
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure for the product of each of the given Lewis acid-base association reactions is to be derived by using curved-arrow notation. The formal charge on each species is to be assigned. The Lewis acid and the Lewis base is to be labeled. The atom that donates electrons in each case is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Lewis acid-base association reaction involves the transfer of a proton from a base to an acid. Lewis acid accepts an electron pair and acts as an electrophile. Lewis base donates an electron pair and acts as a nucleophile.
Answer to Problem 3.1P
The Lewis acid and Lewis base are
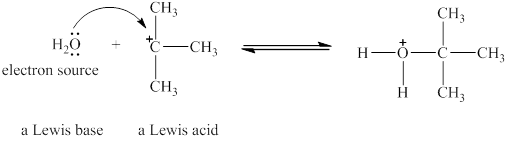
Explanation of Solution
Lewis acids are electron donor, whereas Lewis bases are electron pair accepter. In water molecule oxygen consists of a lone pair. Thus, it will act a Lewis base and oxygen atom has tendnecy to donate its electrons. The
The oxygen in
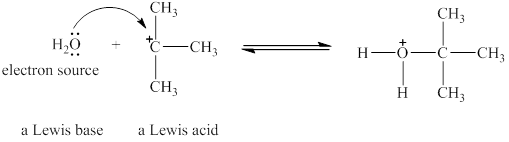
Figure 1
The Lewis acid and Lewis base are
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure for the product of each of the given Lewis acid-base association reactions is to be derived by using curved-arrow notation. The formal charge on each species is to be assigned. The Lewis acid and the Lewis base is to be labeled. The atom that donates electrons in each case is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Lewis acid-base association reaction involves the transfer of a proton from a base to an acid. Lewis acid accepts an electron pair. It acts as an electrophile Lewis base donates an electron pair. It acts as nucleophile.
Answer to Problem 3.1P
The Lewis acid and Lewis base are
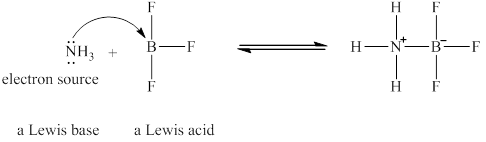
Explanation of Solution
Lewis acids are electron donor, whereas Lewis bases are electron accepter. In
The nitrogen in
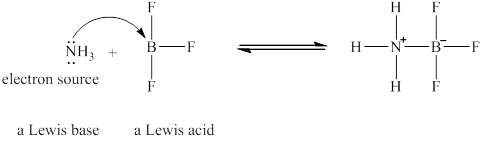
Figure 2
The Lewis acid and Lewis base are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Ebook And Single-course Homework Access
- If CoCl2/H2O is dissolved in a mixture of H2O and concentrated HCl in a test tube, the tube is gently heated over a flame to approximately 80°C and then cooled externally. Explain the color changes that occur.arrow_forwardWhen producing silica gel, color changes occur at the end of the drying process. Explain these color changes.arrow_forwardDesign experiments in UV-Vis to figure the optimal mole ratio of copper (1:1, 2:1, 3:1 and etc)versus ethambutol using all necessary chemicals including dihydrochloride and copper nitrate hemipentahydrate and sodium hydroxide. Show how UV-Vis absorbance and maximum wavelength would change in responsearrow_forward
- Correct each molecule in the drawing area below so that it has the condensed structure it would have if it were dissolv a 0.1 M aqueous solution of HCI. If there are no changes to be made, check the No changes box under the drawing area. No changes. HO—CH,—C—CH,—OH X 5 2 2 2 HO–CH,—CH,—C—CH,—OH Explanation Check Center Accessi ©2025 on 5 Carrow_forwardMake the calculations to prepare 2M H2SO4, from concentrated H2SO4 (98%; density: 1.84 g/mL).arrow_forwardH CH3 CH3 b) Write the products of your compound and the following reagents. If the reaction would not work for your compound, write "no reaction" and explain the problem. NaCN H* H₂NNHCH5 H* -à NaBH -à CH2MgBr Cro₁₂ --à H3O+ -à c) Would your compound give a positive Tollen's test? Why or why not?arrow_forward
- Homework 4 Chem 204 Dr. Hellwig Consider this compound, which will be referred to as "your compound". a) Name your compound according to the IUPAC system. Include stereochemistry (E/Z/R/S) H CH3 CH3arrow_forwardWhat is the mechanism for this?arrow_forward21.50 Determine the combinations of haloalkane(s) and alkoxide(s) that could be used to synthesize the following ethers through Williamson ether synthesis. (a) (c) (d) (e) (f) H₂COarrow_forward
- 1. Arrange the following in order of increasing bond energy (lowest bond energy first, highest bond energy last). Provide your rationale. C=C, C-F, C=C, C-N, C-C List the bond order for each example.arrow_forwardWhat is the major enolate formed when treated with LDA? And why that one?arrow_forward4. Calculate the total number of sigma bonds and total number of pi bonds in each of the following compounds. a. HH :D: +1 I H-N-C-C-O-H I H b. HH H Н :N=C-C-C=C-CEC-H :0: total o H-C-H H-C = `C-H I H. 11 H-C = C= CH H total o total π total π 1 Harrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


