
ANALYSIS+DESIGN OF LINEAR CIRCUITS(LL)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781119235385
Author: Thomas
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 3.80P
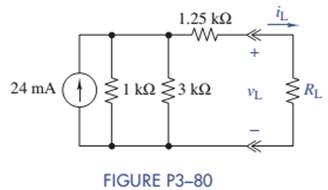
For the circuit of Figure P3-80, find the value of
- Maximum voltage. What is that voltage?
- Maximum current. What is that current?
- Maximum power. What is that power?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Show all the steps please,
Solve for the current through R2 if E2 is replaced by a current source of 10mA using superposition theorem.
R5=470Ω
R2=1000Ω
R6=820Ω
Please solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.
Please solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam today, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.
Chapter 3 Solutions
ANALYSIS+DESIGN OF LINEAR CIRCUITS(LL)
Ch. 3 - Formulate node-voltage equations for the circuit...Ch. 3 - (a) Formulate node-voltage equations for the...Ch. 3 - (a) Formulate node-voltage equations for the...Ch. 3 - Formulate node-voltage equations for the circuit...Ch. 3 - (a) Formulate node-voltage equations for the...Ch. 3 - Choose a ground wisely and formulate node-voltage...Ch. 3 - The following are a set of node-voltage equations;...Ch. 3 - Choose a ground wisely and formulate node-voltage...Ch. 3 - Formulate node-voltage equations for the circuit...Ch. 3 - Formulate node-voltage equations for the circuit...
Ch. 3 - (a) Formulate mesh-current equations for the...Ch. 3 - (a) Formulate mesh-current equations for the...Ch. 3 - (a) Formulate mesh-current equations for the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.16PCh. 3 - Formulate mesh-current equations for the circuit...Ch. 3 - For the circuit of figure P3-19 solve for iA,iB,...Ch. 3 - Formulate mesh-current equations for the circuit...Ch. 3 - The circuit in Figure P3-21 seems to require two...Ch. 3 - Formulate mesh-current equations for the circuit...Ch. 3 - Use simple engineering intuition to find the input...Ch. 3 - In Figure P3-24 all of the resistors are 1k and...Ch. 3 - Use Figure P3-24 and MATLAB to solve the following...Ch. 3 - Formulate mesh-current equations for the circuit...Ch. 3 - Find vO for the block diagram shown in figure...Ch. 3 - Design a voltage-divider circuit that will realize...Ch. 3 - Design a current-divider circuit that will realize...Ch. 3 - Using a single resistor, design a circuit that...Ch. 3 - Find the proportionality constant K=vO/vS for the...Ch. 3 - Find the proportionality constant K=iO/vS for the...Ch. 3 - Find the proportionality constant K=vO/iS for the...Ch. 3 - Find the proportionality constant K=iO/iS for the...Ch. 3 - Find the proportionality constant K=vO/vS for the...Ch. 3 - Use the unit output method to find K and vO in...Ch. 3 - Use the unit output method to find K and vO in...Ch. 3 - Use the unit output method to find K in Figure...Ch. 3 - Use the superposition principle to find vO in...Ch. 3 - Use the superposition principle to find vO in...Ch. 3 - Use the superposition principle to find vO in...Ch. 3 - (a) Use the superposition principle to find vO in...Ch. 3 - A linear circuit containing two sources drives a...Ch. 3 - A block diagram of a linear circuit is shown in...Ch. 3 - A certain linear circuit has four input voltages...Ch. 3 - When the current source is turned off in the...Ch. 3 - For the circuit in Figure P3—51, find the Thévenin...Ch. 3 - For the circuit in Figure P3—52, find the Thévenin...Ch. 3 - For the circuit of Figure P3—53, find the Thévenin...Ch. 3 - Find the Thévenin or Norton equivalent circuit...Ch. 3 - Find the Thévenin or Norton equivalent circuit...Ch. 3 - Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit seen by RL in...Ch. 3 - Find the Norton equivalent seen by RL in Figure...Ch. 3 - You need to determine the Thévenin equivalent...Ch. 3 - Find the Thévenin equivalent seen by RL in figure...Ch. 3 - The purpose of this problem is to use Thévenin...Ch. 3 - The circuit in Figure P3-62 was solved earlier...Ch. 3 - Assume that Figure P3-63 represents a model of the...Ch. 3 - The iv characteristic of the active circuit...Ch. 3 - You have successfully completed the first course...Ch. 3 - The Thévenin equivalent parameters of a practical...Ch. 3 - Use a sequence of source transformations to find...Ch. 3 - The circuit in Figure P3-68 provides power to a...Ch. 3 - A nonlinear resistor is connected across a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.71PCh. 3 - Find the Norton equivalent seen by RL in Figure...Ch. 3 - Find the Thévenin equivalent seen by RL in Figure...Ch. 3 - Find the Thévenin equivalent seen by RL in Figure...Ch. 3 - For the circuit of Figure P3-75, find the value of...Ch. 3 - For the circuit of Figure P3-76, find the value of...Ch. 3 - The resistance R in Figure P3-77 is adjusted until...Ch. 3 - When a 5-k resistor is connected across a...Ch. 3 - Find the value of R in the circuit of Figure P3-79...Ch. 3 - For the circuit of Figure P3-80, find the value of...Ch. 3 - A 1-k load needs 10 mA to operate correctly....Ch. 3 - A practical source delivers 25 mA to a load. The...Ch. 3 - A 10-V source is shown in Figure P3-83 that is...Ch. 3 - (a)Select RL and design an interface circuit for...Ch. 3 - The source in Figure P3-85 has a 100-mA output...Ch. 3 - Figure P3-86 shows an interface circuit connecting...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.87PCh. 3 - In this problem, you will design two interface...Ch. 3 - Two teams are competing to design the interface...Ch. 3 - The bridge-T attenuation pad shown in FigureP3-90...Ch. 3 - Design two interface circuits in Figure P3-91 so...Ch. 3 - Design the interface circuit in Figure P3-91 so...Ch. 3 - Design the interface circuit in Figure P3-93 so...Ch. 3 - It is claimed that both interface circuits in...Ch. 3 - Audio Speaker Resistance-Matching Network A...Ch. 3 - Interface Circuit Design Using no more than three...Ch. 3 - Battery Design A satellite requires a battery with...Ch. 3 - Design Interface Competition The output of a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.106IP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If C is the circle |z|=4 evaluate f f (z)dz for each of the following functions using residue. 1 f(z) = z(z²+6z+4)arrow_forwardIf C is the circle |z|=4 evaluate ff(z)dz for each of the following functions using residue. f(z) z(z²+6z+4)arrow_forwardDetermine X(w) for the given function shown in Figure (1) by applying the differentiation property of the Fourier Transform. 1 x(t) Figure (1) -2 I -1 1 2arrow_forward
- Please solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forward
- Please solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forward
- Please solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forwardPlease solve it by explaining the steps. I am trying to prepare for my exam tomorrow, so any tips and tricks to solve similar problems are highly appreciated. Plus, this is a past exam I am using to prepare.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Current Divider Rule; Author: Neso Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hRU1mKWUehY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY