
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781305577213
Author: Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 3, Problem 3.6QAP
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The values for
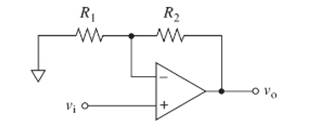
Concept introduction:
From the given circuit, the relation between the input and output voltage is obtained using virtual short and potential divider concept. The output is observed to follow the input with a gain with the relation,
Based on the input-output relation given
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
What is the total energy cost associated with the compound below adopting the shown conformation?
CH3
HH
DH
CH3
ΗΝ,
Draw Final Product
C
cyclohexanone
pH 4-5
Edit Enamine
H3O+
CH3CH2Br
THF, reflux
H
Edit Iminium Ion
How many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.1QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.2QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.3QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.4QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.5QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.6QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.7QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.8QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.9QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.10QAP
Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.11QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.12QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.13QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.14QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.15QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.16QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.17QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.18QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.19QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.20QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.21QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.22QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.23QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.24QAPCh. 3 - Prob. 3.25QAP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Identify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forward
- Why isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forward
- Complete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781285199023Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781285199023Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199023
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning