
Pearson eText Biology: Science for Life with Physiology -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780135214114
Author: Colleen Belk, Virginia Maier
Publisher: PEARSON+
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 2LTB
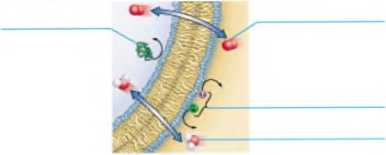
Add labels to the figure that follows, which illustrates some molecules that can and cannot pass through cell membranes unaided.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Identify the indicated cavity (Fucus).
a. antheridia
b. conceptacel
c. receptacle
d. oogonium
e. none of these
Identify the indicated structure (Saprolegnia).
a. antheridium
O b. oospore
c.sperm
d. auxospore
e. tetraspore
Of. zygospore
Using information from the primary literature (several references have been provided as a starting point below) please answer the following question: Based on your review of the literature on rewilding, what are the major scientific pros and cons for rewilding?
Please note that the focus of this assignment are the (biological) scientific issues associated with rewilding. As will be discussed in class, there are a number of non-scientific issues involved or implicated in rewilding, all ultimately affecting the public acceptability of rewilding. Although these issues are important – indeed, critical – in this assignment you should focus on the biological science issues and questions.
Details:
You must enumerate at least two pros and at least two cons.
Your answer should be no more than 500 well-chosen words, excluding references. Think carefully about how best to organize and structure your answer. Aim for high information density: say a lot, but say it succinctly. Recall Nietzche’s…
Chapter 3 Solutions
Pearson eText Biology: Science for Life with Physiology -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
Ch. 3 - Prob. 1LTBCh. 3 - Add labels to the figure that follows, which...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3LTBCh. 3 - Which of the following is not a function of water?...Ch. 3 - Prob. 5LTBCh. 3 - Prob. 6LTBCh. 3 - Prob. 7LTBCh. 3 - Prob. 8LTBCh. 3 - Which of the following forms of membrane transport...Ch. 3 - Prob. 10LTB
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using information from the primary literature (several references have been provided as a starting point below) please answer the following question: Based on your review of the literature on rewilding, what are the major scientific pros and cons for rewilding? Please note that the focus of this assignment are the (biological) scientific issues associated with rewilding. As will be discussed in class, there are a number of non-scientific issues involved or implicated in rewilding, all ultimately affecting the public acceptability of rewilding. Although these issues are important – indeed, critical – in this assignment you should focus on the biological science issues and questions. Details: You must enumerate at least two pros and at least two cons. Your answer should be no more than 500 well-chosen words, excluding references. Think carefully about how best to organize and structure your answer. Aim for high information density: say a lot, but say it succinctly. Recall Nietzche’s…arrow_forwardNow draw a rough sketch of what the control data might look like if in addition to the specific binding, there was also a considerable amount of nonspecific binding (again using a normal dose/response curve) (do % total bound ligand vs concentration)arrow_forwardWhat are functions of cuboidal cells in the kidney? Select all that apply. Concentration of gases Dilution of chemicals Secretion of molecules Nutrition to tissues Support of tissues Absorption of moleculesarrow_forward
- question1 In plants, epithelial tissue is only found as the outermost cell layer and acts as a barrier. In humans, epithelial tissue is found inside the body as well as on the surface. What function(s) does/do epithelial tissue carry out in humans? Select all that apply. Waste storage Filtration Oxygen transport Protection Diffusion Osmosis Absorptionarrow_forwardWhat words best describes this organism? a. Unicellular/nonmotile Ob. unicellular/motile c. colonial/nonmotile d. colonial/motile e. multicelluar O f. siphonous g. none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the phylum or class. a. Euglenophyta b. Dinoflagellata c. Bacillariophyceae d. Oomycetes e. Phaeophyceae O f. Myxomycota g. Xanthophyceae ○ h. Chrysophyceae i. Dictyosteliomycota O j. Rhodophyta Ok. Chlorophyceaens I. Charophyceaensarrow_forward
- What is produced inside the indicated structure (Fucus). a. eggs O b. antheridia ○ c. sperm d. zygotes e. none of thesearrow_forwardGreen Algae, as a group, is actually paraphyletic with one subgroup more closely related to higher plants than the other. Which of the following green algae groups is more closely related to higher plants: a. Charophyceans b. Chlorophyceans c. Rhodophyta d. Xanthophyceansarrow_forwardA single-celled green algal genus that is motile with 2 flagella, has a cup shaped chloroplast, and an eyespot: a. Volvox b. Chlamydomonas c. Euglena d. Codiumarrow_forward
- A[n] ___ is produced by members of the Myxomycota when there is a lack of moisture. a. plasmodiocarp b. aethalium c. sclerotium d. plasmodiumarrow_forwardWhich of the following is not true about the life-cycle of Fucus. a. 8 eggs per oogonium b. 64 sperm per antheridium c. eggs are flagellated d. sperm are flagellatedarrow_forwardGreen Algae, as a group, is actually paraphyletic with one subgroup more closely related to higher plants than the other. Which of the following green algae groups is more closely related to higher plants: a. Charophyceans b. Chlorophyceans c. Rhodophyta d. Xanthophyceansarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax
The Cell Membrane; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AsffT7XIXbA;License: Standard youtube license