
Concept explainers
(a)
To Draw:
A graph of vx versus time for a projectile and identify the points where the object reaches its highest point and where it hits the ground at the end of its flight.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Consider an object that undergoes a projectile motion. The object is projected with a velocity v at an angle θ to the horizontal. The velocity has an initial horizontal component
For the purpose of drawing a graph showing the variation of vx with time, assume the value of
On a spread sheet insert the values as shown and draw a graph as shown.
| t in s | vx in m/s |
| 0 | 25 |
| 1 | 25 |
| 2 | 25 |
| 3 | 25 |
| 4 | 25 |
| 5 | 25 |
| 6 | 25 |
| 7 | 25 |
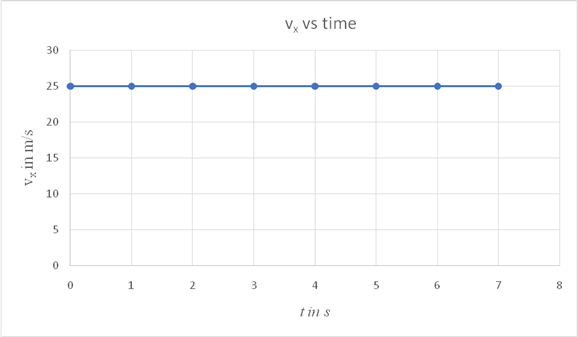
Conclusion:
The graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis. From the above graph, it is not possible to identify the points where the object reaches its maximum height or when it reaches the ground, since the graph shows no variation of the horizontal component with time.
(b)
To Draw:
A graph of vy versus time for a projectile and identify the points where the object reaches its highest point and where it hits the ground at the end of its flight.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Consider an object that undergoes a projectile motion. The object is projected with a velocity v at an angle θ to the horizontal. The velocity has an initial horizontal component
The projectile after it is launched is under the action of the acceleration of free fall. The vertical component of the projectile varies under the action of the acceleration due to gravity g.
The expression which shows the variation of vy with time is given by,
The acceleration due to gravity g is directed downwards, opposite to the direction of the vertical component of the velocity at the moment of launch. Therefore, it is given a value
Assume, the value of
On a spreadsheet, use the following equation to plot the variation of vy with time.
| t in s | vy in m/s |
| 0 | 30 |
| 0.1 | 29.019 |
| 0.2 | 28.038 |
| 0.3 | 27.057 |
| 0.4 | 26.076 |
| 0.5 | 25.095 |
| 0.6 | 24.114 |
| 0.7 | 23.133 |
| 0.8 | 22.152 |
| 0.9 | 21.171 |
| 1 | 20.19 |
| 1.1 | 19.209 |
| 1.2 | 18.228 |
| 1.3 | 17.247 |
| 1.4 | 16.266 |
| 1.5 | 15.285 |
| 1.6 | 14.304 |
| 1.7 | 13.323 |
| 1.8 | 12.342 |
| 1.9 | 11.361 |
| 2 | 10.38 |
| 2.1 | 9.399 |
| 2.2 | 8.418 |
| 2.3 | 7.437 |
| 2.4 | 6.456 |
| 2.5 | 5.475 |
| 2.6 | 4.494 |
| 2.7 | 3.513 |
| 2.8 | 2.532 |
| 2.9 | 1.551 |
| 3 | 0.57 |
| 3.1 | -0.411 |
| 3.2 | -1.392 |
| 3.3 | -2.373 |
| 3.4 | -3.354 |
| 3.5 | -4.335 |
| 3.6 | -5.316 |
| 3.7 | -6.297 |
| 3.8 | -7.278 |
| 3.9 | -8.259 |
| 4 | -9.24 |
| 4.1 | -10.221 |
| 4.2 | -11.202 |
| 4.3 | -12.183 |
| 4.4 | -13.164 |
| 4.5 | -14.145 |
| 4.6 | -15.126 |
| 4.7 | -16.107 |
| 4.8 | -17.088 |
| 4.9 | -18.069 |
| 5 | -19.05 |
| 5.1 | -20.031 |
| 5.2 | -21.012 |
| 5.3 | -21.993 |
| 5.4 | -22.974 |
| 5.5 | -23.955 |
| 5.6 | -24.936 |
| 5.7 | -25.917 |
| 5.8 | -26.898 |
| 5.9 | -27.879 |
| 6 | -28.86 |
| 6.1 | -29.841 |
| 6.2 | -30.822 |
From the graph, the following points are noted:
1.The maximum positive value of vy is at point O, which the point at which it is launched.
2. As the object rises, the vertical component of its velocity reduces under the action of acceleration due to gravity g. When it reaches the maximum height, this component attains a value zero. This is seen from the graph as point A. The time taken by this projectile to reach its maximum height is seen to be equal to 3.05 s.
3. As the object descends from the position of maximum height, the vertical component of its velocity is directed downwards and hence it has a negative value. Its value increases as it moves downwards, since now, the vertical component vy and the acceleration due to gravity are both directed downwards. When it hits the ground, the vertical component vy has a magnitude of 30 m/s and it is directed downwards, hence negative. Point B represents the point when it reaches the ground. The total time of flight from the graph is 6.1 s.
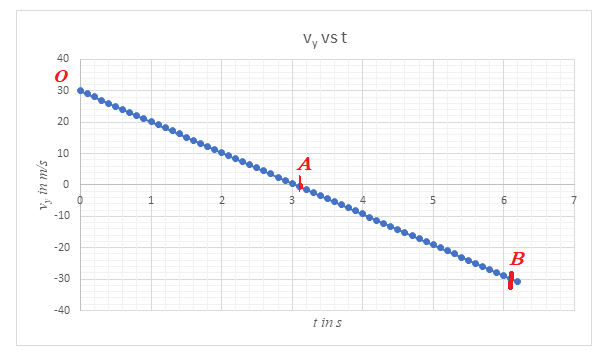
Conclusion:
The object with a vertical component of magnitude 30 m/s, reaches the position of maximum height in time 3.05 s and reaches the ground after 6.1 s. The graph varies linearly with time. The gradient of the graph is equal to g which has a value
(c)
To Draw:
A graph showing the variation of ax with time.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
A projectile travels a parabolic path under the action of acceleration due to gravity, if no air resistance acts on it.
The only force acting on the projectile is the gravitational force, which is directed downwards, towards the center of the Earth. This force is constant at points close to the surface of the earth. Since it is directed towards the ground, it has no component along the horizontal direction. Hence,
On a spreadsheet, use
| tin s | ax in m/s2 |
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 |
| 6 | 0 |
| 7 | 0 |
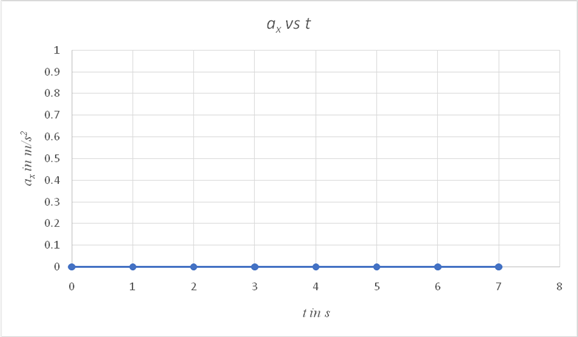
Conclusion:
Since the only force acting on the projectile is the gravitational force and it has no component along the horizontal direction, the horizontal component of its acceleration is zero at all times, as shown in the graph.
(d)
To Draw:
A graph showing the variation of ay with time.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
A projectile travel in a parabolic path under the action of acceleration due to gravity. If no air resistance acts on the object, the only force acting on it is the gravitational force. Hence the vertical component of the object's acceleration is
The gravitational force is a constant at points close to the surface of the earth. The acceleration due to gravity has a constant value of
On a spreadsheet, use the expression
| tin s | ay in m/s2 |
| 0 | -9.81 |
| 1 | -9.81 |
| 2 | -9.81 |
| 3 | -9.81 |
| 4 | -9.81 |
| 5 | -9.81 |
| 6 | -9.81 |
| 7 | -9.81 |
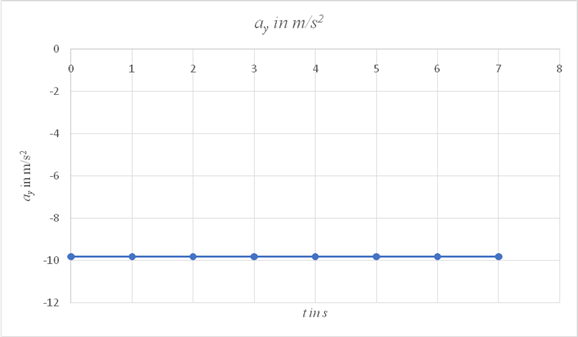
Conclusion:
The graph of ay vs time is a straight line parallel to the time axis and has a constant value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS
- Consider a uniformly charged ring of radius R with total charge Q, centered at the origin inthe xy-plane. Find the electric field (as a vector) at a point on the z-axis at a distance z above thecenter of the ring. Assume the charge density is constant along the ring.arrow_forward3) If the slider block C is moving at 3m/s, determine the angular velocity of BC and the crank AB at the instant shown. (Use equation Vs Vc wx fuc, then use equation Vs VA + Ve/athen write it in terms of w and the appropriate r equate the two and solve) 0.5 m B 1 m 60° A 45° vc = 3 m/sarrow_forward3) If the slider block C is moving at 3m/s, determine the angular velocity of BC and the crank AB at the instant shown. (Use equation Vs Vc wxf, then use equation V, VA + Va/Athen write it in terms of w and the appropriate r equate the two and solve) f-3marrow_forward
- Pls help ASAParrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward14. A boy is out walking his dog. From his house, he walks 30 m North, then 23 m East, then 120 cm South, then 95 m West, and finally 10 m East. Draw a diagram showing the path that the boy walked, his total displacement, and then determine the magnitude and direction of his total displacement.arrow_forward
- Pls help ASAParrow_forward12. A motorboat traveling 6 m/s, West encounters a water current travelling 3.5 m/s, South. a) Draw a vector diagram showing the resultant velocity, then determine the resultant velocity of the motorboat. b) If the width of the river is 112 m wide, then how much time does it take for the boat to travel shore to shore? c) What distance downstream does the boat reach the opposite shore?arrow_forwardLake Erie contains roughly 4.00⋅10114.00⋅1011 m3 of water. Assume the density of this water is 1000. kg/m3 and the specific heat of water is 4186 J/kg˚C. It takes 2.31x10^19 J of energy to raise the temperature of that volume of water from 12.0 °C to 25.8 ˚C. An electric power plant can produce about 1110 MW. How many years would it take to supply this amount of energy by using the 1110 MW from an electric power plant?arrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





