
The
*$15,000 tax liability ($50,000 income ×30%)- $12,000 tax lass carryover ($40,000 × 30%)
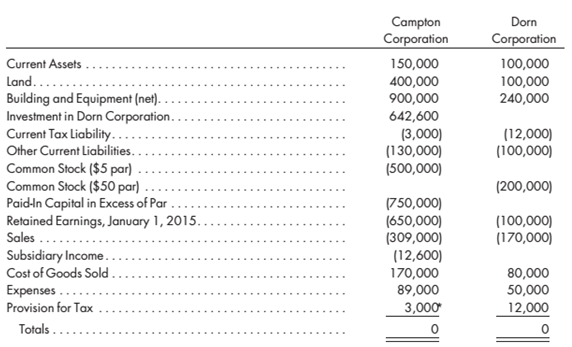
On January 1, 2015. Campion purchases 90% of the outstanding stock of Dorn Corporation for $630,000. The acquisition is a tax-free exchange for the seller. At the purchase date, Dorn's equipment is undervalued by $100,000 and has a remaining life of 10 years. All other assets have book values that approximate their fair values. Dorn Corporation has a tax loss carryover of $200,000, of which $50,000 is utilizable in 2015 and the balance in future periods. 1 he tax loss carryover is expected to be fully utilized. Any remaining excess is considered to be
2. Prepare the 2015 consolidated worksheet. Include columns for the eliminations and adjustments, the consolidated income statement, the NCl, the controlling
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Advanced Accounting


