
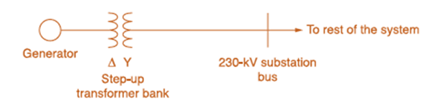
Consider the oneline diagram shown in Figure 3.40. The three-phase transformer bank is made up of three identical single-phase transformers, each specified by
(a) Determine the primary current magnitude, primary voltage (line-to-line) magnitude, and the three-phase complex power supplied by the generator. Choose the line-to-neutral voltage at the bus,
(b) Find the phase shift between the primary and secondary voltages.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 3 Solutions
MindTap Engineering, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card for Glover/Overbye/Sarma's Power System Analysis and Design, 6th
- 2. On a distortionless transmission line, the voltage wave is given by v(L,t) = 110e0.005L Cos(10³t + 2L) +55e-0.005L Cos(108t-2L) where L is the length of the transmission line as measured from the load. If Z = 30002, find a,ẞ, vp, and Zo.arrow_forwardA 50 transmission line is to be connected to a 72 load through a 1/4 quarter wave matching transformer. (a) What must be the characteristic impedance of the transmission line that is used to form the quarter wave transformer? (b) If the frequency of operation is 7 MHz and the phase velocity through the quarter wave section is 2c/3, what is the length of the quarter wave section? You may assume the transmission line forming the quarter wave section is lossless.arrow_forwardWhat is the SWR on a transmission line if the forward power arriving at the load is 5W but only 4.6W is dissipated by the load?arrow_forward
- Please do not send the AI solution as it is full of errors. Solve the question yourself, please. Q- If you have a unipolar winding stepper motor, draw the driver and the control circuit. In subject (A stepper motor driver circuit and direction control using Arduino microcontroller)arrow_forward1- Draw the complete circuit diagram that illustrates the experiment concept as in figure 5 by showing the pins number. Show the following in your plot (Arduino board, steppermotor coils and the driver circuit). Note: The drawing should be on paper and not with artificial intelligence, please.arrow_forwardIn the circuit shown, find the following: 1) The current Ix. 2) The average power dissipated in the capacitor. 3) The total average power dissipated in the two resistors. 4) The average power of the independent voltage source and specify whether it is supplied or absorbed. 5) The total impedance seen from the terminals of the independent voltage source (Z=V/I). 20 -201 12/00V(+ 21 www 202arrow_forward
- 2- If you have a unipolar winding stepper motor, draw the driver and the control circuit. Note: The drawing is on paper.arrow_forwardGiven the following reaction system, where Xo is the input, i.e u(t) = k₁ × Xo: $Xo -> x1; k1*Xo x2; k2*x1 x1 2 x2 ->%; k3*x2^2 x2 ->; k4*x2 Xo 1; k1 = 0.4 k2 4.5; k3 = 0.75 k4= 0.2 a) Build the model in Tellurium and run a simulation. Compute the Jacobian at steady state using the method getFull Jacobian(). Make sure you are at steady state! b) Write out the values for n and p c) Write out the differential equations. d) Write out the state space representation in terms of the rate constants etc. e) Compute the values in the Jacobian matrix from d) by substituting the values of the rate constants etc and any data you need from the simulation. f) Confirm that the Jacobian you get in e) is the same as the one computed from the simulation in a). g) Is the system stable or not? If you find an eigenvalue of zero, that means the system is marginally stable. You can get the eigenvalues using the tellurium method r.getFullEigenvalues()arrow_forwardSolve by Pen and Paper not using chatgpt or AIarrow_forward
- You just got a job at Shin-Etsu Chemical growing Si crystals with different dopants. Howmuch Ga needs to be added to 800 kg of Si melt to achieve a 5-10 Ω.cm (measured at midheight) Si CZ crystal with the following characteristics: height: 7 ft, width: 12 inchesdiameter. Assume, angular rotation 10 RPM, melt viscosity 0.1 poise, pull velocity 2mm/min.a. Generate a plot of the doping distribution throughout the length of the crystal (CGa vs. fs ).b. If a second crystal were to be pulled out of the melt without replenishment of silicon nordopant what would be the average resistivity of this crystal (or resistivity at mid height)arrow_forwardDO NOT USE AI OR CHAT GPT NEED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTIONarrow_forward7. Complete the following problems for the circuit below. (a) When VDD = 120V, What is the voltage drop V1 across the 7Ω resistor? (b) If the voltage source VDD is set to obtain I1 = 2A, find the value of VDD. (c) If I1 = 100A, What is the value of I2arrow_forward
 Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning

