
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
An explanation regarding the arrangement of the compounds in order of their decreasing
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 3.29P
The arrangement of the given compounds in decreasing order of their
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are shown below.
Figure 1
The acidity of an atom is directly proportional to the electronegativity of an atom. The
Compound C contains
Compound A contains sulfur atom which is less electronegative than oxygen atom but it contains a chlorine atom. Chlorine atom is electronegative in nature due to which acidity of compound A increases.
Therefore, the order of acidity of the compounds is shown below.
Figure 2
The
Therefore, the order of decreasing
Figure 3
The order of decreasing
The arrangement of the given compounds in decreasing order of their
(b)
Interpretation:
An explanation regarding the arrangement of the compounds in order of their decreasing
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 3.29P
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
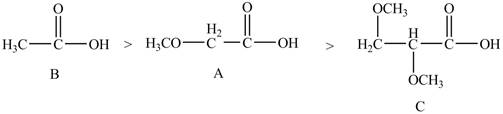
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are shown below.
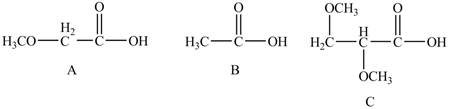
Figure 4
The acidity of an atom is directly proportional to the electronegativity of an atom. Compound C contains two
Compound A contains only one
Compound B contains
Therefore, the order of acidity of the compounds is shown below.
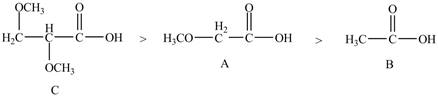
Figure 5
The
Therefore, the order of decreasing
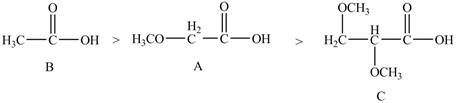
Figure 6
The order of decreasing
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
(c)
Interpretation:
An explanation regarding the arrangement of the compounds in order of their decreasing
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 3.29P
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are shown below.
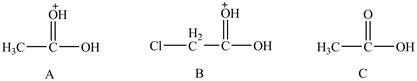
Figure 7
The conjugate bases of the compounds are shown below.
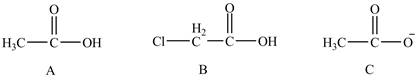
Figure 8
Compound C shown in Figure 8 is more basic than compound A and B due he presence of carboxylate ion. Compound B contains one chlorine atom which is an electron-withdrawing group. Thus, due to
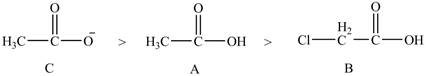
The order of basicity of the compounds is shown below.
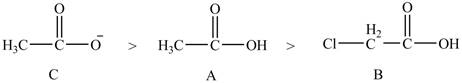
Figure 9
The order of basicity is directly proportional to the
Therefore, the order of decreasing
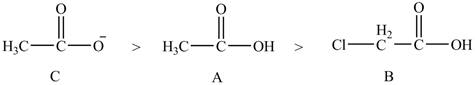
Figure 9
The order of decreasing
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Ebook And Single-course Homework Access
- no Ai walkthroughsarrow_forwardI have a aqueous solution (175 ml) of iridium trichloride containing 8,750 ppm Iridium by ICP OES analysis. What is the percent concentration of Iridium trichloride in aquous solution and provide the concentration in moles per liter, percentage by weight.arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
- 136 PRACTICAL SPECTROSCOPY Compound 78 is a high-boiling liquid (boiling point 189° C) that contains halogen, but will not react with alkoxides to yield an halogen. ether. The Mass, IR, and 'H NMR spectra, along with 13C NMR data, are given below. Elemental Analysis: C, 35.32; H, 2.47; contains BC Spectral Data: doublet, 137.4 ppm; doublet, 130.1 ppm; doublet, 127.4 ppm; singlet, 97.3 ppm Absorbance Mass Spectrum Intensity 77 77 204 M + 128 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 m/e 200 220 280 240 260 300 Infrared Spectrum Wave Number, cm -1 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1300 1200 1100 1000 900 800 700 3 6 7 8 9 10 12 13 15 Wavelength, microns 'H NMR wwwww 5 Structure: www ppm, & ©2000 Brooks/Cole Publishing Com-arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning



