
Interpretation:
The planar densities for planes
Concept introduction:
Planar density is the ratio of the area of the plane to the number of atoms in a plane.
Answer to Problem 3.71P
Planar densities for the plane:
Plane (110) is denser (closely packed) than others.
Explanation of Solution
Planar density is expressed as,
P = No. of atom/Area of plane =Z/A
(a) For plane
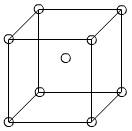
(b) For plane
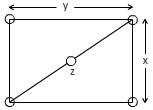
BCC unit cell with the plane (110) is rectangular.
Area of rectangular
Where
Diagonal length =4R.
Using Pythagoras theorem,
Number of atoms in the plane (110),
1 atom at every four corners and 1 center atom within the cell.
Planar density =
[Planar density]2 =
(c) For plane
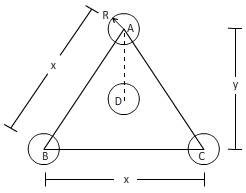
Plane (111)inthe BCC unit cell is having a triangular section.
Now, to calculate middle line length y is from the figure,
Now,
A plane with higher plane density is highly dense.
Plane density for plane
By comparing values of planar density, the plane
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Essentials of Materials Science and Engineering, SI Edition
- please solve this problem step by step like human and give correct answer step by steparrow_forwarda) A 14-ft. tall and12-ft.-8-in. long fully grouted reinforced masonry wall is constructed of 8-in.CMU. It is to be analyzed for out-of-plane loading. Construct thenP -nM curves for the wallwith the following three vertical reinforcement scenarios: (1) 10 No. 6 bars at 16 in. spacing,(2) 10 No. 5 bars at 16 in. spacing, and (3) 7 No. 4 bars at 24 in. spacing. The steel is Grade60 with a modulus of elasticity of 29,000 ksi, and the masonry has a compressive strength of2,000 psi. You may use Excel or Matlab to construct the curves. Also, show the maximumnPallowed by the code for each case.(b) For each of the above reinforcement scenarios, determine the maximum axial loads that arepermitted for the tension-controlled condition and transition condition.(c) Discuss how the amount of vertical reinforcement affects thenPn - Mn curve.arrow_forwardPROBLEM 11: Determine the force, P, that must be exerted on the handles of the bolt cutter. (A) 7.5 N (B) 30.0 N (C) 52.5 N (D) 300 N (E) 325 N .B X 3 cm E 40 cm cm F = 1000 N 10 cm 3 cm boltarrow_forward
- Using the moment-area theorems, determine a) the rotation at A, b) the deflection at L/2, c) the deflection at L/4. (Hint: Use symmetry for Part a (θA= - θB, or θC=0), Use the rotation at A for Parts b and c. Note that all deformations in the scope of our topics are small deformation and for small θ, sinθ=θ).arrow_forwardDistilled water is being cooled by a 20% propylene glycol solution in a 1-1/U counter flow plate and frame heat exchanger. The water enters the heat exchanger at 50°F at a flow rate of 86,000 lbm/h. For safety reasons, the water outlet temperature should never be colder than 35°F. The propylene glycol solution enters the heat exchanger at 28°F with a flow rate of 73,000 lbm/h. The port distances on the heat exchanger are Lv = 35 in and Lh = 18 in. The plate width is Lw = 21.5 2 in. The plate thickness is 0.04 in with a plate pitch of 0.12 in. The chevron angle is 30° and the plate enlargement factor is 1.17. All ports have a 2 in diameter. The fouling factor of the propylene glycol solution can be estimated as 2 ×10−5 h-ft2-°F/Btu. a. Determine the maximum number of plates the heat exchanger can have while ensuring that the water outlet temperature never drops below 35°F. b. Determine the thermal and hydraulic performance of the heat exchanger with the specified number of plates.…arrow_forwardLiquid pentane is flowing in the shell of a shell and tube heat exchanger at a rate of 350,000lbm/hr and an average temperature of 20°F. The shell has a diameter of 27 in and a length of 16ft. The tubes in the heat exchanger are ¾-in 15 BWG tubes on a 1-in triangular pitch. The purposeof this problem is to investigate how the number of baffles impacts the heat transfer and thepressure drop on the shell side of the heat exchanger. Calculate the shell-side convective heattransfer coefficient and pressure drop for the case where the heat exchanger has 10 baffles. Repeatthe calculation for 20 baffles. Then determine thea. Ratio of the shell-side convective heat transfer coefficient for the 20-baffle heat exchangerto the 10-baffle heat exchangerb. Ratio of the shell-side pressure drop for the 20-baffle heat exchanger to the 10-baffle heatexchangerc. If the optimum baffle spacing is somewhere between 0.4Ds and 0.6Ds, how many baffleswould you recommend for this heat exchanger? What are the…arrow_forward
- Can you show why the answer is that for this question using second order differential equations, instead of laplace transformsarrow_forwardI need help to solve the following case, thank youarrow_forwardIf you could help me answer these questions in matlab that would be great, I provided an additional picture detailing what the outcome should look like.arrow_forward
- The evaporator of a vapor compression refrigeration cycle utilizing R-123 as the refrigerant isbeing used to chill water. The evaporator is a shell and tube heat exchanger with the water flowingthrough the tubes. The water enters the heat exchanger at a temperature of 54°F. The approachtemperature difference of the evaporator is 3°R. The evaporating pressure of the refrigeration cycleis 4.8 psia and the condensing pressure is 75 psia. The refrigerant is flowing through the cycle witha flow rate of 18,000 lbm/hr. The R-123 leaves the evaporator as a saturated vapor and leaves thecondenser as a saturated liquid. Determine the following:a. The outlet temperature of the chilled waterb. The volumetric flow rate of the chilled water (gpm)c. The UA product of the evaporator (Btu/h-°F)d. The heat transfer rate between the refrigerant and the water (tons)arrow_forwardhi I would like to get help to resolve the following casearrow_forwardA fully grouted reinforced masonry wall is to be constructed of 8-in. CMU. The wall height is 18feet. It is assumed to be simply supported. The wall is to be designed for an out-of-plane seismicload of 52 lbs./ft.2, which can act in either direction. The wall also supports a roof dead load of600 lbs./ft. and a roof live load of 300 lbs./ft. along the wall length. The roof loads have aneccentricity of 2.5 inches. Since there is seismic load, load combinations (6) and (7) in Chapter 2of ASCE 7-22 should be considered. In these two load combinations,horizontal seismic loadhE =andvertical seismic loadvE = . You may ignorevE in this problem for simplicity. The masonryhas a specified compressive strength of 2,500 psi. (a) Use the strength design provisions of TMS402 to determine the size and spacing of the vertical bars needed. Use the P-δ analysis method inSection 9.3.4.4.2 of TMS 402 to determine Mu. (b) Repeat the design using the momentmagnification method in Section 9.3.4.4.3 instead.arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





