diagram). b) Make the typical block diagram of a control system and identify the components in the refrigerator system. c) Classify the control system.arrow_forward3. Internal combustion engines require a cooling system to function properly, which maintains the engine temperature at an appropriate value. Neither too high nor too low. There are several systems to control this temperature, the two best known are: • The classic one that uses a thermostat that regulates the flow of coolant (water), and where the fan is mechanically coupled to the engine. • In more recent vehicles, in addition to the thermostat, a temperature controller is used that turns an electric fan on and off. Select one of the two systems mentioned above and: a) Explain how it works, using diagrams. b) Make the typical block diagram of a feedback control system, identifying the components of the system. c) Classify the control system.arrow_forwardA 3-phase, star connected, 10 kVA, 380 V, salient pole alternator with direct and quadrature axis reactances of 15 and 8 0/ph respectively, delivers full-load current at 0.8 power factor lagging. Neglect the armature resistance. Determine the following: (a) The load angle, (b) The direct axis and quadrature axis components of armature current, (c) E.M.F induced voltage of the alternator, (d) The voltage regulation, and (e) The developed power by the alternator?arrow_forward
- A 2000 kVA,Y- connected alternator gives an open circuit line voltage of 3.3 kV for a field current of 65 A. For same field current the short circuit current is being equal to full load current. Calculate the full load voltage regulation at both 0.8 lagging p.f. and unity p.f., neglect armature resistance?arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Mesh Current Problems in Circuit Analysis - Electrical Circuits Crash Course - Beginners Electronics; Author: Math and Science;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DYg8B-ElK0s;License: Standard Youtube License